2. Hui CK, Leung N, Yuen ST, Zhang HY, Leung KW, Lu L, et al. Natural history and disease progression in Chinese chronic hepatitis B patients in immune-tolerant phase. Hepatology 2007;46:395-401.


3. Tran TT. Immune tolerant hepatitis B: a clinical dilemma. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 2011;7:511-516.


4. Chu CM, Hung SJ, Lin J, Tai DI, Liaw YF. Natural history of hepatitis B e antigen to antibody seroconversion in patients with normal serum aminotransferase levels. Am J Med 2004;116:829-834.


5. Lee HA, Lee HW, Kim IH, Park SY, Sinn DH, Yu JH, et al. Extremely low risk of hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis B in immune-tolerant phase. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2020;52:196-204.


7. Kim GA, Lim YS, Han S, Choi J, Shim JH, Kim KM, et al. High risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and death in patients with immunetolerant-phase chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2018;67:945-952.


8. Chu CJ, Hussain M, Lok AS. Hepatitis B virus genotype B is associated with earlier HBeAg seroconversion compared with hepatitis B virus genotype C. Gastroenterology 2002;122:1756-1762.


9. Livingston SE, Simonetti JP, Bulkow LR, Homan CE, Snowball MM, Cagle HH, et al. Clearance of hepatitis B e antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B and genotypes A, B, C, D, and F. Gastroenterology 2007;133:1452-1457.


11. Lee PI, Chang MH, Lee CY, Hsu HY, Chen JS, Chen PJ, et al. Changes of serum hepatitis B virus DNA and aminotransferase levels during the course of chronic hepatitis B virus infection in children. Hepatology 1990;12(4 Pt 1):657-660.


12. Lok AS, Lai CL. Acute exacerbations in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Incidence, predisposing factors and etiology. J Hepatol 1990;10:29-34.


13. McMahon BJ. The natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2009;49(5 Suppl):S45-S55.


14. Hsu YS, Chien RN, Yeh CT, Sheen IS, Chiou HY, Chu CM, et al. Long-term outcome after spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2002;35:1522-1527.


15. Bortolotti F, Guido M, Bartolacci S, Cadrobbi P, Crivellaro C, Noventa F, et al. Chronic hepatitis B in children after e antigen seroclearance: final report of a 29-year longitudinal study. Hepatology 2006;43:556-562.


16. Yim HJ, Lok AS. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: what we knew in 1981 and what we know in 2005. Hepatology 2006;43(2 Suppl 1):S173-S181.


17. Lok AS, Lai CL, Wu PC, Leung EK, Lam TS. Spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen to antibody seroconversion and reversion in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology 1987;92:1839-1843.


18. Sheen IS, Liaw YF, Tai DI, Chu CM. Hepatic decompensation associated with hepatitis B e antigen clearance in chronic type B hepatitis. Gastroenterology 1985;89:732-735.


19. Martinot-Peignoux M, Boyer N, Colombat M, Akremi R, Pham BN, Ollivier S, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus DNA levels and liver histology in inactive HBsAg carriers. J Hepatol 2002;36:543-546.


20. Zacharakis GH, Koskinas J, Kotsiou S, Papoutselis M, Tzara F, Vafeiadis N, et al. Natural history of chronic HBV infection: a cohort study with up to 12 years follow-up in North Greece (part of the Interreg I-II/EC-project). J Med Virol 2005;77:173-179.


21. de Franchis R, Meucci G, Vecchi M, Tatarella M, Colombo M, Del Ninno E, et al. The natural history of asymptomatic hepatitis B surface antigen carriers. Ann Intern Med 1993;118:191-194.


22. Fattovich G. Natural history and prognosis of hepatitis B. Semin Liver Dis 2003;23:47-58.

23. Chen YC, Sheen IS, Chu CM, Liaw YF. Prognosis following spontaneous HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B patients with or without concurrent infection. Gastroenterology 2002;123:1084-1089.


24. Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B: update 2009. Hepatology 2009;50:661-662.


25. Funk ML, Rosenberg DM, Lok AS. World-wide epidemiology of HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B and associated precore and core promoter variants. J Viral Hepat 2002;9:52-61.


29. Croagh CM, Bell SJ, Slavin J, Kong YX, Chen RY, Locarnini S, et al. Increasing hepatitis B viral load is associated with risk of significant liver fibrosis in HBeAg-negative but not HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int 2010;30:1115-1122.


30. Yoo BC, Park JW, Kim HJ, Lee DH, Cha YJ, Park SM. Precore and core promoter mutations of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B in Korea. J Hepatol 2003;38:98-103.


31. Raimondo G, Allain JP, Brunetto MR, Buendia MA, Chen DS, Colombo M, et al. Statements from the Taormina expert meeting on occult hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2008;49:652-657.


32. Hoofnagle JH, Doo E, Liang TJ, Fleischer R, Lok AS. Management of hepatitis B: summary of a clinical research workshop. Hepatology 2007;45:1056-1075.


33. Hadziyannis SJ, Vassilopoulos D. Hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2001;34(4 Pt 1):617-624.


34. Wu TT, Hsu HC, Chen DS, Sheu JC, Su IJ, Chen SL, et al. Clearance of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) after surgical resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 1987;4:45-51.


35. Liaw YF, Sheen IS, Chen TJ, Chu CM, Pao CC. Incidence, determinants and significance of delayed clearance of serum HBsAg in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a prospective study. Hepatology 1991;13:627-631.


36. Tout I, Loureiro D, Mansouri A, Soumelis V, Boyer N, Asselah T. Hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance: immune mechanisms, clinical impact, importance for drug development. J Hepatol 2020;73:409-422.


37. Cornberg M, Lok AS, Terrault NA, Zoulim F; 2019 EASL-AASLD HBV Treatment Endpoints Conference Faculty. Guidance for design and endpoints of clinical trials in chronic hepatitis B - report from the 2019 EASL-AASLD HBV Treatment Endpoints Conference‡. J Hepatol 2020;72:539-557.


38. Raimondo G, Locarnini S, Pollicino T, Levrero M, Zoulim F, Lok AS, et al. Update of the statements on biology and clinical impact of occult hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2019;71:397-408.


39. Chu CM, Liaw YF. HBsAg seroclearance in asymptomatic carriers of high endemic areas: appreciably high rates during a long-term follow-up. Hepatology 2007;45:1187-1192.


40. Liu J, Yang HI, Lee MH, Lu SN, Jen CL, Wang LY, et al. Incidence and determinants of spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance: a community-based follow-up study. Gastroenterology 2010;139:474-482.


42. Kim GA, Lee HC, Kim MJ, Ha Y, Park EJ, An J, et al. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma after HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B patients: a need for surveillance. J Hepatol 2015;62:1092-1099.


43. Seto WK, Wong DK, Fung J, Huang FY, Liu KS, Lai CL, et al. Linearized hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B core-related antigen in the natural history of chronic hepatitis B. Clin Microbiol Infect 2014;20:1173-1180.


44. Yip TC, Chan HL, Wong VW, Tse YK, Lam KL, Wong GL. Impact of age and gender on risk of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance. J Hepatol 2017;67:902-908.


45. Yip TC, Wong GL, Chan HL, Tse YK, Lam KL, Lui GC, et al. HBsAg seroclearance further reduces hepatocellular carcinoma risk after complete viral suppression with nucleos(t)ide analogues. J Hepatol 2019;70:361-370.


46. Kim GA, Lim YS, An J, Lee D, Shim JH, Kim KM, et al. HBsAg seroclearance after nucleoside analogue therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B: clinical outcomes and durability. Gut 2014;63:1325-1332.


47. Choi J, Yoo S, Lim YS. Comparison of long-term clinical outcomes between spontaneous and therapy-induced HBsAg seroclearance. Hepatology 2021;73:2155-2166.


48. Yip TC, Wong VW, Tse YK, Liang LY, Hui VW, Zhang X, et al. Similarly low risk of hepatocellular carcinoma after either spontaneous or nucleos(t)ide analogue-induced hepatitis B surface antigen loss. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2021;53:321-331.


51. Hsu YN, Pan CQ, Abbasi A, Xia V, Bansal R, Hu KQ. Clinical presentation and disease phases of chronic hepatitis B using conventional versus modified ALT criteria in Asian Americans. Dig Dis Sci 2014;59:865-871.


52. Yao K, Liu J, Wang J, Yan X, Xia J, Yang Y, et al. Distribution and clinical characteristics of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection in the grey zone. J Viral Hepat 2021;28:1025-1033.


53. Bonacci M, Lens S, Mariño Z, Londoño MC, Rodríguez-Tajes S, Mas A, et al. Anti-viral therapy can be delayed or avoided in a significant proportion of HBeAg-negative Caucasian patients in the grey zone. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2018;47:1397-1408.


54. Choi GH, Kim GA, Choi J, Han S, Lim YS. High risk of clinical events in untreated HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients with high viral load and no significant ALT elevation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2019;50:215-226.


56. Yuen MF, Tanaka Y, Fong DY, Fung J, Wong DK, Yuen JC, et al. Independent risk factors and predictive score for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2009;50:80-88.


57. Teng W, Chang TT, Yang HI, Peng CY, Su CW, Su TH, et al. Risk scores to predict HCC and the benefits of antiviral therapy for CHB patients in gray zone of treatment guidelines. Hepatol Int 2021;15:1421-1430.


58. Lin SM, Sheen IS, Chien RN, Chu CM, Liaw YF. Long-term beneficial effect of interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 1999;29:971-975.


59. Raffetti E, Fattovich G, Donato F. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in untreated subjects with chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Int 2016;36:1239-1251.


60. Lee KJ, Han KH, Chun JY, Moon YM, Lee SI, Park IS, et al. Natural history of chronic hepatitis type B throughout long-term follow-up. Korean J Gastroenterol 1997;29:343-351.
63. Tseng TC, Liu CJ, Yang HC, Chen CL, Yang WT, Tsai CS, et al. Higher proportion of viral basal core promoter mutant increases the risk of liver cirrhosis in hepatitis B carriers. Gut 2015;64:292-302.


64. Jang JW, Chun JY, Park YM, Shin SK, Yoo W, Kim SO, et al. Mutational complex genotype of the hepatitis B virus X/precore regions as a novel predictive marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci 2012;103:296-304.


65. Kim JK, Chang HY, Lee JM, Baatarkhuu O, Yoon YJ, Park JY, et al. Specific mutations in the enhancer II/core promoter/precore regions of hepatitis B virus subgenotype C2 in Korean patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Med Virol 2009;81:1002-1008.


66. Kao JH, Chen PJ, Lai MY, Chen DS. Basal core promoter mutations of hepatitis B virus increase the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B carriers. Gastroenterology 2003;124:327-334.


68. Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Lu SN, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA 2006;295:65-73.


69. Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I, Donato F. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk factors. Gastroenterology 2004;127(5 Suppl 1):S35-S50.


70. Iloeje UH, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Chen CJ, et al. Predicting cirrhosis risk based on the level of circulating hepatitis B viral load. Gastroenterology 2006;130:678-686.


71. Bravi F, Tavani A, Bosetti C, Boffetta P, La Vecchia C. Coffee and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur J Cancer Prev 2017;26:368-377.


76. Lee M, Chung GE, Lee JH, Oh S, Nam JY, Chang Y, et al. Antiplatelet therapy and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients on antiviral treatment. Hepatology 2017;66:1556-1569.


77. Chen CI, Kuan CF, Fang YA, Liu SH, Liu JC, Wu LL, et al. Cancer risk in HBV patients with statin and metformin use: a population-based cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2015;94:e462.


78. Hsiang JC, Wong GL, Tse YK, Wong VW, Yip TC, Chan HL. Statin and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and death in a hospitalbased hepatitis B-infected population: a propensity score landmark analysis. J Hepatol 2015;63:1190-1197.


79. Kim G, Jang SY, Nam CM, Kang ES. Statin use and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients at high risk: a nationwide nested case-control study. J Hepatol 2018;68:476-484.


80. Pradelli D, Soranna D, Scotti L, Zambon A, Catapano A, Mancia G, et al. Statins and primary liver cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur J Cancer Prev 2013;22:229-234.

81. Singh S, Singh PP, Singh AG, Murad MH, Sanchez W. Statins are associated with a reduced risk of hepatocellular cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2013;144:323-332.


83. Goh MJ, Sinn DH, Kim S, Woo SY, Cho H, Kang W, et al. Statin use and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2020;71:2023-2032.


84. Choi WM, Kim HJ, Jo AJ, Choi SH, Han S, Ko MJ, et al. Association of aspirin and statin use with the risk of liver cancer in chronic hepatitis B: a nationwide population-based study. Liver Int 2021;41:2777-2785.


85. Yang HI, Yuen MF, Chan HL, Han KH, Chen PJ, Kim DY, et al. Risk estimation for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B (REACH-B): development and validation of a predictive score. Lancet Oncol 2011;12:568-574.


86. Lee HW, Yoo EJ, Kim BK, Kim SU, Park JY, Kim DY, et al. Prediction of development of liver-related events by transient elastography in hepatitis B patients with complete virological response on antiviral therapy. Am J Gastroenterol 2014;109:1241-1249.


87. Jung KS, Kim SU, Song K, Park JY, Kim DY, Ahn SH, et al. Validation of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma prediction models in the era of antiviral therapy. Hepatology 2015;62:1757-1766.


88. Papatheodoridis G, Dalekos G, Sypsa V, Yurdaydin C, Buti M, Goulis J, et al. PAGE-B predicts the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in Caucasians with chronic hepatitis B on 5-year antiviral therapy. J Hepatol 2016;64:800-806.


89. Kim MN, Hwang SG, Rim KS, Kim BK, Park JY, Kim DY, et al. Validation of PAGE-B model in Asian chronic hepatitis B patients receiving entecavir or tenofovir. Liver Int 2017;37:1788-1795.


90. Chon HY, Lee HA, Suh SJ, Lee JI, Kim BS, Kim IH, et al. Addition of liver stiffness enhances the predictive accuracy of the PAGEB model for hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2021;53:919-927.


91. Kim JH, Kim YD, Lee M, Jun BG, Kim TS, Suk KT, et al. Modified PAGE-B score predicts the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asians with chronic hepatitis B on antiviral therapy. J Hepatol 2018;69:1066-1073.


92. Lee HW, Kim SU, Park JY, Kim DY, Ahn SH, Han KH, et al. External validation of the modified PAGE-B score in Asian chronic hepatitis B patients receiving antiviral therapy. Liver Int 2019;39:1624-1630.


93. Sharma SA, Kowgier M, Hansen BE, Brouwer WP, Maan R, Wong D, et al. Toronto HCC risk index: a validated scoring system to predict 10-year risk of HCC in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2018;68:92-99.

94. Papatheodoridis GV, Sypsa V, Dalekos GN, Yurdaydin C, Van Boemmel F, Buti M, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma prediction beyond year 5 of oral therapy in a large cohort of Caucasian patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2020;72:1088-1096.


95. Ji JH, Park SY, Son WJ, Shin HJ, Lee H, Lee HW, et al. External validation of CAGE-B and SAGE-B scores for Asian chronic hepatitis B patients with well-controlled viremia by antivirals. J Viral Hepat 2021;28:951-958.


96. Chon HY, Lee JS, Lee HW, Chun HS, Kim BK, Tak WY, et al. Predictive performance of CAGE-B and SAGE-B models in Asian treatment-naive patients who started entecavir for chronic hepatitis B. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;20:e794-e807.


97. Nam H, Lee SW, Kwon JH, Lee HL, Yoo SH, Kim HY, et al. Prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma by on-therapy response of noninvasive fibrosis markers in chronic hepatitis B. Am J Gastroenterol 2021;116:1657-1666.


98. Kim HY, Lampertico P, Nam JY, Lee HC, Kim SU, Sinn DH, et al. An artificial intelligence model to predict hepatocellular carcinoma risk in Korean and Caucasian patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2022;76:311-318.


101. Cho JH, Yoon KH, Lee KE, Park DS, Lee YJ, Moon HB, et al. Distribution of hepatitis B virus genotypes in Korea. Korean J Hepatol 2009;15:140-147.


102. Lin CL, Kao JH. Natural history of acute and chronic hepatitis B: the role of HBV genotypes and mutants. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2017;31:249-255.


103. Lin CL, Kao JH. The clinical implications of hepatitis B virus genotype: recent advances. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;26 Suppl 1:123-130.


105. Liu J, Yang HI, Lee MH, Jen CL, Batrla-Utermann R, Lu SN, et al. Serum levels of hepatitis B surface antigen and DNA can predict inactive carriers with low risk of disease progression. Hepatology 2016;64:381-389.


106. Park H, Lee JM, Seo JH, Kim HS, Ahn SH, Kim DY, et al. Predictive value of HBsAg quantification for determining the clinical course of genotype C HBeAg-negative carriers. Liver Int 2012;32:796-802.


107. Tseng TC, Liu CJ, Yang HC, Su TH, Wang CC, Chen CL, et al. High levels of hepatitis B surface antigen increase risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with low HBV load. Gastroenterology 2012;142:1140-1149.e3 quiz e13-e14.


108. Sonneveld MJ, Hansen BE, Piratvisuth T, Jia JD, Zeuzem S, Gane E, et al. Response-guided peginterferon therapy in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B using serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels. Hepatology 2013;58:872-880.


109. Chang ML, Liaw YF, Hadziyannis SJ. Systematic review: cessation of long-term nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2015;42:243-257.


111. Wursthorn K, Jung M, Riva A, Goodman ZD, Lopez P, Bao W, et al. Kinetics of hepatitis B surface antigen decline during 3 years of telbivudine treatment in hepatitis B e antigen-positive patients. Hepatology 2010;52:1611-1620.


112. Park Y, Hong DJ, Shin S, Cho Y, Kim HS. Performance evaluation of new automated hepatitis B viral markers in the clinical laboratory: two quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen assays and an HBV core-related antigen assay. Am J Clin Pathol 2012;137:770-777.


113. Mak LY, Wong DK, Cheung KS, Seto WK, Lai CL, Yuen MF. Review article: hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg): an emerging marker for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2018;47:43-54.


114. Testoni B, Lebossé F, Scholtes C, Berby F, Miaglia C, Subic M, et al. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) correlates with covalently closed circular DNA transcriptional activity in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Hepatol 2019;70:615-625.


115. Wong DK, Seto WK, Cheung KS, Chong CK, Huang FY, Fung J, et al. Hepatitis B virus core-related antigen as a surrogate marker for covalently closed circular DNA. Liver Int 2017;37:995-1001.


116. Wang ML, Deng R, Chen EQ, Tao CM, Liao J, Zhou TY, et al. Performance of serum HBcrAg in chronic hepatitis B patients with 8-year nucleos(t)ide analogs therapy. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 2019;43:301-309.


119. Carey I, Gersch J, Wang B, Moigboi C, Kuhns M, Cloherty G, et al. Pregenomic HBV RNA and hepatitis B core-related antigen predict outcomes in hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B patients suppressed on nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy. Hepatology 2020;72:42-57.


120. Wang J, Shen T, Huang X, Kumar GR, Chen X, Zeng Z, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA is encapsidated pregenome RNA that may be associated with persistence of viral infection and rebound. J Hepatol 2016;65:700-710.


121. Giersch K, Allweiss L, Volz T, Dandri M, Lütgehetmann M. Serum HBV pgRNA as a clinical marker for cccDNA activity. J Hepatol 2017;66:460-462.


122. Seto WK, Liu KS, Mak LY, Cloherty G, Wong DK, Gersch J, et al. Role of serum HBV RNA and hepatitis B surface antigen levels in identifying Asian patients with chronic hepatitis B suitable for entecavir cessation. Gut 2021;70:775-783.


124. Kaewdech A, Tangkijvanich P, Sripongpun P, Witeerungrot T, Jandee S, Tanaka Y, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen, core-related antigen and HBV RNA: predicting clinical relapse after NA therapy discontinuation. Liver Int 2020;40:2961-2971.


125. Liu S, Deng R, Zhou B, Liang X, Liu Z, Peng J, et al. Association of serum hepatitis B virus RNA with hepatocellular carcinoma risk in chronic hepatitis B patients under nucleos(t)ide analogues therapy. J Infect Dis 2021 Dec;jiab597.

126. Ding WB, Wang MC, Yu J, Huang G, Sun DP, Liu L, et al. HBV/pregenomic RNA increases the stemness and promotes the development of HBV-related HCC through reciprocal regulation with insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3. Hepatology 2021;74:1480-1495.


128. Nassal M. HBV cccDNA: viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015;64:1972-1984.


129. Kumar R, Pérez-Del-Pulgar S, Testoni B, Lebossé F, Zoulim F. Clinical relevance of the study of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA. Liver Int 2016;36 Suppl 1:72-77.


133. Sung WK, Zheng H, Li S, Chen R, Liu X, Li Y, et al. Genome-wide survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet 2012;44:765-769.


134. An J, Kim D, Oh B, Oh YJ, Song J, Park N, et al. Comprehensive characterization of viral integrations and genomic aberrations in HBV-infected intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas. Hepatology 2022;75:997-1011.


135. Mendizabal M, Piñero F, Ridruejo E, Herz Wolff F, Anders M, Reggiardo V, et al. Disease progression in patients with hepatitis C virus infection treated with direct-acting antiviral agents. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;18:2554-2563 e3.


136. Zheng B, Liu XL, Fan R, Bai J, Wen H, Du LT, et al. The landscape of cell-free HBV integrations and mutations in cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Clin Cancer Res 2021;27:3772-3783.


137. Tang LSY, Covert E, Wilson E, Kottilil S. Chronic hepatitis B infection: a review. JAMA 2018;319:1802-1813.


138. Lok AS, McMahon BJ, Brown RS Jr, Wong JB, Ahmed AT, Farah W, et al. Antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B viral infection in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2016;63:284-306.


139. Xiao G, Yang J, Yan L. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index and fibrosis-4 index for detecting liver fibrosis in adult patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2015;61:292-302.


141. Zhu X, Wang LC, Chen EQ, Chen XB, Chen LY, Liu L, et al. Prospective evaluation of FibroScan for the diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis compared with liver biopsy/AST platelet ratio index and FIB-4 in patients with chronic HBV infection. Dig Dis Sci 2011;56:2742-2749.


142. Bedossa P, Poynard T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR cooperative study group. Hepatology 1996;24:289-293.


143. Andreani T, Serfaty L, Mohand D, Dernaika S, Wendum D, Chazouillères O, et al. Chronic hepatitis B virus carriers in the immunotolerant phase of infection: histologic findings and outcome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;5:636-641.


149. Kim MN, Kim SU, Kim BK, Park JY, Kim DY, Ahn SH, et al. Increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients with transient elastography-defined subclinical cirrhosis. Hepatology 2015;61:1851-1859.


150. Park JY, Park YN, Kim DY, Paik YH, Lee KS, Moon BS, et al. High prevalence of significant histology in asymptomatic chronic hepatitis B patients with genotype C and high serum HBV DNA levels. J Viral Hepat 2008;15:615-621.


151. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2017;67:370-398.


152. Kim GA, Han S, Choi GH, Choi J, Lim YS. Moderate levels of serum hepatitis B virus DNA are associated with the highest risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2020;51:1169-1179.


153. Shim JJ, Kim JW, Oh CH, Lee YR, Lee JS, Park SY, et al. Serum alanine aminotransferase level and liver-related mortality in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a large national cohort study. Liver Int 2018;38:1751-1759.


154. Chan HL, Chan CK, Hui AJ, Chan S, Poordad F, Chang TT, et al. Effects of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in hepatitis B e antigenpositive patients with normal levels of alanine aminotransferase and high levels of hepatitis B virus DNA. Gastroenterology 2014;146:1240-1248.


155. Wong VW, Hui AJ, Wong GL, Chan RS, Chim AM, Lo AO, et al. Four-year outcomes after cessation of tenofovir in immune-tolerant chronic hepatitis B patients. J Clin Gastroenterol 2018;52:347-352.


156. Chang Y, Choe WH, Sinn DH, Lee JH, Ahn SH, Lee H, et al. Nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment for patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV) e antigen-positive chronic HBV genotype C infection: a nationwide, multicenter, retrospective study. J Infect Dis 2017;216:1407-1414.


157. Kim HL, Kim GA, Park JA, Kang HR, Lee EK, Lim YS. Cost-effectiveness of antiviral treatment in adult patients with immune-tolerant phase chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2021;70:2172-2182.


158. Cho JY, Paik YH, Sohn W, Cho HC, Gwak GY, Choi MS, et al. Patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with oral antiviral therapy retain a higher risk for HCC compared with patients with inactive stage disease. Gut 2014;63:1943-1950.


159. Choi J, Han S, Kim N, Lim YS. Increasing burden of liver cancer despite extensive use of antiviral agents in a hepatitis B virusendemic population. Hepatology 2017;66:1454-1463.


160. Kwo PY, Cohen SM, Lim JK. ACG clinical guideline: evaluation of abnormal liver chemistries. Am J Gastroenterol 2017;112:18-35.


161. Lee JK, Shim JH, Lee HC, Lee SH, Kim KM, Lim YS, et al. Estimation of the healthy upper limits for serum alanine aminotransferase in Asian populations with normal liver histology. Hepatology 2010;51:1577-1583.


162. Prati D, Taioli E, Zanella A, Della Torre E, Butelli S, Del Vecchio E, et al. Updated definitions of healthy ranges for serum alanine aminotransferase levels. Ann Intern Med 2002;137:1-10.


164. Chao DT, Lim JK, Ayoub WS, Nguyen LH, Nguyen MH. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the proportion of chronic hepatitis B patients with normal alanine transaminase ≤ 40 IU/L and significant hepatic fibrosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014;39:349-358.


165. Chen CF, Lee WC, Yang HI, Chang HC, Jen CL, Iloeje UH, et al. Changes in serum levels of HBV DNA and alanine aminotransferase determine risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2011;141:1240-1248 1248.e1-e2.


167. Park HN, Sinn DH, Gwak GY, Kim JE, Rhee SY, Eo SJ, et al. Upper normal threshold of serum alanine aminotransferase in identifying individuals at risk for chronic liver disease. Liver Int 2012;32:937-944.


168. Chang TT, Gish RG, de Man R, Gadano A, Sollano J, Chao YC, et al. A comparison of entecavir and lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2006;354:1001-1010.


169. Lai CL, Shouval D, Lok AS, Chang TT, Cheinquer H, Goodman Z, et al. Entecavir versus lamivudine for patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2006;354:1011-1020.


170. Marcellin P, Heathcote EJ, Buti M, Gane E, de Man RA, Krastev Z, et al. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate versus adefovir dipivoxil for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2008;359:2442-2455.


171. Lai CL, Gane E, Liaw YF, Hsu CW, Thongsawat S, Wang Y, et al. Telbivudine versus lamivudine in patients with chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2007;357:2576-2588.


172. Hadziyannis SJ, Tassopoulos NC, Heathcote EJ, Chang TT, Kitis G, Rizzetto M, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2003;348:800-807.


173. Marcellin P, Chang TT, Lim SG, Tong MJ, Sievert W, Shiffman ML, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigenpositive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2003;348:808-816.


174. Rockey DC, Caldwell SH, Goodman ZD, Nelson RC, Smith AD; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Liver biopsy. Hepatology 2009;49:1017-1044.


175. European Association for Study of Liver; Asociacion Latinoamericana para el Estudio del Higado. EASL-ALEH clinical practice guidelines: non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis. J Hepatol 2015;63:237-264.


178. Kim HS, Kim HJ, Shin WG, Kim KH, Lee JH, Kim HY, et al. Predictive factors for early HBeAg seroconversion in acute exacerbation of patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2009;136:505-512.


179. Huang KW, Tam KW, Luo JC, Kuan YC. Efficacy and safety of lamivudine versus entecavir for treating chronic hepatitis B virus-related acute exacerbation and acute-on-chronic liver failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Gastroenterol 2017;51:539-547.


181. Chen CH, Lee CM, Lu SN, Wang JH, Tung HD, Hung CH, et al. Comparison of clinical outcome between patients continuing and discontinuing lamivudine therapy after biochemical breakthrough of YMDD mutants. J Hepatol 2004;41:454-461.


182. Kim KH, Sinn DH, Yun WK, Cho HC, Lee YY, Gwak GY, et al. Defining virologic relapse in chronic hepatitis B. Dig Dis Sci 2011;56:2432-2438.


184. Garg H, Sarin SK, Kumar M, Garg V, Sharma BC, Kumar A. Tenofovir improves the outcome in patients with spontaneous reactivation of hepatitis B presenting as acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatology 2011;53:774-780.


185. Wong VW, Wong GL, Yiu KK, Chim AM, Chu SH, Chan HY, et al. Entecavir treatment in patients with severe acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2011;54:236-242.


188. Park JG, Lee YR, Park SY, Lee HJ, Tak WY, Kweon YO, et al. Tenofovir, entecavir, and lamivudine in patients with severe acute exacerbation and hepatic decompensation of chronic hepatitis B. Dig Liver Dis 2018;50:163-167.


189. Chen CH, Lin CL, Hu TH, Hung CH, Tseng PL, Wang JH, et al. Entecavir vs. lamivudine in chronic hepatitis B patients with severe acute exacerbation and hepatic decompensation. J Hepatol 2014;60:1127-1134.


190. Yasui S, Fujiwara K, Nakamura M, Miyamura T, Yonemitsu Y, Mikata R, et al. Virological efficacy of combination therapy with corticosteroid and nucleoside analogue for severe acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat 2015;22:94-102.


191. Yue-Meng W, Yang LH, Yang JH, Xu Y, Yang J, Song GB. The effect of plasma exchange on entecavir-treated chronic hepatitis B patients with hepatic de-compensation and acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatol Int 2016;10:462-469.


193. Sinn DH, Kim SE, Kim BK, Kim JH, Choi MS. The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among chronic hepatitis B virus-infected patients outside current treatment criteria. J Viral Hepat 2019;26:1465-1472.


194. Paik N, Sinn DH, Lee JH, Oh IS, Kim JH, Kang W, et al. Non-invasive tests for liver disease severity and the hepatocellular carcinoma risk in chronic hepatitis B patients with low-level viremia. Liver Int 2018;38:68-75.


195. Cao Z, Liu Y, Ma L, Lu J, Jin Y, Ren S, et al. A potent hepatitis B surface antigen response in subjects with inactive hepatitis B surface antigen carrier treated with pegylated-interferon alpha. Hepatology 2017;66:1058-1066.


196. de Niet A, Jansen L, Stelma F, Willemse SB, Kuiken SD, Weijer S, et al. Peg-interferon plus nucleotide analogue treatment versus no treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B with a low viral load: a randomised controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;2:576-584.


198. Marcellin P, Gane E, Buti M, Afdhal N, Sievert W, Jacobson IM, et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B: a 5-year open-label followup study. Lancet 2013;381:468-475.


199. Chang TT, Liaw YF, Wu SS, Schiff E, Han KH, Lai CL, et al. Longterm entecavir therapy results in the reversal of fibrosis/cirrhosis and continued histological improvement in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2010;52:886-893.


201. Kim JH, Sinn DH, Kang W, Gwak GY, Paik YH, Choi MS, et al. Lowlevel viremia and the increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients receiving entecavir treatment. Hepatology 2017;66:335-343.


202. Sinn DH, Lee J, Goo J, Kim K, Gwak GY, Paik YH, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma risk in chronic hepatitis B virus-infected compensated cirrhosis patients with low viral load. Hepatology 2015;62:694-701.


203. Jang JW, Yoo SH, Nam HC, Jang BH, Sung Sung PS, Lee W, et al. Association of prophylactic anti-hepatitis B virus therapy with improved long-term survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transarterial therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2020;71:546-555.


204. Cho YY, Lee JH, Chang Y, Nam JY, Cho H, Lee DH, et al. Comparison of overall survival between antiviral-induced viral suppression and inactive phase chronic hepatitis B patients. J Viral Hepat 2018;25:1161-1171.


205. Lee HW, Park SY, Lee YR, Lee H, Lee JS, Kim SU, et al. Episodic detectable viremia does not affect prognosis in untreated compensated cirrhosis with serum hepatitis B virus DNA <2,000 IU/mL. Am J Gastroenterol 2022;117:288-294.


206. Jang JW, Choi JY, Kim YS, Woo HY, Choi SK, Lee CH, et al. Longterm effect of antiviral therapy on disease course after decompensation in patients with hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis. Hepatology 2015;61:1809-1820.


207. Shim JH, Lee HC, Kim KM, Lim YS, Chung YH, Lee YS, et al. Efficacy of entecavir in treatment-naïve patients with hepatitis B virusrelated decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2010;52:176-182.


208. Fontana RJ, Hann HW, Perrillo RP, Vierling JM, Wright T, Rakela J, et al. Determinants of early mortality in patients with decompensated chronic hepatitis B treated with antiviral therapy. Gastroenterology 2002;123:719-727.


209. Perrillo R, Tamburro C, Regenstein F, Balart L, Bodenheimer H, Silva M, et al. Low-dose, titratable interferon alfa in decompensated liver disease caused by chronic infection with hepatitis B virus. Gastroenterology 1995;109:908-916.


210. Marcellin P, Ahn SH, Ma X, Caruntu FA, Tak WY, Elkashab M, et al. Combination of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and peginterferon α-2a increases loss of hepatitis B surface antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2016;150:134-144 e10.


213. Yuen MF, Gane EJ, Kim DJ, Weilert F, Yuen Chan HL, Lalezari J, et al. Antiviral activity, safety, and pharmacokinetics of capsid assembly modulator NVR 3-778 in patients with chronic HBV infection. Gastroenterology 2019;156:1392-1403 e7.


214. Yuen MF, Agarwal K, Gane EJ, Schwabe C, Ahn SH, Kim DJ, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and antiviral effects of ABI-H0731, a hepatitis B virus core inhibitor: a randomised, placebo-controlled phase 1 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;5:152-166.


215. Zoulim F, Lenz O, Vandenbossche JJ, Talloen W, Verbinnen T, Moscalu I, et al. JNJ-56136379, an HBV capsid assembly modulator, is well-tolerated and has antiviral activity in a phase 1 study of patients with chronic infection. Gastroenterology 2020;159:521-533.e9.


216. Yuen MF, Agarwal K, Ma X, Nguyen T, Schiff ER, Hann HW, et al. Antiviral activity and safety of the hepatitis B core inhibitor ABIH0731 administered with a nucleos(t)ide reverse transcriptase inhibitor in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B infection in a long-term extension study. J Hepatol 2020;73:S140.

217. Janssen H, Hou J, Asselah T, Chan H, Zoulim F, Tanaka Y, et al. Efficacy and safety results of the phase 2 JNJ-56136379 JADE study in patients with chronic hepatitis B: interim week 24 data. J Hepatol 2020;73:S129-S130.

222. Gish RG, Yuen MF, Chan HL, Given BD, Lai CL, Locarnini SA, et al. Synthetic RNAi triggers and their use in chronic hepatitis B therapies with curative intent. Antiviral Res 2015;121:97-108.


225. Gane E, Locarnini S, Lim TH, Strasser S, Sievert W, Cheng W, et al. Short interfering RNA JNJ-3989 combination therapy in chronic hepatitis B shows potent reduction of all viral markers but no correlate was identified for HBsAg reduction and baseline factors. J Hepatol 2021;75:S289-S290.
226. Yuen MF, Berliba E, Sukeepaisarnjaroen W, Tangkijvanich P, Leerapun A, Holmes JA, et al. Low HBsAg levels maintained following cessation of the GalNac-siRNA, AB-729, in chronic hepatitis B subjects on nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy. Hepatology 2021;74:1402A-1403A.
227. Yuen MF, Lim YS, Cloutier D, Thanawala V, Shen L, Arizpe A, et al. Preliminary results from a phase 2 study evaluating VIR-2218 alone and in combination with pegylated interferon alfa-2a in participants with chronic hepatitis B infection. Hepatology 2021;74:63A.
228. Yuen MF, Lim TH, Kim W, Tangkijvanich P, Yoon JH, Sievert W, et al. HBV RNAi inhibitor RG6346 in phase 1b-2a trial was safe, welltolerated, and resulted in substantial and durable reductions in serum HBsAg levels. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases the Liver Meeting; 2020 Nov 13-16.
229. Bazinet M, Pântea V, Placinta G, Moscalu I, Cebotarescu V, Cojuhari L, et al. Safety and efficacy of 48 weeks REP 2139 or REP 2165, tenofovir disoproxil, and pegylated interferon alfa-2a in patients with chronic HBV infection naïve to nucleos(t)ide therapy. Gastroenterology 2020;158:2180-2194.


231. Gane E, Dunbar PR, Brooks A, Zhao Y, Tan S, Lau A, et al. Efficacy and safety of 24 weeks treatment with oral TLR8 agonist, selgantolimod, in virally-suppressed adult patients with chronic hepatitis B: a phase 2 study. J Hepatol 2020;73:S52.

232. Janssen HL, Lim YS, Kim HJ, Tseng CH, Coffin CS, Elkashab M, et al. Safety and efficacy of oral TLR8 agonist, selgantolimod, in viremic adult patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2021;75:S757-S758.
233. Gane E, Verdon DJ, Brooks AE, Gaggar A, Nguyen AH, Subramanian GM, et al. Anti-PD-1 blockade with nivolumab with and without therapeutic vaccination for virally suppressed chronic hepatitis B: a pilot study. J Hepatol 2019;71:900-907.


234. Wang G, Qian J, Cui Y, Yan Y, He H, Wu J. A phase IIa trial of subcutaneously administered PD-L1 antibody ASC22 (envafolimab) in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2021;74:62A.
235. Yoshida O, Imai Y, Shiraishi K, Sanada T, Kohara M, Tsukiyama-Kohara K, et al. Long term HBsAg reduction by a nasal administrative therapeutic vaccine containing HBsAg and HBcAg mixed with mucoadhesive CVP (CVP-NASVAC) in patients with chronic HBV infection: the results of 30 months follow up. Hepatology 2021;74:64A.
236. Lok AS, Pan CQ, Han SH, Trinh HN, Fessel WJ, Rodell T, et al. Randomized phase II study of GS-4774 as a therapeutic vaccine in virally suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2016;65:509-516.


237. Boni C, Janssen HLA, Rossi M, Yoon SK, Vecchi A, Barili V, et al. Combined GS-4774 and tenofovir therapy can improve HBV-specific T-cell responses in patients with chronic hepatitis. Gastroenterology 2019;157:227-241.e7.


238. Lee JH, Lee YB, Cho EJ, Yu SJ, Yoon JH, Kim YJ. Entecavir plus pegylated interferon and sequential hepatitis B virus vaccination increases hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance: a randomized controlled proof-of-concept study. Clin Infect Dis 2021;73:e3308-e3316.


239. Yuen MF, Locarnini S, Given B, Schluep T, Hamilton J, Biermer M, et al. First clinical experience with RNA interference-based triple combination therapy in chronic hepatitis B: JNJ-3989, JNJ-6379 and a nucleos(t)ide analogue. Hepatology 2019;70:1489A.
240. Yuen MF, Asselah T, Jacobson IM, Brunetto MR, Janssen HL, Takehara T, et al. Efficacy and safety of the siRNA JNJ-3989 and/or the capsid assembly modulator (CAM) JNJ-6379 for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection (CHB): results from the phase 2B REEF-1 study. Hepatology 2021;74:1390A-1391A.
241. Lee HW, Ahn SH, Chan HL. Hepatitis B core-related antigen: from virology to clinical application. Semin Liver Dis 2021;41:182-190.


243. Kao JH, Jeng WJ, Ning Q, Su TH, Tseng TC, Ueno Y, et al. APASL guidance on stopping nucleos(t)ide analogues in chronic hepatitis B patients. Hepatol Int 2021;15:833-851.


245. Liem KS, Gehring AJ, Feld JJ, Janssen HLA. Challenges with stopping long-term nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2020;158:1185-1190.


246. Hall SAL, Vogrin S, Wawryk O, Burns GS, Visvanathan K, Sundararajan V, et al. Discontinuation of nucleot(s)ide analogue therapy in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B: a meta-analysis. Gut 2021 Sep 7;doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323979.

247. Jung KS, Park JY, Chon YE, Kim HS, Kang W, Kim BK, et al. Clinical outcomes and predictors for relapse after cessation of oral antiviral treatment in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Gastroenterol 2016;51:830-839.


248. Song DS, Jang JW, Yoo SH, Kwon JH, Nam SW, Bae SH, et al. Improving the prediction of relapse after nucleos(t)ide analogue discontinuation in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Clin Infect Dis 2021;73:e892-e903.


249. Kang SH, Kang K, Eun YJ, Lee YS, Kim TS, Yoo YJ, et al. Antiviral response is not sustained after cessation of lamivudine treatment in chronic hepatitis B patients: a 10-year follow-up study. J Med Virol 2017;89:849-856.


250. Tout I, Lampertico P, Berg T, Asselah T. Perspectives on stopping nucleos(t)ide analogues therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Antiviral Res 2021;185:104992.


253. Marcellin P, Lau GK, Bonino F, Farci P, Hadziyannis S, Jin R, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a alone, lamivudine alone, and the two in combination in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2004;351:1206-1217.


254. Liaw YF, Jia JD, Chan HL, Han KH, Tanwandee T, Chuang WL, et al. Shorter durations and lower doses of peginterferon alfa-2a are associated with inferior hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion rates in hepatitis B virus genotypes B or C. Hepatology 2011;54:1591-1599.


255. Lampertico P, Viganò M, Di Costanzo GG, Sagnelli E, Fasano M, Di Marco V, et al. Randomised study comparing 48 and 96 weeks peginterferon α-2a therapy in genotype D HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2013;62:290-298.


256. Chon YE, Jung KS, Ha Y, Kim MN, Lee JH, Hwang SG, et al. High body mass index hinders fibrosis improvement in patients receiving long-term tenofovir therapy in hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis. J Viral Hepat 2020;27:1119-1126.


257. Yang HC, Shih YF, Liu CJ. Viral factors affecting the clinical outcomes of chronic hepatitis B. J Infect Dis 2017;216(suppl_8):S757-S764.


258. Mommeja-Marin H, Mondou E, Blum MR, Rousseau F. Serum HBV DNA as a marker of efficacy during therapy for chronic HBV infection: analysis and review of the literature. Hepatology 2003;37:1309-1319.


259. Chon YE, Kim SU, Seo YS, Lee HW, Lee HA, Kim MN, et al. Longterm effects of entecavir and tenofovir treatment on the fibrotic burden in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;37:200-207.


260. Chon YE, Park JY, Myoung SM, Jung KS, Kim BK, Kim SU, et al. Improvement of liver fibrosis after long-term antiviral therapy assessed by fibroscan in chronic hepatitis B patients with advanced fibrosis. Am J Gastroenterol 2017;112:882-891.


262. Kim WR, Loomba R, Berg T, Aguilar Schall RE, Yee LJ, Dinh PV, et al. Impact of long-term tenofovir disoproxil fumarate on incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Cancer 2015;121:3631-3638.


265. Papatheodoridis G, Vlachogiannakos I, Cholongitas E, Wursthorn K, Thomadakis C, Touloumi G, et al. Discontinuation of oral antivirals in chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review. Hepatology 2016;63:1481-1492.


267. Lee HW, Lee HJ, Hwang JS, Sohn JH, Jang JY, Han KJ, et al. Lamivudine maintenance beyond one year after HBeAg seroconversion is a major factor for sustained virologic response in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2010;51:415-421.


268. Chong CH, Lim SG. When can we stop nucleoside analogues in patients with chronic hepatitis B? Liver Int 2017;37 Suppl 1:52-58.


269. Cornberg M, Wong VW, Locarnini S, Brunetto M, Janssen HLA, Chan HL. The role of quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen revisited. J Hepatol 2017;66:398-411.


270. Liu J, Li T, Zhang L, Xu A. The role of hepatitis B surface antigen in nucleos(t)ide analogues cessation among Asian patients with chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review. Hepatology 2019;70:1045-1055.


271. Chen CH, Lu SN, Hung CH, Wang JH, Hu TH, Changchien CS, et al. The role of hepatitis B surface antigen quantification in predicting HBsAg loss and HBV relapse after discontinuation of lamivudine treatment. J Hepatol 2014;61:515-522.


272. Wang CC, Tseng KC, Hsieh TY, Tseng TC, Lin HH, Kao JH. Assessing the durability of entecavir-treated hepatitis B using quantitative HBsAg. Am J Gastroenterol 2016;111:1286-1294.


273. Jeng WJ, Chen YC, Chien RN, Sheen IS, Liaw YF. Incidence and predictors of hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance after cessation of nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy in hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2018;68:425-434.


274. Chen CH, Hsu YC, Lu SN, Hung CH, Wang JH, Lee CM, et al. The incidence and predictors of HBV relapse after cessation of tenofovir therapy in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Viral Hepat 2018;25:590-597.


275. Huang PY, Wang JH, Hung CH, Lu SN, Hu TH, Chen CH. The role of hepatitis B virus core-related antigen in predicting hepatitis B virus relapse after cessation of entecavir in hepatitis B e antigennegative patients. J Viral Hepat 2021;28:1141-1149.


276. Hsu YC, Nguyen MH, Mo LR, Wu MS, Yang TH, Chen CC, et al. Combining hepatitis B core-related and surface antigens at end of nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment to predict off-therapy relapse risk. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2019;49:107-115.


277. Sonneveld MJ, Park JY, Kaewdech A, Seto WK, Tanaka Y, Carey I, et al. Prediction of Sustained response after nucleo(s)tide analogue cessation using HBsAg and HBcrAg levels: a multicenter study (CREATE). Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;20:e784-e793.


278. Sonneveld MJ, Chiu SM, Park JY, Brakenhoff SM, Kaewdech A, Seto WK, et al. Probability of HBsAg loss after nucleo(s)tide analogue withdrawal depends on HBV genotype and viral antigen levels. J Hepatol 2022 Jan 29;doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.01.007.

279. Fan R, Peng J, Xie Q, Tan D, Xu M, Niu J, et al. Combining hepatitis B virus RNA and hepatitis B core-related antigen: guidance for safely stopping nucleos(t)ide analogues in hepatitis B e antigen-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Infect Dis 2020;222:611-618.


280. Kim JH, Lee YS, Lee HJ, Yoon E, Jung YK, Jong ES, et al. HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B: implications for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Gastroenterol 2011;45:64-68.

281. Yip TC, Wong GL, Wong VW, Tse YK, Lui GC, Lam KL, et al. Durability of hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in untreated and nucleos(t)ide analogue-treated patients. J Hepatol 2018;68:63-72.

282. Kim MA, Kim SU, Sinn DH, Jang JW, Lim YS, Ahn SH, et al. Discontinuation of nucleos(t)ide analogues is not associated with a higher risk of HBsAg seroreversion after antiviral-induced HBsAg seroclearance: a nationwide multicentre study. Gut 2020;69:2214-2222.


283. Papatheodoridi M, Tampaki M, Lok AS, Papatheodoridis GV. Risk of HBV reactivation during therapies for HCC: a systematic review. Hepatology 2021 Nov 13;doi: 10.1002/hep.32241.

285. Dan JQ, Zhang YJ, Huang JT, Chen MS, Gao HJ, Peng ZW, et al. Hepatitis B virus reactivation after radiofrequency ablation or hepatic resection for HBV-related small hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study. Eur J Surg Oncol 2013;39:865-872.


287. Lee JI, Kim JK, Chang HY, Lee JW, Kim JM, Chung HJ, et al. Impact of postoperative hepatitis B virus reactivation in hepatocellular carcinoma patients who formerly had naturally suppressed virus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;29:1019-1027.


289. Sohn W, Paik YH, Cho JY, Ahn JM, Choi GS, Kim JM, et al. Influence of hepatitis B virus reactivation on the recurrence of HBVrelated hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection in patients with low viral load. J Viral Hepat 2015;22:539-550.


290. Chang JI, Sinn DH, Cho H, Kim S, Kang W, Gwak GY, et al. Clinical outcomes of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma patients with undetectable serum HBV DNA levels. Dig Dis Sci 2021 Nov 20;doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-07312-8.

291. Wu CY, Chen YJ, Ho HJ, Hsu YC, Kuo KN, Wu MS, et al. Association between nucleoside analogues and risk of hepatitis B virus–related hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence following liver resection. JAMA 2012;308:1906-1914.


292. Yin J, Li N, Han Y, Xue J, Deng Y, Shi J, et al. Effect of antiviral treatment with nucleotide/nucleoside analogs on postoperative prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: a two-stage longitudinal clinical study. J Clin Oncol 2013;31:3647-3655.


293. Huang G, Li PP, Lau WY, Pan ZY, Zhao LH, Wang ZG, et al. Antiviral therapy reduces hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence in patients with low HBV-DNA levels: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg 2018;268:943-954.


294. Lee TY, Lin JT, Zeng YS, Chen YJ, Wu MS, Wu CY. Association between nucleos(t)ide analog and tumor recurrence in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation. Hepatology 2016;63:1517-1527.


295. Wong JS, Wong GL, Tsoi KK, Wong VW, Cheung SY, Chong CN, et al. Meta-analysis: the efficacy of anti-viral therapy in prevention of recurrence after curative treatment of chronic hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2011;33:1104-1112.


296. Cho H, Ahn H, Lee DH, Lee JH, Jung YJ, Chang Y, et al. Entecavir and tenofovir reduce hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence more effectively than other antivirals. J Viral Hepat 2018;25:707-717.


297. Choi J, Jo C, Lim YS. Tenofovir versus entecavir on recurrence of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection. Hepatology 2021;73:661-673.


298. Tsai MC, Wang CC, Lee WC, Liu YW, Lin CC, Hu TH. Tenofovir is superior to entecavir on recurrence in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;36:163.

299. Lee JH, Kim BK, Park SY, Tak WY, Park JY, Kim DY, et al. The efficacies of entecavir and tenofovir in terms of enhancing prognosis after curative treatment of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Intern Med 2021;89:48-55.


300. Lao XM, Luo G, Ye LT, Luo C, Shi M, Wang D, et al. Effects of antiviral therapy on hepatitis B virus reactivation and liver function after resection or chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int 2013;33:595-604.


301. Lao XM, Wang D, Shi M, Liu G, Li S, Guo R, et al. Changes in hepatitis B virus DNA levels and liver function after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res 2011;41:553-563.


302. Jang JW, Choi JY, Bae SH, Yoon SK, Chang UI, Kim CW, et al. A randomized controlled study of preemptive lamivudine in patients receiving transarterial chemo-lipiodolization. Hepatology 2006;43:233-240.


303. Park JW, Park KW, Cho SH, Park HS, Lee WJ, Lee DH, et al. Risk of hepatitis B exacerbation is low after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization therapy for patients with HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma: report of a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol 2005;100:2194-2200.


304. Yeo W, Lam KC, Zee B, Chan PS, Mo FK, Ho WM, et al. Hepatitis B reactivation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing systemic chemotherapy. Ann Oncol 2004;15:1661-1666.


305. Nagamatsu H, Itano S, Nagaoka S, Akiyoshi J, Matsugaki S, Kurogi J, et al. Prophylactic lamivudine administration prevents exacerbation of liver damage in HBe antigen positive patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transhepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. Am J Gastroenterol 2004;99:2369-2375.


306. Tamori A, Nishiguchi S, Tanaka M, Kurooka H, Fujimoto S, Nakamura K, et al. Lamivudine therapy for hepatitis B virus reactivation in a patient receiving intra-arterial chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res 2003;26:77-80.


307. Nagamatsu H, Kumashiro R, Itano S, Matsugaki S, Sata M. Investigation of associating factors in exacerbation of liver damage after chemotherapy in patients with HBV-related HCC. Hepatol Res 2003;26:293-301.


309. Kim JH, Park JW, Kim TH, Koh DW, Lee WJ, Kim CM. Hepatitis B virus reactivation after three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007;69:813-819.


311. Jang JW, Kwon JH, You CR, Kim JD, Woo HY, Bae SH, et al. Risk of HBV reactivation according to viral status and treatment intensity in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Antivir Ther 2011;16:969-977.


313. Peng JW, Lin GN, Xiao JJ, Jiang XM. Hepatitis B virus reactivation in hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing transcatheter arterial chemoembolization therapy. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2012;8:356-361.


314. Yang Y, Wen F, Li J, Zhang P, Yan W, Hao P, et al. A high baseline HBV load and antiviral therapy affect the survival of patients with advanced HBV-related HCC treated with sorafenib. Liver Int 2015;35:2147-2154.


315. Lim S, Han J, Kim GM, Han KH, Choi HJ. Hepatitis B viral load predicts survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with sorafenib. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;30:1024-1031.


317. Yoo S, Lee D, Shim JH, Kim KM, Lim YS, Lee HC, et al. Risk of hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients treated with immunotherapy for anti-cancer treatment. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;20:898-907.


318. Sun X, Hu D, Yang Z, Liu Z, Wang J, Chen J, et al. Baseline HBV loads do not affect the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma receiving anti-programmed cell death-1 immunotherapy. J Hepatocell Carcinoma 2020;7:337-345.


319. He MK, Peng C, Zhao Y, Liang RB, Lai ZC, Kan A, et al. Comparison of HBV reactivation between patients with high HBV-DNA and low HBV-DNA loads undergoing PD-1 inhibitor and concurrent antiviral prophylaxis. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2021;70:3207-3216.


321. Lampertico P, Chan HL, Janssen HL, Strasser SI, Schindler R, Berg T. Review article: long-term safety of nucleoside and nucleotide analogues in HBV-monoinfected patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2016;44:16-34.


323. Maggi P, Montinaro V, Leone A, Fasano M, Volpe A, Bellacosa C, et al. Bone and kidney toxicity induced by nucleotide analogues in patients affected by HBV-related chronic hepatitis: a longitudinal study. J Antimicrob Chemother 2015;70:1150-1154.


324. López-Alcorocho JM, Barril G, Ortiz-Movilla N, Traver JA, Bartolomé J, Sanz P, et al. Prevalence of hepatitis B, hepatitis C, GB virus C/hepatitis G and TT viruses in predialysis and hemodialysis patients. J Med Virol 2001;63:103-107.


325. Gwak GY, Huh W, Lee DH, Min BH, Koh KC, Kim JJ, et al. Occult hepatitis B virus infection in chronic hemodialysis patients in Korea. Hepatogastroenterology 2008;55:1721-1724.

326. Minuk GY, Sun DF, Greenberg R, Zhang M, Hawkins K, Uhanova J, et al. Occult hepatitis B virus infection in a North American adult hemodialysis patient population. Hepatology 2004;40:1072-1077.


327. Burdick RA, Bragg-Gresham JL, Woods JD, Hedderwick SA, Kurokawa K, Combe C, et al. Patterns of hepatitis B prevalence and seroconversion in hemodialysis units from three continents: the DOPPS. Kidney Int 2003;63:2222-2229.


328. Johnson DW, Dent H, Yao Q, Tranaeus A, Huang CC, Han DS, et al. Frequencies of hepatitis B and C infections among haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients in Asia-Pacific countries: analysis of registry data. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2009;24:1598-1603.


329. Finelli L, Miller JT, Tokars JI, Alter MJ, Arduino MJ. National surveillance of dialysis-associated diseases in the United States, 2002. Semin Dial 2005;18:52-61.


330. Agarwal K, Brunetto M, Seto WK, Lim YS, Fung S, Marcellin P, et al. 96 weeks treatment of tenofovir alafenamide vs. tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2018;68:672-681.


331. Buti M, Gane E, Seto WK, Chan HL, Chuang WL, Stepanova T, et al. Tenofovir alafenamide versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;1:196-206.


332. Chan HL, Fung S, Seto WK, Chuang WL, Chen CY, Kim HJ, et al. Tenofovir alafenamide versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;1:185-195.


333. Ahn SH, Kim W, Jung YK, Yang JM, Jang JY, Kweon YO, et al. Efficacy and safety of besifovir dipivoxil maleate compared With tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;17:1850-1859 e4.


334. Chan HLY, Buti M, Agarwal K, Marcellin P, Lim YS, Brunetto MR, et al. Maintenance of high levels of viral suppression and improved safety profile of tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) relative to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) in chronic hepatitis B patients treated for 5 years in 2 ongoing phase 3 studies. American Associatio for the Study of Liver Diseases the Liver Meeting; 2020 Nov 13-16.

335. Lampertico P, Buti M, Fung S, Ahn SH, Chuang WL, Tak WY, et al. Switching from tenofovir disoproxil fumarate to tenofovir alafenamide in virologically suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3, multicentre non-inferiority study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;5:441-453.


336. Byun KS, Choi J, Kim JH, Lee YS, Lee HC, Kim YJ, et al. Tenofovir alafenamide for drug-resistant hepatitis B: a randomized trial for switching from tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;20:427-437 e5.


339. Gupta S, Govindarajan S, Fong TL, Redeker AG. Spontaneous reactivation in chronic hepatitis B: patterns and natural history. J Clin Gastroenterol 1990;12:562-568.

340. Lok AS, McMahon BJ; Practice Guidelines Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Chronic hepatitis B: update of recommendations. Hepatology 2004;39:857-861.


341. Tanaka Y, Esumi M, Shikata T. Persistence of hepatitis B virus DNA after serological clearance of hepatitis B virus. Liver 1990;10:6-10.


342. Koo YX, Tan DS, Tan IB, Tao M, Chow WC, Lim ST. Hepatitis B virus reactivation and role of antiviral prophylaxis in lymphoma patients with past hepatitis B virus infection who are receiving chemoimmunotherapy. Cancer 2010;116:115-121.


343. Yeo W, Johnson PJ. Diagnosis, prevention and management of hepatitis B virus reactivation during anticancer therapy. Hepatology 2006;43:209-220.


346. Lok AS, Liang RH, Chiu EK, Wong KL, Chan TK, Todd D. Reactivation of hepatitis B virus replication in patients receiving cytotoxic therapy. Report of a prospective study. Gastroenterology 1991;100:182-188.


347. Yeo W, Chan PK, Zhong S, Ho WM, Steinberg JL, Tam JS, et al. Frequency of hepatitis B virus reactivation in cancer patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy: a prospective study of 626 patients with identification of risk factors. J Med Virol 2000;62:299-307.


349. Kwak LW, Halpern J, Olshen RA, Horning SJ. Prognostic significance of actual dose intensity in diffuse large-cell lymphoma: results of a tree-structured survival analysis. J Clin Oncol 1990;8:963-977.


350. Bonadonna G, Valagussa P, Moliterni A, Zambetti M, Brambilla C. Adjuvant cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil in node-positive breast cancer: the results of 20 years of follow-up. N Engl J Med 1995;332:901-906.


351. Yeo W, Chan PK, Hui P, Ho WM, Lam KC, Kwan WH, et al. Hepatitis B virus reactivation in breast cancer patients receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy: a prospective study. J Med Virol 2003;70:553-561.


353. Perrillo RP, Gish R, Falck-Ytter YT. American Gastroenterological Association Institute technical review on prevention and treatment of hepatitis B virus reactivation during immunosuppressive drug therapy. Gastroenterology 2015;148:221-244.e3.


354. Reddy KR, Beavers KL, Hammond SP, Lim JK, Falck-Ytter YT; American Gastroenterological Association Institute. American Gastroenterological Association Institute guideline on the prevention and treatment of hepatitis B virus reactivation during immunosuppressive drug therapy. Gastroenterology 2015;148:215-219 quiz e16-e17.


355. Takai S, Tsurumi H, Ando K, Kasahara S, Sawada M, Yamada T, et al. Prevalence of hepatitis B and C virus infection in haematological malignancies and liver injury following chemotherapy. Eur J Haematol 2005;74:158-165.


356. Hsu C, Hsiung CA, Su IJ, Hwang WS, Wang MC, Lin SF, et al. A revisit of prophylactic lamivudine for chemotherapy-associated hepatitis B reactivation in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a randomized trial. Hepatology 2008;47:844-853.


358. Cheng AL, Hsiung CA, Su IJ, Chen PJ, Chang MC, Tsao CJ, et al. Steroid-free chemotherapy decreases risk of hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation in HBV-carriers with lymphoma. Hepatology 2003;37:1320-1328.


359. Yeo W, Chan TC, Leung NW, Lam WY, Mo FK, Chu MT, et al. Hepatitis B virus reactivation in lymphoma patients with prior resolved hepatitis B undergoing anticancer therapy with or without rituximab. J Clin Oncol 2009;27:605-611.


360. Dong HJ, Ni LN, Sheng GF, Song HL, Xu JZ, Ling Y. Risk of hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation in non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients receiving rituximab-chemotherapy: a meta-analysis. J Clin Virol 2013;57:209-214.


361. Kim SJ, Hsu C, Song YQ, Tay K, Hong XN, Cao J, et al. Hepatitis B virus reactivation in B-cell lymphoma patients treated with rituximab: analysis from the Asia Lymphoma Study Group. Eur J Cancer 2013;49:3486-3496.


362. Tang Z, Li X, Wu S, Liu Y, Qiao Y, Xu D, et al. Risk of hepatitis B reactivation in HBsAg-negative/HBcAb-positive patients with undetectable serum HBV DNA after treatment with rituximab for lymphoma: a meta-analysis. Hepatol Int 2017;11:429-433.


363. Hsu C, Tsou HH, Lin SJ, Wang MC, Yao M, Hwang WL, et al. Chemotherapy-induced hepatitis B reactivation in lymphoma patients with resolved HBV infection: a prospective study. Hepatology 2014;59:2092-2100.


364. Chen XQ, Peng JW, Lin GN, Li M, Xia ZJ. The effect of prophylactic lamivudine on hepatitis B virus reactivation in HBsAg-positive patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma undergoing prolonged rituximab therapy. Med Oncol 2012;29:1237-1241.


365. Zurawska U, Hicks LK, Woo G, Bell CM, Krahn M, Chan KK, et al. Hepatitis B virus screening before chemotherapy for lymphoma: a cost-effectiveness analysis. J Clin Oncol 2012;30:3167-3173.


367. Lau GK, He ML, Fong DY, Bartholomeusz A, Au WY, Lie AK, et al. Preemptive use of lamivudine reduces hepatitis B exacerbation after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Hepatology 2002;36:702-709.


368. Sarmati L, Andreoni M, Antonelli G, Arcese W, Bruno R, Coppola N, et al. Recommendations for screening, monitoring, prevention, prophylaxis and therapy of hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients with haematologic malignancies and patients who underwent haematologic stem cell transplantation-a position paper. Clin Microbiol Infect 2017;23:935-940.


370. Chen FW, Coyle L, Jones BE, Pattullo V. Entecavir versus lamivudine for hepatitis B prophylaxis in patients with haematological disease. Liver Int 2013;33:1203-1210.


371. Lee SK, Sung PS, Park SS, Min CK, Nam H, Jang JW, et al. Reactivation of resolved hepatitis B after daratumumab for multiple myeloma. Clin Infect Dis 2021;73:e1372-e1375.


373. Dai MS, Wu PF, Shyu RY, Lu JJ, Chao TY. Hepatitis B virus reactivation in breast cancer patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy and the role of preemptive lamivudine administration. Liver Int 2004;24:540-546.


375. Xu Z, Dai W, Wu YT, Arshad B, Li X, Wu H, et al. Prophylactic effect of lamivudine on chemotherapy-induced hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients with solid tumour: a meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 2018;27:e12799.


376. El-Sayed MH, Mohamed MM, Karim A, Maina AM, Oliveri F, Brunetto MR, et al. Severe liver disease is caused by HBV rather than HCV in children with hematological malignancies. Hematol J 2003;4:321-327.


377. Yeo W, Chan PK, Ho WM, Zee B, Lam KC, Lei KI, et al. Lamivudine for the prevention of hepatitis B virus reactivation in hepatitis B santigen seropositive cancer patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 2004;22:927-934.


378. Chung SJ, Kim JK, Park MC, Park YB, Lee SK. Reactivation of hepatitis B viral infection in inactive HBsAg carriers following anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy. J Rheumatol 2009;36:2416-2420.


380. Kim YJ, Bae SC, Sung YK, Kim TH, Jun JB, Yoo DH, et al. Possible reactivation of potential hepatitis B virus occult infection by tumor necrosis factor-alpha blocker in the treatment of rheumatic diseases. J Rheumatol 2010;37:346-350.


381. Alameel T, Al Sulais E. Risk of HBV reactivation among IBD patients with occult hepatitis B virus infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;19:621-622.


382. Lee YH, Bae SC, Song GG. Hepatitis B virus reactivation in HBsAgpositive patients with rheumatic diseases undergoing anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy or DMARDs. Int J Rheum Dis 2013;16:527-531.


383. Pérez-Alvarez R, Díaz-Lagares C, García-Hernández F, Lopez-Roses L, Brito-Zerón P, Pérez-de-Lis M, et al. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation in patients receiving tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-targeted therapy: analysis of 257 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 2011;90:359-371.


386. Wang N, Hu X, Cao W, Li C, Xiao Y, Cao Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of CAR19/22 T-cell cocktail therapy in patients with refractory/ relapsed B-cell malignancies. Blood 2020;135:17-27.


387. Lau GK, Yiu HH, Fong DY, Cheng HC, Au WY, Lai LS, et al. Early is superior to deferred preemptive lamivudine therapy for hepatitis B patients undergoing chemotherapy. Gastroenterology 2003;125:1742-1749.


388. Saab S, Dong MH, Joseph TA, Tong MJ. Hepatitis B prophylaxis in patients undergoing chemotherapy for lymphoma: a decision analysis model. Hepatology 2007;46:1049-1056.


389. Viganò M, Serra G, Casella G, Grossi G, Lampertico P. Reactivation of hepatitis B virus during targeted therapies for cancer and immune-mediated disorders. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2016;16:917-926.


391. Cerva C, Colagrossi L, Maffongelli G, Salpini R, Di Carlo D, Malagnino V, et al. Persistent risk of HBV reactivation despite extensive lamivudine prophylaxis in haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients who are anti-HBc-positive or HBV-negative recipients with an anti-HBc-positive donor. Clin Microbiol Infect 2016;22:946.e1-946.e8.


392. Liu WP, Wang XP, Zheng W, Ping LY, Zhang C, Wang GQ, et al. Hepatitis B virus reactivation after withdrawal of prophylactic antiviral therapy in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 2016;57:1355-1362.


393. Nakaya A, Fujita S, Satake A, Nakanishi T, Azuma Y, Tsubokura Y, et al. Delayed HBV reactivation in rituximab-containing chemotherapy: how long should we continue anti-virus prophylaxis or monitoring HBV-DNA? Leuk Res 2016;50:46-49.


395. Cho Y, Yu SJ, Cho EJ, Lee JH, Kim TM, Heo DS, et al. High titers of anti-HBs prevent rituximab-related viral reactivation in resolved hepatitis B patient with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Med Virol 2016;88:1010-1017.


396. Rossi G, Pelizzari A, Motta M, Puoti M. Primary prophylaxis with lamivudine of hepatitis B virus reactivation in chronic HbsAg carriers with lymphoid malignancies treated with chemotherapy. Br J Haematol 2001;115:58-62.


397. Li HR, Huang JJ, Guo HQ, Zhang X, Xie Y, Zhu HL, et al. Comparison of entecavir and lamivudine in preventing hepatitis B reactivation in lymphoma patients during chemotherapy. J Viral Hepat 2011;18:877-883.


398. Huang H, Li X, Zhu J, Ye S, Zhang H, Wang W, et al. Entecavir vs lamivudine for prevention of hepatitis B virus reactivation among patients with untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma receiving R-CHOP chemotherapy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2014;312:2521-2530.


399. Yu S, Luo H, Pan M, Luis AP, Xiong Z, Shuai P, et al. Comparison of entecavir and lamivudine in preventing HBV reactivation in lymphoma patients undergoing chemotherapy: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pharm 2016;38:1035-1043.


400. Kim HY, Yoo JJ, Oh S, Yu SJ, Kim YJ, Yoon JH, et al. Scoring system for risk stratification of viral reactivation during prophylactic antiviral treatment in Korean patients with hepatitis B undergoing anticancer chemotherapy: a multicenter study. J Med Virol 2018;90:1593-1603.


402. Lau GK, Leung YH, Fong DY, Au WY, Kwong YL, Lie A, et al. High hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA viral load as the most important risk factor for HBV reactivation in patients positive for HBV surface antigen undergoing autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood 2002;99:2324-2330.


403. Li J, Liu J, Huang B, Zheng D, Chen M, Zhou Z, et al. Hepatitis B virus infection status is an independent risk factor for multiple myeloma patients after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Tumour Biol 2013;34:1723-1728.


404. Huang H, Cai Q, Lin T, Lin X, Liu Y, Gao Y, et al. Lamivudine for the prevention of hepatitis B virus reactivation after high-dose chemotherapy and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with advanced or relapsed non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma single institution experience. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2009;10:2399-2406.


405. Shang J, Wang H, Sun J, Fan Z, Huang F, Zhang Y, et al. A comparison of lamivudine vs entecavir for prophylaxis of hepatitis B virus reactivation in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients: a single-institutional experience. Bone Marrow Transplant 2016;51:581-586.


407. Seto WK, Chan TS, Hwang YY, Wong DK, Fung J, Liu KS, et al. Hepatitis B reactivation in occult viral carriers undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a prospective study. Hepatology 2017;65:1451-1461.


408. Park S, Kim K, Kim DH, Jang JH, Kim SJ, Kim WS, et al. Changes of hepatitis B virus serologic status after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and impact of donor immunity on hepatitis B virus. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011;17:1630-1637.


409. Yoo JJ, Cho EJ, Cho YY, Lee M, Lee DH, Cho Y, et al. Efficacy of antiviral prophylaxis in HBsAg-negative, anti-HBc positive patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Liver Int 2015;35:2530-2536.


412. Hwang JP, Feld JJ, Hammond SP, Wang SH, Alston-Johnson DE, Cryer DR, et al. Hepatitis B virus screening and management for patients with cancer prior to therapy: ASCO provisional clinical opinion update. J Clin Oncol 2020;38:3698-3715.


414. Lee HL, Jang JW, Han JW, Lee SW, Bae SH, Choi JY, et al. Early hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance following antiviral treatment in patients with reactivation of resolved hepatitis B. Dig Dis Sci 2019;64:2992-3000.


415. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: liver transplantation. J Hepatol 2016;64:433-485.


416. Sripongpun P, Mannalithara A, Kwo PY, Kim WR. Potential benefits of switching liver transplant recipients to tenofovir alafenamide prophylaxis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;18:747-749.


418. Wesdorp DJ, Knoester M, Braat AE, Coenraad MJ, Vossen AC, Claas EC, et al. Nucleoside plus nucleotide analogs and cessation of hepatitis B immunoglobulin after liver transplantation in chronic hepatitis B is safe and effective. J Clin Virol 2013;58:67-73.


419. Teperman LW, Poordad F, Bzowej N, Martin P, Pungpapong S, Schiano T, et al. Randomized trial of emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate after hepatitis B immunoglobulin withdrawal after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 2013;19:594-601.


420. Stravitz RT, Shiffman ML, Kimmel M, Puri P, Luketic VA, Sterling RK, et al. Substitution of tenofovir/emtricitabine for hepatitis B immune globulin prevents recurrence of hepatitis B after liver transplantation. Liver Int 2012;32:1138-1145.


422. Cholongitas E, Goulis I, Antoniadis N, Fouzas I, Imvrios G, Papanikolaou V, et al. New nucleos(t)ide analogue monoprophylaxis after cessation of hepatitis B immunoglobulin is effective against hepatitis B recurrence. Transpl Int 2014;27:1022-1028.


423. Radhakrishnan K, Chi A, Quan DJ, Roberts JP, Terrault NA. Short course of postoperative hepatitis B immunoglobulin plus antivirals prevents reinfection of liver transplant recipients. Transplantation 2017;101:2079-2082.


424. Manini MA, Whitehouse G, Bruce M, Passerini M, Lim TY, Carey I, et al. Entecavir or tenofovir monotherapy prevents HBV recurrence in liver transplant recipients: a 5-year follow-up study after hepatitis B immunoglobulin withdrawal. Dig Liver Dis 2018;50:944-953.


425. Tanaka T, Benmousa A, Marquez M, Therapondos G, Renner EL, Lilly LB. The long-term efficacy of nucleos(t)ide analog plus a year of low-dose HBIG to prevent HBV recurrence post-liver transplantation. Clin Transplant 2012;26:E561-E569.


426. Fung J, Wong T, Chok K, Chan A, Cheung TT, Dai JW, et al. Longterm outcomes of entecavir monotherapy for chronic hepatitis B after liver transplantation: results up to 8 years. Hepatology 2017;66:1036-1044.


427. Fung J, Chan SC, Cheung C, Yuen MF, Chok KS, Sharr W, et al. Oral nucleoside/nucleotide analogs without hepatitis B immune globulin after liver transplantation for hepatitis B. Am J Gastroenterol 2013;108:942-948.


429. Miyaaki H, Tamada Y, Hayashi K, Taura N, Miuma S, Shibata H, et al. Recurrent hepatitis B and D virus infection in a liver transplant recipient. Transplant Proc 2017;49:175-177.


430. Mederacke I, Filmann N, Yurdaydin C, Bremer B, Puls F, Zacher BJ, et al. Rapid early HDV RNA decline in the peripheral blood but prolonged intrahepatic hepatitis delta antigen persistence after liver transplantation. J Hepatol 2012;56:115-122.


431. Cholongitas E, Papatheodoridis GV, Burroughs AK. Liver grafts from anti-hepatitis B core positive donors: a systematic review. J Hepatol 2010;52:272-279.


432. Skagen CL, Jou JH, Said A. Risk of de novo hepatitis in liver recipients from hepatitis-B core antibody-positive grafts - a systematic analysis. Clin Transplant 2011;25:E243-E249.


433. Perrillo R. Hepatitis B virus prevention strategies for antibody to hepatitis B core antigen-positive liver donation: a survey of North American, European, and Asian-Pacific transplant programs. Liver Transpl 2009;15:223-232.


434. Huprikar S, Danziger-Isakov L, Ahn J, Naugler S, Blumberg E, Avery RK, et al. Solid organ transplantation from hepatitis B virus-positive donors: consensus guidelines for recipient management. Am J Transplant 2015;15:1162-1172.


437. Yap DY, Yung S, Tang CS, Seto WK, Ma MK, Mok MM, et al. Entecavir treatment in kidney transplant recipients infected with hepatitis B. Clin Transplant 2014;28:1010-1015.


438. Hu TH, Tsai MC, Chien YS, Chen YT, Chen TC, Lin MT, et al. A novel experience of antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B in renal transplant recipients. Antivir Ther 2012;17:745-753.


439. Nho KW, Kim YH, Han DJ, Park SK, Kim SB. Kidney transplantation alone in end-stage renal disease patients with hepatitis B liver cirrhosis: a single-center experience. Transplantation 2015;99:133-138.


440. Veroux M, Puliatti C, Gagliano M, Cappello D, Macarone M, Vizcarra D, et al. Use of hepatitis B core antibody-positive donor kidneys in hepatitis B surface antibody-positive and -negative recipients. Transplant Proc 2005;37:2574-2575.


441. Wachs ME, Amend WJ, Ascher NL, Bretan PN, Emond J, Lake JR, et al. The risk of transmission of hepatitis B from HBsAg(-), HBcAb(+), HBIgM(-) organ donors. Transplantation 1995;59:230-234.


442. Fong TL, Bunnapradist S, Jordan SC, Cho YW. Impact of hepatitis B core antibody status on outcomes of cadaveric renal transplantation: analysis of united network of organ sharing database between 1994 and 1999. Transplantation 2002;73:85-89.


443. Jeon JW, Kim SM, Cho H, Baek CH, Kim H, Shin S, et al. Presence of hepatitis B surface antibody in addition to hepatitis B core antibody confers protection against hepatitis B virus infection in hepatitis B surface antigen-negative patients undergoing kidney transplantation. Transplantation 2018;102:1717-1723.


445. Duhart BT Jr, Honaker MR, Shokouh-Amiri MH, Riely CA, Vera SR, Taylor SL, et al. Retrospective evaluation of the risk of hepatitis B virus reactivation after transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis 2003;5:126-131.


446. Blanpain C, Knoop C, Delforge ML, Antoine M, Peny MO, Liesnard C, et al. Reactivation of hepatitis B after transplantation in patients with pre-existing anti-hepatitis B surface antigen antibodies: report on three cases and review of the literature. Transplantation 1998;66:883-886.


447. Knöll A, Pietrzyk M, Loss M, Goetz WA, Jilg W. Solid-organ transplantation in HBsAg-negative patients with antibodies to HBV core antigen: low risk of HBV reactivation. Transplantation 2005;79:1631-1633.


448. Berger A, Preiser W, Kachel HG, Stürmer M, Doerr HW. HBV reactivation after kidney transplantation. J Clin Virol 2005;32:162-165.


449. Kanaan N, Kabamba B, Maréchal C, Pirson Y, Beguin C, Goffin E, et al. Significant rate of hepatitis B reactivation following kidney transplantation in patients with resolved infection. J Clin Virol 2012;55:233-238.


450. Bae E, Park CH, Ki CS, Kim SJ, Huh W, Oh HY, et al. Prevalence and clinical significance of occult hepatitis B virus infection among renal transplant recipients in Korea. Scand J Infect Dis 2012;44:788-792.


451. Nishimura K, Kishikawa H, Yoshida Y, Ueda N, Nakazawa S, Yamanaka K, et al. Clinical and virologic courses of hepatitis B surface antigen-negative and hepatitis B core or hepatitis B surface antibody-positive renal transplant recipients. Transplant Proc 2013;45:1600-1602.


452. Lee J, Park JY, Huh KH, Kim BS, Kim MS, Kim SI, et al. Rituximab and hepatitis B reactivation in HBsAg-negative/ anti-HBc-positive kidney transplant recipients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2017;32:722-729.


453. Chen GD, Gu JL, Qiu J, Chen LZ. Outcomes and risk factors for hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation after kidney transplantation in occult HBV carriers. Transpl Infect Dis 2013;15:300-305.


456. Sagnelli E, Pasquale G, Coppola N, Scarano F, Marrocco C, Scolastico C, et al. Influence of chronic coinfection with hepatitis B and C virus on liver histology. Infection 2004;32:144-148.


457. Lee LP, Dai CY, Chuang WL, Chang WY, Hou NJ, Hsieh MY, et al. Comparison of liver histopathology between chronic hepatitis C patients and chronic hepatitis B and C-coinfected patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;22:515-517.


459. Pol S, Haour G, Fontaine H, Dorival C, Petrov-Sanchez V, Bourliere M, et al. The negative impact of HBV/HCV coinfection on cirrhosis and its consequences. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2017;46:1054-1060.


460. Chen G, Wang C, Chen J, Ji D, Wang Y, Wu V, et al. Hepatitis B reactivation in hepatitis B and C coinfected patients treated with antiviral agents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2017;66:13-26.


461. Yeh ML, Huang CF, Huang CI, Holmes JA, Hsieh MH, Tsai YS, et al. Hepatitis B-related outcomes following direct-acting antiviral therapy in Taiwanese patients with chronic HBV/HCV co-infection. J Hepatol 2020;73:62-71.


462. Calvaruso V, Ferraro D, Licata A, Bavetta MG, Petta S, Bronte F, et al. HBV reactivation in patients with HCV/HBV cirrhosis on treatment with direct-acting antivirals. J Viral Hepat 2018;25:72-79.


463. Bunnell KL, Vibhakar S, Glowacki RC, Gallagher MA, Osei AM, Huhn G. Nephrotoxicity associated with concomitant use of ledipasvir-sofosbuvir and tenofovir in a patient with hepatitis C virus and human immunodeficiency virus coinfection. Pharmacotherapy 2016;36:e148-e153.


465. Mücke VT, Mücke MM, Peiffer KH, Weiler N, Welzel TM, Sarrazin C, et al. No evidence of hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients with resolved infection treated with direct-acting antivirals for hepatitis C in a large real-world cohort. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2017;46:432-439.


466. Tamori A, Abiru S, Enomoto H, Kioka K, Korenaga M, Tani J, et al. Low incidence of hepatitis B virus reactivation and subsequent hepatitis in patients with chronic hepatitis C receiving direct-acting antiviral therapy. J Viral Hepat 2018;25:608-611.


467. Sulkowski MS, Chuang WL, Kao JH, Yang JC, Gao B, Brainard DM, et al. No evidence of reactivation of hepatitis B virus among patients treated with ledipasvir-sofosbuvir for hepatitis C virus infection. Clin Infect Dis 2016;63:1202-1204.


470. Kim HS, Kim SJ, Park HW, Shin WG, Kim KH, Lee JH, et al. Prevalence and clinical significance of hepatitis D virus coinfection in patients with chronic hepatitis B in Korea. J Med Virol 2011;83:1172-1177.


471. Jeong SH, Kim JM, Ahn HJ, Park MJ, Paik KH, Choi W, et al. The prevalence and clinical characteristics of hepatitis-delta infection in Korea. Korean J Hepatol 2005;11:43-50.

472. Alfaiate D, Clément S, Gomes D, Goossens N, Negro F. Chronic hepatitis D and hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Hepatol 2020;73:533-539.


473. Bahcecioglu IH, Aygun C, Gozel N, Poyrazoglu OK, Bulut Y, Yalniz M. Prevalence of hepatitis delta virus (HDV) infection in chronic hepatitis B patients in eastern Turkey: still a serious problem to consider. J Viral Hepat 2011;18:518-524.


475. Wedemeyer H, Yurdaydìn C, Dalekos GN, Erhardt A, Çakaloğlu Y, Değertekin H, et al. Peginterferon plus adefovir versus either drug alone for hepatitis delta. N Engl J Med 2011;364:322-331.


476. Abbas Z, Memon MS, Mithani H, Jafri W, Hamid S. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D patients with pegylated interferon: a real-world experience. Antivir Ther 2014;19:463-468.


477. Keskin O, Wedemeyer H, Tüzün A, Zachou K, Deda X, Dalekos GN, et al. Association between level of hepatitis D virus RNA at week 24 of pegylated interferon therapy and outcome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;13:2342-2349 e1-e2.


478. Heidrich B, Yurdaydın C, Kabaçam G, Ratsch BA, Zachou K, Bremer B, et al. Late HDV RNA relapse after peginterferon alpha-based therapy of chronic hepatitis delta. Hepatology 2014;60:87-97.


479. Triantos C, Kalafateli M, Nikolopoulou V, Burroughs A. Metaanalysis: antiviral treatment for hepatitis D. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2012;35:663-673.


480. Karaca C, Soyer OM, Baran B, Ormeci AC, Gokturk S, Aydin E, et al. Efficacy of pegylated interferon-α treatment for 24 months in chronic delta hepatitis and predictors of response. Antivir Ther 2013;18:561-566.


481. Bogomolov P, Alexandrov A, Voronkova N, Macievich M, Kokina K, Petrachenkova M, et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D with the entry inhibitor myrcludex B: first results of a phase Ib/IIa study. J Hepatol 2016;65:490-498.


482. Wedemeyer H, Aleman S, Andreone P, Blank A, Brunetto M, Bogomolov P, et al. Bulevirtide monotherapy at low and high dose in patients with chronic hepatitis delta: 24 weeks interim data of the phase 3 MYR301 study. J Hepatol 2021;75:S294-S295.

484. Yurdaydin C, Keskin O, Yurdcu E, Çalişkan A, Önem S, Karakaya F, et al. A phase 2 dose-finding study of lonafarnib and ritonavir with or without interferon alpha for chronic delta hepatitis. Hepatology 2021 Dec 3;doi: 10.1002/hep.32259.

485. Bazinet M, Pântea V, Cebotarescu V, Cojuhari L, Jimbei P, Albrecht J, et al. Safety and efficacy of REP 2139 and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus co-infection (REP 301 and REP 301-LTF): a non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;2:877-889.


487. Wong VW, Chan SL, Mo F, Chan TC, Loong HH, Wong GL, et al. Clinical scoring system to predict hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B carriers. J Clin Oncol 2010;28:1660-1665.


488. Wong GL, Chan HL, Wong CK, Leung C, Chan CY, Ho PP, et al. Liver stiffness-based optimization of hepatocellular carcinoma risk score in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 2014;60:339-345.


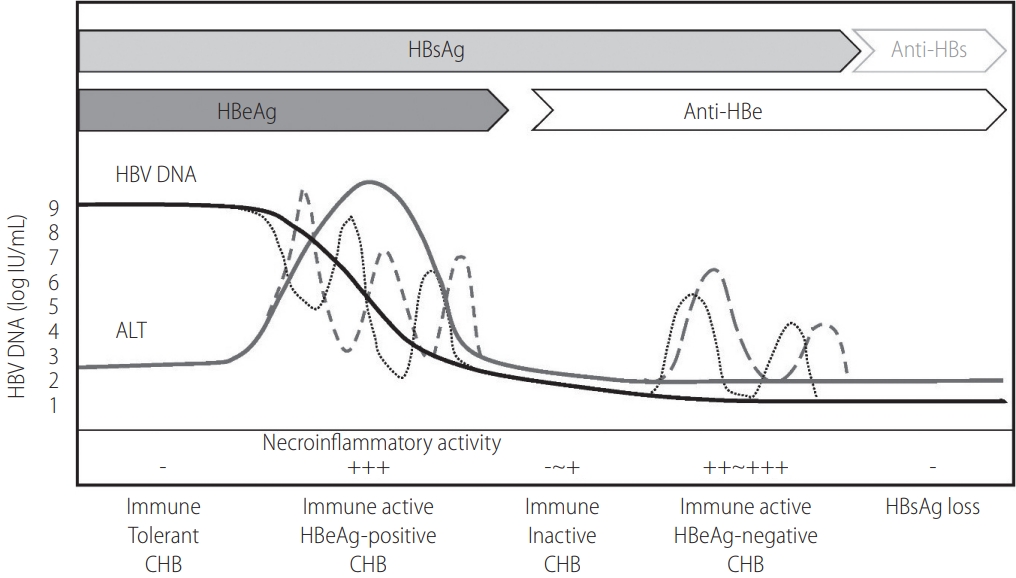
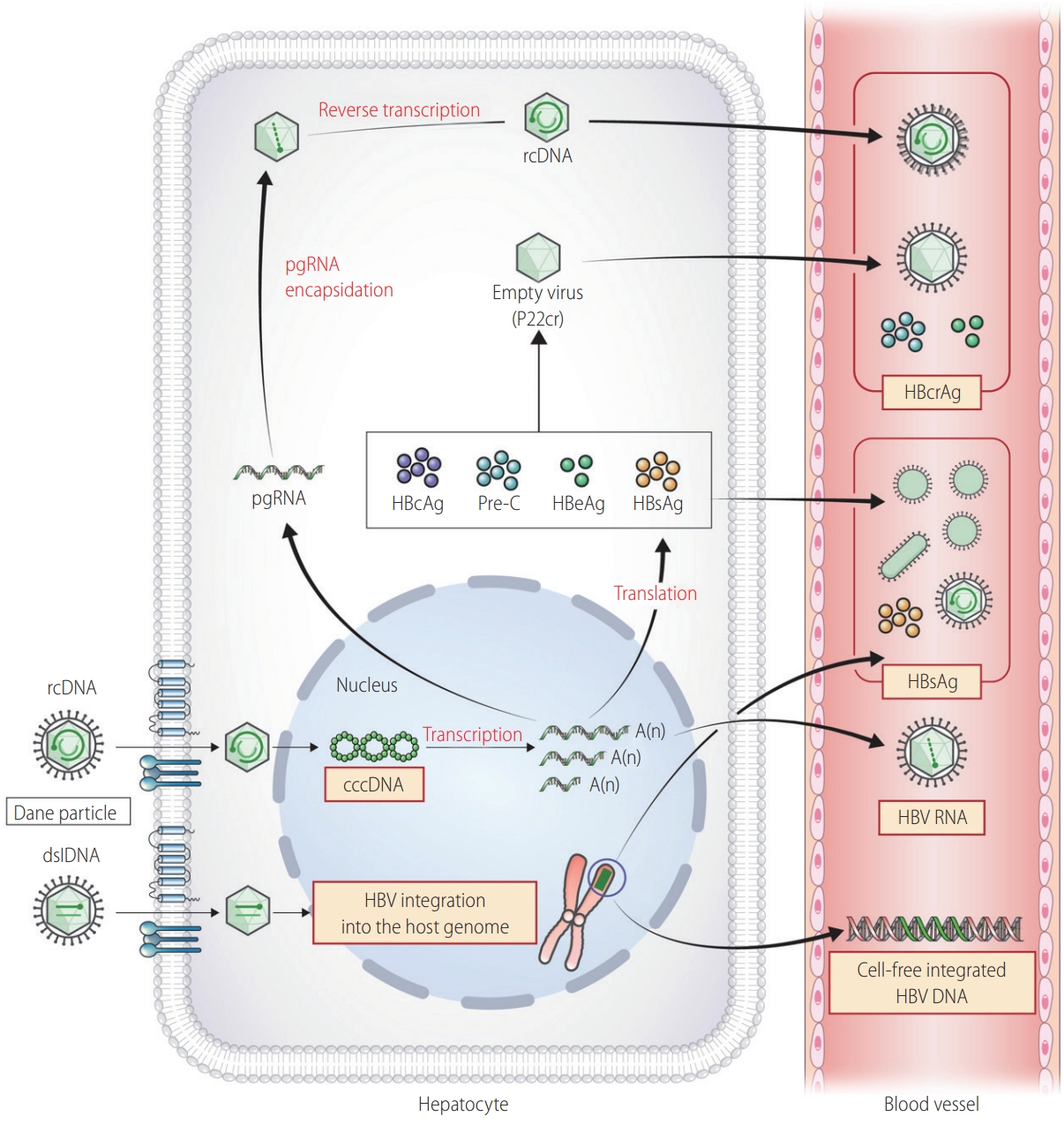
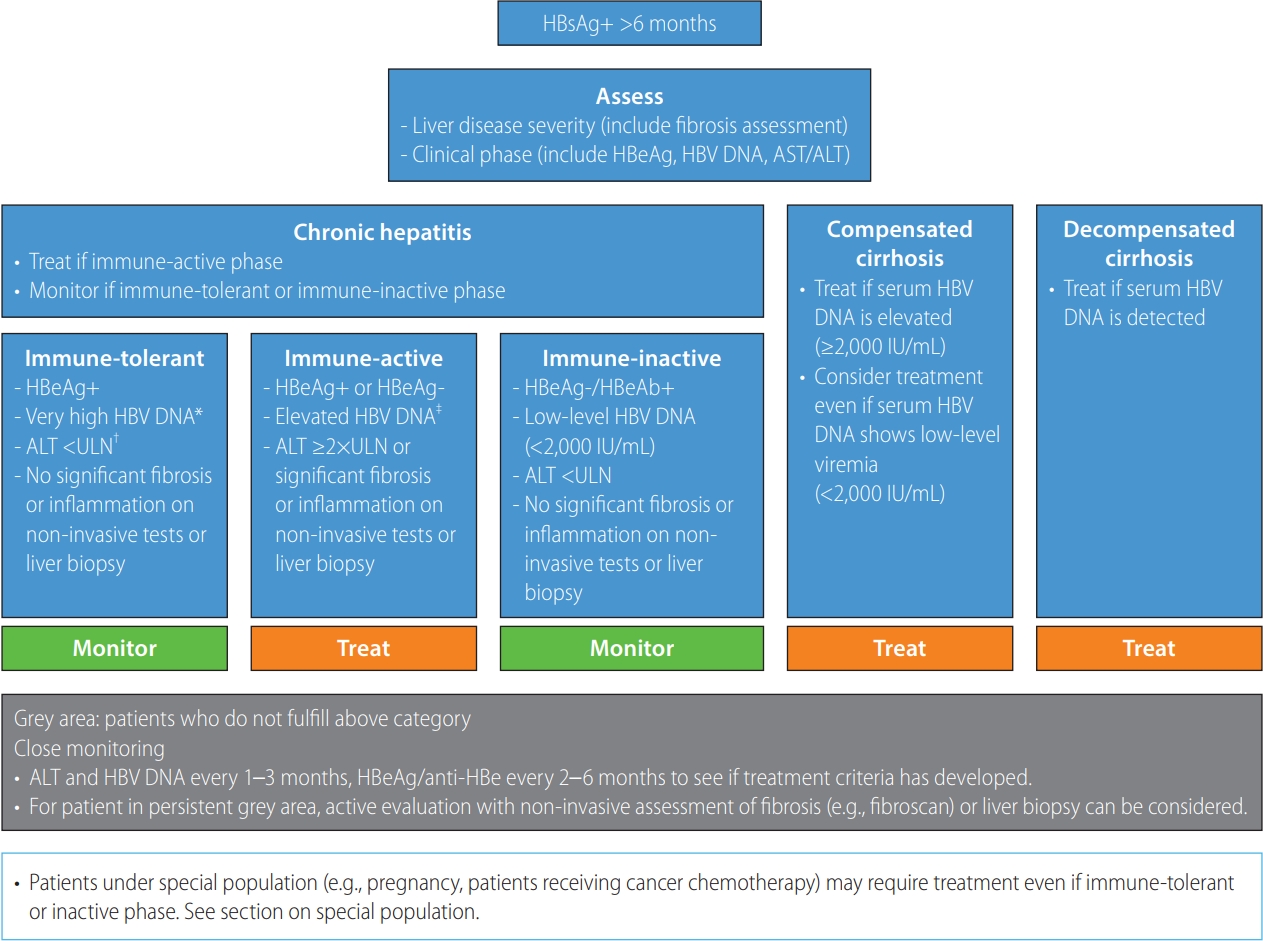







 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



