| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 28(4); 2022 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Background/Aims
Methods
Results
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
FOOTNOTES
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā1.
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā2.
Supplementary┬ĀTable┬Ā1.
Supplementary┬ĀTable┬Ā2.
Supplementary┬ĀTable┬Ā3.
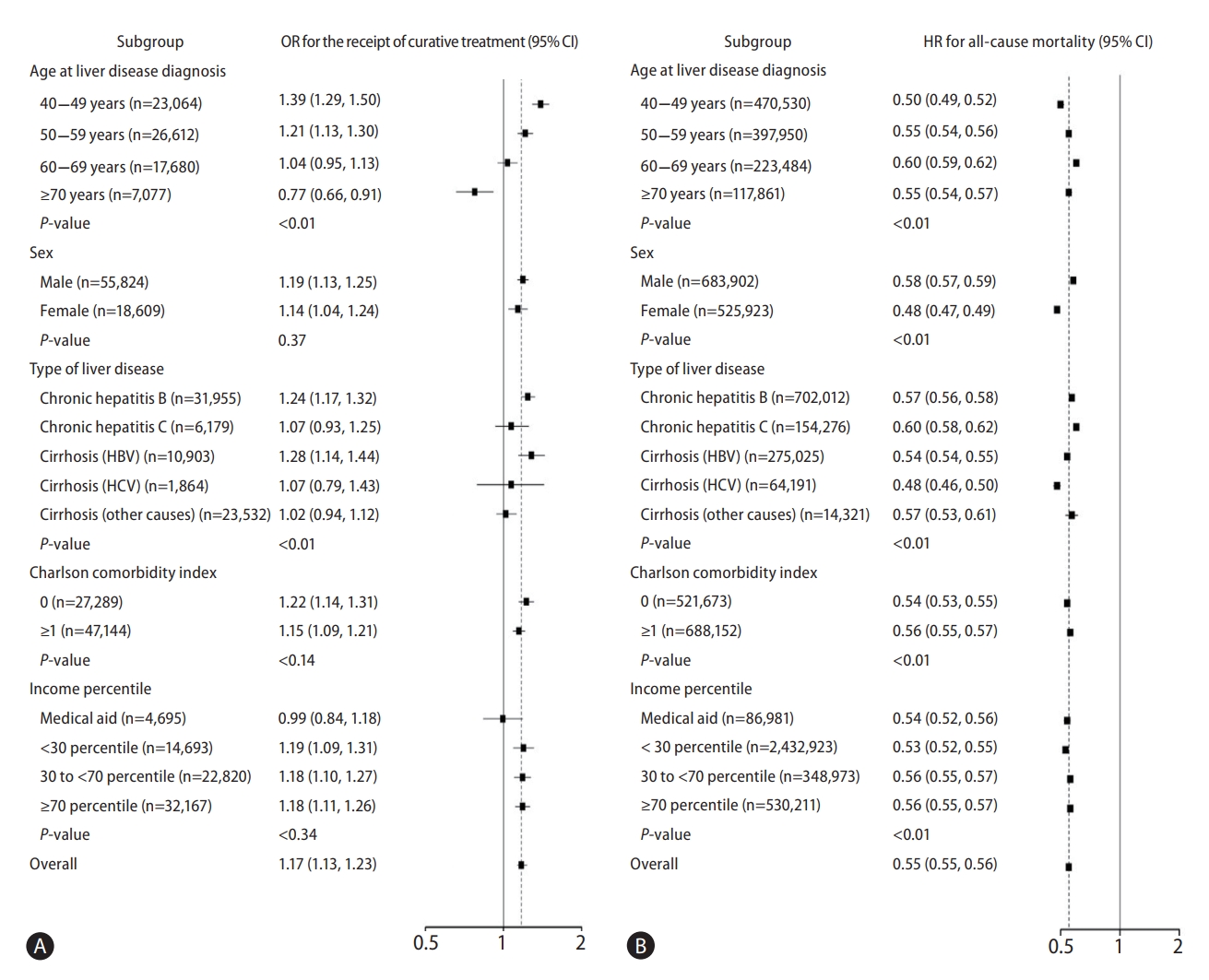
Figure┬Ā2.
Table┬Ā1.
| Characteristic |
HCC surveillance |
P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No (n=551,936) | Yes (n=657,889) | ||
| Age* (years) | 53.0 (47.0ŌĆō64.0) | 52.0 (46.0ŌĆō55.0) | <0.01 |
| Sex | <0.01 | ||
| ŌĆāMale | 331,678 (60.1) | 352,224 (53.5) | |
| ŌĆāFemale | 220,258 (39.9) | 305,665 (46.5) | |
| Type of liver disease | <0.01 | ||
| ŌĆāChronic hepatitis BŌĆĀ | 275,035 (49.8) | 426,977 (64.9) | |
| ŌĆāChronic hepatitis C | 69,651 (12.6) | 84,625 (12.9) | |
| ŌĆāCirrhosis (HBVŌĆĀ) | 30,123 (5.5) | 34,068 (5.2) | |
| ŌĆāCirrhosis (HCV) | 7,604 (1.4) | 6,717 (1.0) | |
| ŌĆāCirrhosis (other causes) | 169,523 (30.7) | 105,502 (16.0) | |
| Charlson comorbidity index | <0.01 | ||
| ŌĆā0 | 237,917 (43.1) | 283,756 (43.1) | |
| ŌĆā1 | 164,743 (29.8) | 215,045 (32.7) | |
| ŌĆāŌēź2 | 149,276 (27.1) | 159,088 (24.2) | |
| Residential area | <0.01 | ||
| ŌĆāMetropolitan | 349,192 (63.3) | 426,542 (64.8) | |
| ŌĆāRural | 202,519 (36.7) | 231,186 (35.1) | |
| ŌĆāUnknown | 225 (0.0) | 161 (0.1) | |
| Income percentile | <0.01 | ||
| ŌĆāMedical aid | 48,846 (8.8) | 38,135 (5.7) | |
| ŌĆā<30 percentile | 109,308 (19.8) | 133,984 (20.4) | |
| ŌĆā30 to <70 percentile | 155,815 (28.2) | 193,158 (29.4) | |
| ŌĆāŌēź70 percentile | 237,756 (43.1) | 292,455 (44.5) | |
| ŌĆāUnknown | 211 (0.1) | 157 (0.0) | |
Table┬Ā2.
| Characteristic | Crude OR (95% CI) | Adjusted* OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| AgeŌĆĀ | 1.03 (1.03ŌĆō1.03) | 1.02 (1.02ŌĆō1.02) |
| ŌĆā40ŌĆō49 years | 1.02 (1.02ŌĆō1.04) | 1.07 (1.06ŌĆō1.08) |
| ŌĆā50ŌĆō59 years | Reference | Reference |
| ŌĆā60ŌĆō69 years | 1.23 (1.31ŌĆō1.24) | 1.16 (1.15ŌĆō1.18) |
| ŌĆāŌēź70 years | 3.06 (3.02ŌĆō3.11) | 2.96 (2.92ŌĆō3.00) |
| Sex | ||
| ŌĆāMale | 1.36 (1.35ŌĆō1.37) | 1.24 (1.22ŌĆō1.24) |
| ŌĆāFemale | Reference | Reference |
| Type of liver disease | ||
| ŌĆāChronic hepatitis BŌĆĪ | Reference | Reference |
| ŌĆāChronic hepatitis C | 1.28 (1.26ŌĆō1.29) | 1.20 (1.19ŌĆō1.21) |
| ŌĆāCirrhosis (HBVŌĆĪ) | 1.37 (1.35ŌĆō1.40) | 1.35 (1.33ŌĆō1.38) |
| ŌĆāCirrhosis (HCV) | 1.76 (1.70ŌĆō1.82) | 1.54 (1.49ŌĆō1.60) |
| ŌĆāCirrhosis (other causes) | 2.49 (1.47ŌĆō2.52) | 2.19 (2.17ŌĆō2.21) |
| Charlson comorbidity index | ||
| ŌĆā0 | 1.00 (0.99ŌĆō1.01) | 1.17 (1.16ŌĆō1.17) |
| ŌĆāŌēź1 | Reference | Reference |
| Residential area | ||
| ŌĆāMetropolitan | Reference | Reference |
| ŌĆāRural | 1.07 (1.06ŌĆō1.08) | 0.97 (0.97ŌĆō0.98) |
| Income percentile | ||
| ŌĆāMedical aid | 1.58 (1.55ŌĆō1.60) | 1.29 (1.27ŌĆō1.31) |
| ŌĆā<30 percentile | 1.00 (0.99ŌĆō1.01) | 0.99 (0.99ŌĆō1.00) |
| ŌĆā30 to <70 percentile | 0.99 (0.98ŌĆō1.00) | 0.99 (0.98ŌĆō1.00) |
| ŌĆāŌēź70 percentile | Reference | Reference |
HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus.
* Adjusted for age, sex, year of chronic liver disease diagnosis (chronic hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis C, and liver cirrhosis), region, income, HBV infection, HCV infection, liver cirrhosis, and Charlson comorbidity index score.
Table┬Ā3.
|
Incidence of HCC |
Receipt of curative treatment* |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence cases | Incidence rate per 1,000 person years | HR (95% CI): crude | HR (95% CI): adjustedŌĆĀ | Incidence cases | Incidence rate per 1,000 person years | HR (95% CI): crude | HR (95% CI): adjustedŌĆĀ | |||
| Overall (n=1,209,825) | ||||||||||
| Surveillance | ||||||||||
| No (n=551,936) | 63,829 | 6 | Reference | Reference | 30,393 | 3 | Reference | Reference | ||
| Yes (n=657,889) | 10,604 | 23 | 4.17 (4.08ŌĆō4.26) | 5.34 (5.23ŌĆō5.46) | 5,613 | 12 | 4.59 (4.46ŌĆō4.73) | 5.64 (5.48ŌĆō5.81) | ||
| With cirrhosis (n=353,537) | ||||||||||
| Surveillance | ||||||||||
| No (n=207,250) | 32,525 | 13 | Reference | Reference | 15,083 | 6 | Reference | Reference | ||
| Yes (n=146,287) | 3,774 | 42 | 3.84 (3.71ŌĆō3.97) | 4.50 (4.35ŌĆō4.66) | 1,883 | 21 | 4.10 (3.91ŌĆō4.30) | 4.64 (4.42ŌĆō4.87) | ||
| Without cirrhosis (n=856,288) | ||||||||||
| Surveillance | ||||||||||
| No (n=344,686) | 31,304 | 4 | Reference | Reference | 15,319 | 2 | Reference | Reference | ||
| Yes (n=511,602) | 6,830 | 19 | 5.01 (4.88ŌĆō5.15) | 6.03 (5.87ŌĆō6.19) | 3,730 | 10 | 5.54 (5.35ŌĆō5.75) | 6.41 (6.18ŌĆō6.65) | ||
Table┬Ā4.
| Number of deaths | Mortality rate per 1,000 person years | Crude HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR (95% CI)* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall (n=1,209,825) | ||||||
| HCC surveillance | ||||||
| No (n=551,936) | 153,501 | 22 | Reference | Reference | ||
| Yes (n=657,889) | 45,263 | 12 | 0.46 (0.46ŌĆō0.47) | 0.56 (0.55ŌĆō0.56) | ||
| P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | ||||
| Patients with cirrhosis (n=353,537) | ||||||
| HCC surveillance | ||||||
| No (n=207,250) | 97,127 | 47 | Reference | Reference | ||
| Yes (n=146,287) | 22,725 | 28 | 0.51 (0.51ŌĆō0.52) | 0.54 (0.53ŌĆō0.55) | ||
| P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | ||||
| Patients without cirrhosis (n=856,288) | ||||||
| HCC surveillance | ||||||
| No (n=344,686) | 56,374 | 12 | Reference | Reference | ||
| Yes (n=511,602) | 22,538 | 7 | 0.56 (0.55ŌĆō0.57) | 0.58 (0.57ŌĆō0.59) | ||
| P-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | ||||
* Adjusted for age, sex, year of liver disease diagnosis (chronic hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis C, and liver cirrhosis), region, income, hepatitis B virus infection, hepatitis C virus infection, liver cirrhosis, Charlson comorbidity index score, and the use of antiviral agents for chronic viral hepatitis.
Abbreviations
REFERENCES
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- ORCID iDs
-
Juhee Cho

https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9081-0266Yong-Han Paik

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3076-2327 - Related articles





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement1
Supplement1 Print
Print



