| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 26(2); 2020 > Article |
|
Patients with decompensated cirrhosis with complications have a very poor prognosis and require careful management. Varices are common complications in patients with cirrhosis. Although the prognosis of variceal bleeding has improved with recent advances in diagnosis and treatment, the mortality rate remains 12ŌĆō22%. Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is known to occur in 10ŌĆō14% of patients with cirrhosis and 16ŌĆō21% of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. More than 20% of cirrhotic patients who visit emergency rooms in Korea present with HE. Therefore, cirrhosis is a serious disease in Korea and requires specific Korean guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. In 2005, the Korean Association for the Study of the Liver (KASL) enacted a clinical practice guideline (CPG) for the treatment of cirrhosis complications including ascites, hepatorenal syndrome, varices, and HE. In 2011, the guidelines for the treatment of cirrhosis were revised to integrate antifibrotic treatment and update the diagnosis and treatment advice for variceal bleeding, cirrhotic ascites, and HE. In 2017, the CPG for liver cirrhosis was revised for ascites and related complications. At this time, KASL is revising the CPG for liver cirrhosis to address varices and HE following ascites and related complications. To date, many studies have addressed the prevention and treatment of gastroesophageal variceal bleeding and HE, and many guidelines have been based on those studies, but most of them contain foreign data that are difficult to apply to Korean clinical practice. Therefore, these revised guidelines for the treatment of varices and HE are offered for Korean practice to reflect the latest research results and extensive discussions within the revision committee. This guideline contains the opinions of experts and is intended to be a practical reference for the care of patients with varices and HE; it is not an absolute standard of care. The best choices for each patientŌĆÖs care vary from case to case, and the judgment of the doctor in charge is important. As medical evidence and new findings accumulate in the future, these guidelines will require ongoing supplementation and revision. This guideline may not be modified or altered without permission.
This guideline discusses patients with varices, HE, and related complications (esophageal varices [EVs] and bleeding, gastric varices and bleeding, portal hypertensive gastropathy, covert and overt HE) caused by liver cirrhosis. It is intended for clinicians and other medical personnel who are in charge of diagnosing and treating patients with liver cirrhosis. This guideline is also intended to provide practical clinical and educational information and directions for resident physicians and fellows in training, practitioners, and their trainers and supervisors.
Comprising 14 hepatologists, the Clinical Practice Guideline Committee for Liver Cirrhosis: Varices, HE, and related complications (the Committee) was organized by the KASL Board of Executives. Funding for the revisions was provided by KASL. Each committee member collected and analyzed source data in his or her own field, and the members then wrote the manuscript together.
The Committee selected keywords and questions using PICO (Patient/Problem, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome) assessments and systematically collected and reviewed international and domestic literature available in PubMed, MEDLINE, KoreaMed, the Korean Medical Database, and other databases. In addition to published articles, abstracts of important meetings published before January 2019 were evaluated.
The Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) system (Table 1) was applied to grade the evidence and recommendations. The levels of evidence are based on the possibility of change in the estimate of clinical effect by further research and are described as high (A), moderate (B), or low (C). The recommendations are also classified as strong (1) or weak (2) by the GRADE system based on the quality of evidence, the balance between the desirable and undesirable effects of an intervention, generalizability, and socioeconomic aspects (including cost and availability). Each recommendation is labeled with the level of relevant evidence (AŌĆōC) and corresponding recommendation grade (1, 2) as follows: A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, C2.
The Committee selected the following key questions about varices, HE, and related complications to cover in this guideline.
1) How should varices be monitored?
2) Who needs monitoring for varices?
3) How can the development and progression of EVs be prevented?
4) Who needs treatment to prevent initial esophageal variceal bleeding?
5) What is the proper management for preventing initial esophageal variceal bleeding?
6) How can acute esophageal variceal bleeding be diagnosed?
7) What is the appropriate pharmacological treatment for acute esophageal variceal bleeding?
8) What is the proper endoscopic treatment for acute esophageal variceal bleeding?
9) What are the options for rescue treatment when endoscopic treatment of acute variceal bleeding fails?
10) What is the primary treatment to prevent EVs from rebleeding?
11) What are the options for rescue treatment when primary treatment to prevent EVs from rebleeding fails?
12) Who needs treatment to prevent gastric variceal bleeding?
13) What is the proper treatment to prevent gastric variceal bleeding?
14) What is the proper treatment of acute gastric variceal bleeding?
15) What is the primary treatment to prevent gastric varices from rebleeding?
16) How should portal hypertensive gastropathy be classified?
17) How should portal hypertensive gastropathy be managed?
1) How should HE be diagnosed and classified?
2) How should overt HE be defined and diagnosed?
3) What are the precipitating factors of overt HE?
4) What differential diagnoses should be considered in diagnosing overt HE?
5) Is the measurement of serum ammonia helpful in diagnosing overt HE?
6) Is radiologic image evaluation of the central nervous system helpful in diagnosing overt HE?
7) What neurophysiological or neuropsychological tests are clinically necessary to diagnose overt HE?
8) How should the acute phase of overt HE be treated, and how should recurrence be prevented?
9) Are branched chain amino acids helpful in treating and preventing overt HE?
10) Is L-ornithine-L-aspartate (LOLA) helpful in treating and preventing overt HE?
11) Is proper education helpful in preventing the recurrence of and readmission for HE?
12) How should covert HE be defined and diagnosed?
13) What is the clinical significance of covert HE?
14) How should covert HE be treated?
15) How should the quality of life of HE patients be assessed? Does treating HE improve patient quality of life?
Each manuscript written by members was reviewed and approved through meetings of the Committee. An updated manuscript was reviewed at a meeting of the advisory board and opened to a public hearing attended by KASL members, members of related organizations, and representatives from patient associations. The final manuscript was approved by the KASL Board of Executives.
The revised guideline (The KASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for Liver Cirrhosis: Varices, Hepatic Encephalopathy and Related Complications) was released at a KASL meeting on 22 June 2019. The Korean version of the guideline is available on the KASL website (http://www.kasl.org).
Varices are a frequent complication of liver cirrhosis and a leading cause of mortality in patients with liver cirrhosis. Varices were present in 52.2% of patients who received endoscopy for variceal screening [1], and the incidence of varices was significantly higher in patients with Child-Pugh class B/C than in those with Child-Pugh class A (35ŌĆō43% vs. 48ŌĆō72%) [1,2]. Portal hypertension, which is the most common complication of liver cirrhosis, is the main determinant in the development of varices. Increased intrahepatic vascular resistance to portal flow leads to the development of portal hypertension, which is aggravated by splanchnic vasodilatation and an increase in portal blood flow caused by hyperdynamic circulation [3-5]. When the portal pressure increases above a threshold, collaterals develop at the site of communication between the portal and systemic circulation, of which varices are the most important. With the aggravation of portal hypertension, the collaterals grow and eventually rupture. Bleeding from varices is a major complication of portal hypertension and a leading cause of mortality in patients with liver cirrhosis. Therefore, preventing variceal development and progression, preventing bleeding from varices, appropriately managing acute bleeding from varices, and preventing variceal rebleeding are critical in patients with liver cirrhosis.
The incidence of varices in cirrhotic patients without varices at baseline is 5ŌĆō9% at 1 year and 14ŌĆō17% at 2 years [6,7]. The main risk factor for variceal development in these patients is a higher hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) [6]. Small EVs often progress to large varices; the incidence of progression from small to large EVs is 12% at 1 year and 25% at 2 years. The independent risk factors of EV progression are alcoholic cirrhosis, decompensated disease, and splenomegaly [7]. The 1-year incidence of variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis and varices without a previous history of bleeding is approximately 12% (5% for small varices and 15% for large varices), and the main risk factors of bleeding are larger varices, the presence of redness over the varices, and decompensated disease [8]. Although the mortality rate has decreased significantly during the past several decades thanks to improvements in diagnostic and therapeutic modalities [9,10], it remains as high as 12ŌĆō22% [11-14]. In addition, rebleeding is frequent, up to 60% within 1 year, without appropriate treatment to prevent it [15].
Given the high prevalence of varices and poor prognosis with variceal bleeding, monitoring varices is important in patients with liver cirrhosis. Therefore, upon first diagnosis with liver cirrhosis, endoscopy should be performed to look for varices and assess the risk of bleeding. Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis is not difficult in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis accompanied by ascites or variceal bleeding, but a liver biopsy is needed to diagnose patients with compensated cirrhosis who have no clinical symptoms or signs. However, liver biopsy is an invasive procedure with a risk of serious complications [16]. Furthermore, doubt has been cast on the accuracy of liver biopsy because of the risk of sampling errors [17,18] and intra- and interobserver variability [18,19].
Liver cirrhosis can disappear with appropriate treatment of the underlying liver disease [20,21], though portal hypertension can accompany the severe stage of fibrosis (F3) [22,23]. Various practice guidelines recommend surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with liver fibrosis, even before the development of cirrhosis [24,25]. Therefore, the alternative term compensated advanced chronic liver disease (cACLD) has been proposed for patients with severe fibrosis (F3) and compensated liver cirrhosis to better reflect that the spectrum of severe fibrosis and cirrhosis is a continuum in asymptomatic patients and that distinguishing between these two conditions is often clinically impossible [26]. A liver stiffness value, measured by transient elastography, of <10 kPa can rule out cACLD, and a value between 10 and 15 kPa is suggestive of cACLD but needs further tests for confirmation. A value >15 kPa is highly suggestive of cACLD [26]. Endoscopic surveillance of all patients with cACLD can cause problems, such as an increase in medical costs due to an increase in unnecessary tests. Therefore, noninvasive screening tests have been proposed for patients with EVs, especially those whose EVs have a high risk of bleeding, to reduce unnecessary endoscopic surveillance. The Baveno VI criteria suggest that endoscopic surveillance can be avoided in cACLD patients with a liver stiffness <20 kPa and a platelet count >150├Ś109/L because they are at very low risk for varices that need to be treated [26]. Augustin et al. [27] expanded the Baveno VI criteria to say that endoscopic surveillance can be avoided in cACLD patients with liver stiffness <25 kPa and a platelet count >110├Ś109/L. However, considering that noninvasive screening for varices that need to be treated is not particularly reliable [28,29] and endoscopy is more easily accessed in Korea than in Western countries, we do not deem screening by noninvasive test to be useful in Korea.
The incidence of EV development in cirrhotic patients without varices is 5ŌĆō9% at 1 year and 14ŌĆō17% at 2 years [6,7]. Small EVs progress to large varices at the rate of 12% after 1 year and 25% after 2 years [7]. Therefore, endoscopic surveillance should be performed more frequently in patients with small EVs than in those without EVs. In addition, because the type of underlying liver disease (e.g., alcoholic cirrhosis) and liver function (e.g., decompensated cirrhosis) are risk factors for the progression of EVs, they should be taken into account when determining the surveillance interval. Endoscopic surveillance should be performed at 2ŌĆō3-year intervals in patients with compensated liver cirrhosis and at 1ŌĆō2-year intervals in those with decompensated liver cirrhosis [30,31].
EVs can be classified as large or small according to their size, with a breakpoint at 5 mm in diameter [32], or they can be classified as F1 (linearly dilated, small and straight varices), F2 (beady varices, tortuous and occupying less than one third of the esophageal lumen), or F3(nodular varices, large and occupying more than one third of the esophageal lumen) [33]. However, because the F2 and F3 classifications are fairly subjective and prophylactic treatment is recommended both for F2 and F3, F1 is usually classified as small, and F2 and F3 are classified together as large.
[Recommendations]
1. In patients diagnosed with liver cirrhosis, screening endoscopy is recommended to determine the presence of varices and assess the risk of bleeding. (A1)
2. In endoscopy, EVs are classified as small (F1) and large (F2 or F3), and the presence of redness should be evaluated. (B1)
3. To identif y the development and progression of EVs, endoscopic surveillance should be performed at 2ŌĆō3-year-intervals in patients with compensated liver cirrhosis and at 1ŌĆō2-year intervals in those with decompensated liver cirrhosis. The frequency of endoscopic surveillance could be modified according to the type and severity of underlying liver disease. (B1)
Appropriate treatment for the underlying liver disease can improve liver fibrosis, which could improve portal hypertension and prevent the development of complications. In patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis, the cirrhosis disappeared from the liver biopsy reports of 74% after 5 years of treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate [20], and in a meta-analysis, hepatic histologic improvement was observed in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with pegylated interferon┬▒ribavirin [34]. In an earlier study of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, the degree of weight loss correlated with the degree of histologic improvement [35]. Furthermore, the incidence of EVs was significantly lower in patients with a sustained virologic response (SVR) to pegylated interferon+ribavirin treatment than in those without an SVR [36-38]. In a recent study, portal pressure was significantly lower in patients with an SVR to direct-acting agents than in those without an SVR in patients with hepatitis C virus-related liver cirrhosis [39].
Because the development of GEVs is a direct consequence of portal hypertension, reducing the portal pressure through the use of nonselective beta-blockers (NSBBs) from the early stage of liver cirrhosis could theoretically ameliorate the formation of GEVs. However, a placebo-controlled study to determine whether NSBBs could prevent the formation of varices in 213 patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension without GEVs, the incidence of varices or bleeding from varices did not differ between timolol group and the placebo group (39% vs. 40%, P=0.89), and serious adverse events developed more frequently in the timolol group than the placebo group (18% vs. 6%, P=0.006) [6]. Therefore, the use of NSBBs to prevent the formation of varices is not recommended.
Several studies have evaluated whether NSBBs can prevent or delay the growth of small varices, and the results conflict. One study found a significant reduction in the rate of progression to large EVs in the nadolol group compared with the placebo group in patients with cirrhosis and small EVs (7% vs. 31% at 2 years, 20% vs. 51% at 5 years; P<0.001) [40], but another study showed that propranolol offered no benefit for the prevention of progression to large varices (23% in the propranolol group vs. 19% in the placebo group, P=0.786), even though the reduction in portal pressure was significantly greater in the propranolol group [41]. A recent meta-analysis suggests that NSBBs are not effective in preventing the progression from small to large varices [42]. Another study found that the incidence of progression to large varices across 24 months was significantly lower in the carvedilol group than the placebo group (20.6% vs. 38.6%, P=0.04), leading those researchers to suggest that carvedilol is a safe and effective way to delay the progression of small to large EVs in patients with cirrhosis [43].
Carvedilol reduces portal pressure by means of an anti-a1-mediated decrease in intrahepatic resistance and splanchnic vasoconstriction. Because intrahepatic vasoconstriction is the main pathologic mechanism in the development of portal hypertension during early-stage liver cirrhosis, it could be more effective than other medications in preventing the progression of varices in patients with early-stage cirrhosis [44]. However, further studies are needed to confirm the effects of carvedilol.
[Recommendations]
1. Appropriate treatment for the underlying liver disease is recommended to prevent the formation of EVs. (A1)
2. NSBBs (propranolol and nadolol) are not recommended to prevent the formation of EVs in cirrhotic patients without EVs. (A1)
3. In patients with small EVs that are not red, NSBBs (propranolol and nadolol) or carvedilol could be considered to prevent the progression of EVs. (B2)
In patients with liver cirrhosis and EVs, variceal bleeding occurs at a yearly rate of 5ŌĆō15% of cases. Active prevention of the first variceal bleeding is indicated in patients at a high risk of bleeding, such as patients with large varices (F2, F3), decompensated cirrhosis, or varices with red color signs on endoscopy [8,45].
In cirrhotic patients with small EVs, the risk of bleeding is low (3% at 2 years and 8% at 4 years) and remains low in patients whose varices remain small at the follow-up endoscopy, though it increases significantly when the varices become large. An increase in Child-Pugh score during follow-up appears to be a significant predictor of enlarged varices and thus an increase in bleeding risk [46]. The prevention of first bleeding in patients with small EVs depends on their risk of bleeding. Patients with small varices with red color signs on endoscopy or decompensated cirrhosis have an increased risk of bleeding and should consider using NSBBs [26,47].
Meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have shown that the use of NSBBs can prevent first variceal bleeding in cirrhotic patients with large EVs [48,49]. A study comparing NSBBs and EVL as primary prophylaxis in patients with high-risk EVs found no significant difference between them in bleeding rates (relative risk [RR], 0.86; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55ŌĆō1.35) [50]. A meta-analysis of RCTs evaluating the efficacy of EVL and pharmacological therapy in preventing first EV bleeding in patients with cirrhosis also found no significant difference in the rate of variceal bleeding between the two groups [51]. Another meta-analysis found that EVL significantly reduced the rate of first variceal bleeding and severe adverse events than NSBBs in patients with large EVs [52]. Thus, in most studies, the efficacy of EVL in preventing first variceal bleeding was similar to that of NSBBs, and in some studies, the efficacy of EVL was superior to NSBBs. Therefore, either NSBBs or EVL is recommended for the prevention of first variceal bleeding in patients with large EVs. The choice of treatment should be based on clinician expertise and patient preference, characteristics, contraindications, and adverse events [26,47].
Carvedilol is known to be more effective in reducing portal pressure than propranolol [53-55]. In a multicenter RCT comparing the efficacy of carvedilol and EVL in preventing first variceal bleeding in cirrhotic patients with large EVs, carvedilol had lower rates of first variceal bleeding (10% vs. 23%, P=0.04), but there was no significant difference in overall mortality or bleeding-related mortality during follow up [56]. In another RCT comparing the efficacy of carvedilol and EVL for primary prophylaxis of EV bleeding, the carvedilol and EVL groups had comparable variceal bleeding rates (8.5% vs. 6.9%, P=0.61) [57]. In a study assessing the efficacy of carvedilol, propranolol, and EVL for the primary prevention of variceal bleeding in patients with large varices, no significant differences among the groups were found in the risk of bleeding (15.4% vs. 10.8% vs. 10.2%, P=0.071), but the incidence of adverse events was the highest in the propranolol group [58]. In studies comparing the efficacy of carvedilol, NSBBs, and EVL for the primary prevention of EV bleeding, carvedilol was similar to NSBBs and EVL or superior to EVL. Therefore, carvedilol can also be used to prevent first variceal bleeding in patients with high-risk EVs.
The combination of EVL and NSBBs for the primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding could have a synergistic effect from the direct eradication of varices by EVL and the reduction of portal pressure by NSBBs. Several studies have compared the efficacy of combination therapy with that of monotherapy based on that hypothesis. In RCTs comparing EVL plus propranolol with EVL alone for preventing first variceal bleeding in patients with high-risk EVs, the combination therapy did not show any difference from EVL alone in first bleed occurrence or mortality during follow up. However, the recurrence of varices was lower in the combination group than in the EVL alone group [59,60]. No difference in the rate of first variceal bleeding was also found between EVL plus nadolol combination therapy and nadolol alone (14% vs. 13%, P=0.90) [61]. However, another study reported that EVL and propranolol combination therapy lowered the rate of first variceal bleeding compared with propranolol alone (6% vs. 31%, P=0.03) [62]. Because most studies have shown that EVL and NSBBs combination therapy for the primary prophylaxis of EV bleeding do not differ in bleeding rate or mortality compared with monotherapy, combination therapy is generally not recommended. However, some studies have reported that EVL and NSBBs combination therapy reduced the rate of first variceal bleeding and variceal recurrence compared with monotherapy. Therefore, combination therapy can be considered in selected patients. A recent meta-analysis of RCTs showed that combination therapy with EVL and NSBBs reduced the rate of first variceal bleeding compared with placebo and isosorbide-5-mononitrate (ISMN) [63].
In an RCT of cirrhotic patients with EVs, the ISMN group and propranolol group had no significant difference in bleeding rate, but the mortality rate during follow up was higher in the ISMN group (72.3% vs. 47.8% at 6 years, P=0.006) [64]. In a multicenter RCT comparing EVL, propranolol, and ISMN, the EVL and propranolol groups did not differ significantly, but the EVL group had a significantly lower rate of first variceal bleeding than the ISMN group (7.5% vs. 33% at 2 years, P=0.03) [65]. A multicenter RCT compared propranolol plus placebo with propranolol plus ISMN for the prevention of EV bleeding. The rate of first variceal bleeding did not differ significantly between the groups (10.6% vs. 12.5% at 2 years, P>0.05) [66]. Therefore, ISMN alone or in combination with NSBBs is not recommended for the prevention of first variceal bleeding.
The advantages of NSBBs include low cost, ease of administration, and not requiring follow-up endoscopies. Propranolol is started at 20ŌĆō40 mg twice a day and adjusted every 2ŌĆō3 days until the treatment goal (resting heart rate of 55ŌĆō60 beats per minute) is achieved. The maximum dose is 320 mg daily in patients without ascites and 160 mg daily in patients with ascites. Nadolol is started at 20ŌĆō40 mg once a day and adjusted every 2ŌĆō3 days until the treatment goal is achieved. The maximum dose is 160 mg daily in patients without ascites and 80 mg daily in patients with ascites. Systolic blood pressure should not decrease <90 mmHg [47].
The disadvantages of NSBBs are that about 15% of patients have contraindications to therapy, and another 15% or so require dose reduction or discontinuation because of side effects [47]. Contraindications to NSBBs include sinus bradycardia, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, obstructive pulmonary disease, heart failure, aortic valve disease, second- or third-degree atrioventricular heart block, and peripheral arterial insufficiency [67]. Side effects of NSBBs include dizziness, fatigue, general weakness, dyspnea, headache, hypotension, bradycardia, and erectile dysfunction [47,58,66,67]. Discontinuing NSBBs can increase the risk of variceal bleeding and mortality. Thus, treatment with NSBBs should be continued indefinitely [68,69]. In patients with contraindications or discontinuation due to severe side effects or poor compliance with NSBBs, EVL is recommended [68].
In patients with end-stage liver disease, such as refractory ascites or spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, the administration of NSBBs has not yet been established. In cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites, the use of NSBBs can lower arterial pressure, decrease survival time [70], and increase the risk of paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction [71]. In addition, among patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, NSBBs increase the risk of hepatorenal syndrome and acute kidney injury and reduce survival time [72]. However, other studies have reported that the use of NSBBs increased or did not affect survival time in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites [73,74]. Another study found that treatment with low-dose propranolol (80 mg/day) increased survival time in patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis [75]. The role of NSBBs in patients with refractory ascites or spontaneous bacterial peritonitis thus remains uncertain, and clinicians must carefully consider the risks and benefits when deciding whether to administer them. If NSBBs are administered, thorough monitoring of blood pressure and renal function is necessary, and dose reduction or discontinuation should be considered in patients who develop low blood pressure or impaired renal function. Discontinuation of NSBBs can increase the risk of EV bleeding; thus, if NSBBs are stopped, EVL should be considered [26].
Adjusting the dose of carvedilol is easier than adjusting the dose of NSBBs because it is not guided by heart rate. Carvedilol is started at 6.25 mg once a day (or 3.125 mg twice a day), and after 3 days increased to 6.25 mg twice a day. The maximum dose is 12.5 mg daily. Systolic blood pressure should not be decreased <90 mmHg [47].
The advantages of EVL are that it can be performed in the same session as screening endoscopy, and it has few contraindications. The disadvantages of EVL are the side effects associated with sedation and the risk of causing dysphagia, esophageal ulcerations, strictures, and bleeding. Although the incidence of side effects is higher with NSBBs, severe side effects, such as ulcer bleeding at the ligation site, are more likely to be associated with EVL [47]. Some studies have reported that proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) significantly reduce the size of post-EVL ulcers or the rate of post-EVL ulcer bleeding [76-78]. In cirrhotic patients, the long-term use of PPIs can increase the risk of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and HE, so PPIs should be used with caution [79-81]. Meanwhile, because EVL is a local therapy that does not act on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension, not only is it unable to prevent complications other than variceal bleeding, but it also requires follow-up endoscopies to assess variceal recurrence, even after variceal eradication [47], defined as a case in which varices are not seen or become too small to be ligated. Repeat EVL can be performed at intervals of 2ŌĆō8 weeks until variceal eradication is achieved. Follow-up endoscopies should be performed 1ŌĆō6 months after variceal eradication and every 6ŌĆō12 months thereafter [47,59,82].
[Recommendations]
1. In cirrhotic patients with small EVs that have a high risk of bleeding (decompensated cirrhosis or red color signs on endoscopy), the use of a NSBBs (propranolol or nadolol) should be considered to prevent first variceal bleeding. (B1) NSBBs are adjusted every 2ŌĆō3 days until the resting heart rate reaches 55ŌĆō60 beats per minute.
2. In cirrhotic patients with large EVs, the use of a NSBBs (propranolol or nadolol), carvedilol, or EVL is recommended to prevent first variceal bleeding. (A1) A combination of NSBBs and EVL can also be considered. (B2)
In patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding, variceal bleeding caused by portal hypertension can be suspected if the patients show jaundice, ascites, HE, splenomegaly, collateral circulation of the abdominal vessels, lower extremity edema, or spider angiomas. A definite diagnosis can be established by endoscopic examination. If blood clots or white nipples appear on the surface of the varices, or if blood is found in the stomach without a potential bleeding focus other than EVs, acute EV bleeding can be diagnosed [45].
Acute EV bleeding is a medical emergency requiring intensive care. It is essential to protect the circulatory and respiratory status of the patient regardless of the cause of bleeding. Volume resuscitation via adequate fluid therapy and a packed red blood cell (PRBC) transfusion should be initiated to restore and maintain hemodynamic stability. A recent RCT showed that bleeding-related mortality (5% vs. 9%, P=0.02) and the incidence of serious adverse events (12% vs. 18%, P=0.01) were significantly decreased in the ŌĆ£restrictiveŌĆØ PRBC transfusion group (initiating PRBC transfusion at a hemoglobin threshold of 7 g/dL and maintaining it at 7ŌĆō9 g/dL) compared with the ŌĆ£liberalŌĆØ PRBC transfusion group [83]. Improved survival in the restrictive transfusion group might be associated with lower rates of hemostasis failure and serious adverse events. In patients with acute EV bleeding, adequate fluid therapy/PRBC transfusion should be performed while considering age, cardiovascular disease, presence or absence of ongoing bleeding, and hemodynamic status. Excessive fluid therapy/PRBC transfusion may increase the portal pressure and aggravate bleeding from the varices, so that should be taken into account [84]. Regarding correction of coagulopathy, clinical studies of recombinant factor VIIa have not shown a clear benefit, and therefore the routine use of fresh frozen plasma or recombinant factor VIIa is not recommended [85,86]. Although the efficacy of platelet transfusion in patients with acute EV bleeding has not been proven because of a lack of clinical studies, it can be considered in patients with severe thrombocytopenia.
Cirrhotic patients presenting with acute gastrointestinal bleeding have a high risk of developing bacterial infections, therefore initiation of prophylactic antibiotic treatment at the time of admission is necessary. Meta-analyses of RCTs have shown that the use of antibiotic prophylaxis reduces the risk of infections, recurrent bleeding, and bleeding-related death [87,88]. A recent meta-analysis demonstrated that prophylactic antibiotic treatment was associated with a decrease in bleeding-related mortality (RR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.63ŌĆō0.98), mortality from bacterial infections (RR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.19ŌĆō0.97), development of bacterial infections (RR, 0.35; 95% CI, 0.26ŌĆō0.47), and rebleeding (RR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.38ŌĆō0.74) [88]. However, another recent retrospective study questioned the usefulness of the routine antibiotic prophylaxis in cirrhotic patients experiencing acute variceal bleeding because of a very low incidence of bacterial infections (2%) and mortality (0.4%) in Child-Pugh class A patients with acute variceal bleeding, even in the absence of prophylactic antibiotic treatment [89]. No prospective study has evaluated the usefulness of antibiotic prophylaxis, and therefore the routine use of prophylactic antibiotics is recommended for all cirrhotic patients presenting with variceal bleeding, regardless of their Child-Pugh class. In a previous RCT comparing intravenous ceftriaxone (1 g every 24 hours) and oral norfloxacin (400 mg every 12 hours) for the prophylaxis of bacterial infection in cirrhotic patients with gastrointestinal bleeding, the incidence of proven or possible infections (11% vs. 33%, P=0.003), proven infections (11% vs. 26%, P=0.03), and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis or bacteremia (2% vs. 12%, P=0.03) was significantly lower in the ceftriaxone group [90]. However, controversy remains about whether those results are applicable to general cirrhotic patients because that was study conducted in Spain among patients with advanced cirrhosis, and most of the Gram-negative bacilli detected in the patients receiving oral norfloxacin were norfloxacin-resistant strains. Therefore, it is necessary to select appropriate antibiotics based on local antimicrobial susceptibility patterns. Generally, short-term (maximum 7 days) antibiotic prophylaxis with intravenous ceftriaxone (1 g every 24 hours) is recommended in patients with acute variceal bleeding.
Vasoactive agents, such as vasopressin, terlipressin, somatostatin, and octreotide, are effective in supporting hemostasis in patients with acute variceal bleeding by decreasing portal pressure. In a meta-analysis, the use of vasoactive agents in patients with acute variceal bleeding was significantly associated with a reduction in 7-day mortality (RR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.57ŌĆō0.95) and an increase in the hemostasis rate (RR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.13ŌĆō1.30) [91]. In patients with suspected variceal bleeding, vasoactive agents should be initiated as soon as possible, together with prophylactic antibiotics, before the diagnostic endoscopy. Vasopressin reduces portal pressure by inducing systemic and splanchnic vasoconstriction, but it is not now recommended for patients with acute variceal bleeding because of the significant side effects, such as an increase in peripheral vascular resistance and reduction in cardiac output and coronary blood flow. Although terlipressin, a synthetic analogue of vasopressin, is the only drug proven to reduce bleeding-related mortality (RR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.49ŌĆō0.88) [92], its side effects, such as hyponatremia and myocardial ischemia due to coronary artery vasoconstriction, should be considered [93,94]. A recent meta-analysis [91] and a Korean multicenter RCT [11] comparing three vasoactive agents (terlipressin, somatostatin, and octreotide) found no significant differences among them regarding the hemostasis rate and survival time. In patients with acute variceal bleeding, it is recommended that one of the vasoactive agents should be started as soon as possible (Table 2) and continued for 3ŌĆō5 days [26,47].
If acute variceal bleeding is suspected, endoscopy should be performed as soon as possible to confirm the hemorrhagic focus and hemostasis. Endoscopic hemostasis should be done when acute EV hemorrhage is confirmed by endoscopy. EVL is the endoscopic treatment of choice for patients with acute bleeding from EVs. Endoscopic injection sclerotherapy (EIS) is no longer recommended as standard treatment for acute EV bleeding because of its higher incidence of treatment failure, bleeding-related mortality, and adverse events compared with EVL [95-99]. In a meta-analysis comparing EVL and EIS in patients with acute EV bleeding, bleeding-related mortality did not differ significantly (RR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.77ŌĆō1.17), but the risk of rebleeding was reduced (RR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.57ŌĆō0.81) and the rate of variceal eradication was increased (RR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.01ŌĆō1.12) in patients undergoing EVL compared with EIS [100]. Most practice guidelines recommend endoscopy within 12 hours after presentation with suspected variceal bleeding, but that recommendation lacks evidence. A previous Taiwanese retrospective study reported that delayed endoscopy (>15 hours after admission) was an independent risk factor of inhospital mortality (odds ratio [OR], 3.67; 95% CI, 1.27ŌĆō10.39) [101]. In addition, a prospective observational study of 101 patients with acute EV bleeding showed that the 6-week rebleeding rate (18.9% vs. 38.9%, P=0.028) and mortality (27% vs. 52.8%, P=0.031) were significantly lowered in patients undergoing early endoscopy (Ōēż12 hours) compared with those undergoing delayed endoscopy (>12 hours) [102]. However, because those studies were performed without randomization, several confounders that can delay the endoscopy, such as hemodynamic instability, might have influenced the results. Therefore, until the results of large RCTs are reported, endoscopy should be performed as soon as possible in patients with suspected acute EV bleeding. However, the specific timing should be determined by the hemodynamic status of individual patients and the experience and medical resources of the institution.
Once endoscopy and EVL have been performed, early placement of a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) can be considered in carefully selected patients at high risk for rebleeding. Early TIPS placement reduced the rates of treatment failure and bleeding-related mortality in an RCT [103] of patients with a HVPG >20 mmHg and in an RCT [104] of patients with Child-Pugh class C cirrhosis (score of 10ŌĆō13) or Child-Pugh class B cirrhosis with active bleeding on endoscopy despite intravenous administration of a vasoactive agent. However, because these two trials excluded patients with Child-Pugh class A cirrhosis, Child-Pugh class B cirrhosis without active bleeding during endoscopy, ChildPugh class C with a score of 14ŌĆō15, patients >75 years, HCC beyond the Milan criteria, or a creatinine level greater than 3 mg/dL, it should be considered that those study results apply to only a very small portion of patients with acute variceal bleeding. Notably, a recent prospective observational study showed that the 1-year rebleeding risk was significantly decreased (3% vs. 49%, P<0.001), but 1-year survival did not differ between patients with and without a TIPS (66.8┬▒9.4% vs. 74.2┬▒7.8%, P=0.78) [105]. Further studies are needed to evaluate the beneficial effect of early TIPS placement.
Recently, the efficacy of applying hemostatic powder via endoscopy within 2 hours of admission was evaluated in 86 randomized patients with acute variceal bleeding [106]. Cirrhotic patients with acute variceal bleeding received standard medical treatment and were randomized to receive either immediate endoscopy with hemostatic powder application within 2 hours of admission followed by early elective endoscopy the next day (that is, within 12ŌĆō24 hours of admission) for definitive treatment (EVL for EV bleeding or endoscopic variceal obturation [EVO] for gastric variceal bleeding; study group) or early elective endoscopy only (control group). Improved rates of hemostasis and survival time in the study group suggested the therapeutic potential of endoscopic application of hemostatic powder, an easy procedure requiring minimal expertise.
Failure to control acute EV bleeding is defined as death or the need to change therapy (defined by one of the following criteria) within 5 days of an acute bleeding episode [107].
- Fresh hematemesis of Ōēź100 mL of fresh blood Ōēź2 hours after the start of a specific pharmacological treatment or therapeutic endoscopy
- Development of hypovolemic shock
- 3 g drop in hemoglobin (9% drop in hematocrit) within 24 hours without transfusion
TIPS placement is considered the best rescue treatment for patients with inadequate bleeding control despite combined pharmacological and endoscopic therapy [108]. A prospective observational study to evaluate the efficacy of TIPS in 58 patients who failed to achieve hemostasis after EIS and pharmacological treatment reported that the TIPS achieved control of the bleeding in 52 patients (90%), and 1-year and 3-year survival rates were 51.7% and 40.2%, respectively [108]. Balloon tamponade is still used as a bridge therapy and provides hemostasis in 80ŌĆō90% of patients, but the rebleeding rate after deflation is as high as approximately 50% [109,110]. Moreover, because it is associated with a high rate of serious complications, such as esophageal ulceration, esophageal rupture, and aspiration pneumonia, balloon tamponade should not exceed 24 hours [111]. In a small RCT, a self-expandable, esophageal covered metal stent was tested as an alternative to balloon tamponade in patients in whom pharmacological and endoscopic treatment failed to control bleeding [112]. Although survival in the esophageal stent group was not improved compared with the balloon tamponade group, bleeding control was higher (85% vs. 47%, P=0.037), and serious adverse events were lower (15% vs. 47%, P=0.077) in the esophageal stent group [112]. This stent can be placed endoscopically without radiological guidance, and it can stay in place for up to 2 weeks. However, because only 28 patients were included in that study, further study is warranted.
[Recommendations]
1. Endoscopy should be performed in patients with suspected esophageal variceal bleeding. (A1)
2. Endoscopic treatment should be performed in patients with acute esophageal variceal bleeding. (A1)
3. In patients with acute esophageal variceal bleeding, restrictive PRBC transfusion is recommended with the goal of maintaining a hemoglobin level of 7ŌĆō9 g/dL. (A1)
4. Short-term antibiotic prophylaxis should be instituted in patients with acute esophageal variceal bleeding. (A1)
5. If esophageal variceal bleeding is suspected, vasoactive agents should be initiated as soon as possible after admission. (A1)
6. Early TIPS placement can be considered in patients at high risk of rebleeding. (B2)
7. A TIPS is a possible rescue treatment for patients in whom bleeding control fails despite combined pharmacological and endoscopic therapy. (A2)
8. Balloon tamponade can be considered as a bridge therapy for patients who fail to achieve hemostasis after endoscopic treatment. (B2)
EV rebleeding is defined as recurrent bleeding after an absence of bleeding for at least 5 days following recovery from acute EV bleeding [107]. An average of 60% of patients with acute EV bleeding experience rebleeding within 1ŌĆō2 years, and the mortality rate from rebleeding is 33%. Therefore, appropriate treatment to prevent rebleeding is necessary [15,48].
The diagnosis of EV rebleeding is the same as the diagnosis of acute EV bleeding. Clinically significant rebleeding can be suspected in a patient who has recurrent melena or hematemesis with 1) hospitalization or the need for a transfusion, 2) a decrease in hemoglobin of more than 3 g /dL, or 3) death within 6 weeks [107].
NSBBs and EVL are the most common methods used to prevent EV rebleeding. NSBBs, which reduce portal pressure, have been reported to be more effective than placebo at preventing rebleeding in several RCTs [113-115]. The combination of an NSBBs plus ISMN could improve portal pressure reduction [116], but it could also increase the incidence of side effects such as headache and dizziness [117]. EVL is the endoscopic treatment of choice for the prevention of EV rebleeding. EVL should be repeated every 2ŌĆō8 weeks until variceal eradication is achieved. Periodic endoscopic follow-up is needed to detect the recurrence of varices even after achievement of variceal eradication. Several systematic reviews and meta-analyses comparing EVL alone to NSBBs alone demonstrated no difference in the rebleeding rate [51,118,119], but the overall mortality rate during follow-up was significant higher with EVL alone (RR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.01ŌĆō1.55) [51] or not different [119]. In a long-term follow-up study, the rebleeding rate was higher (30% vs. 64%, P=0.001) but the survival time was longer (30% vs. 49%, P=0.013) in patients treated with the combination of an NSBBs plus ISMN [120].
Several RCTs and meta-analyses comparing the combination of EVL plus NSBBs to EVL alone or NSBBs alone showed that the combination therapy had lower overall rebleeding and variceal rebleeding [121-124]. Therefore, the combination of EVL plus an NSBBs has been suggested as the primary treatment for preventing EV rebleeding. A recent meta-analysis demonstrated that the rebleeding rate decreased (RR, 0.44; 95% CI, 0.28ŌĆō0.69) and the mortality rate during follow-up tended to decrease with the combination of EVL plus a NSBBs (RR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.33ŌĆō1.03) compared with EVL alone. However, although the overall rebleeding rate tended to decrease (RR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.58ŌĆō1.00), the mortality rate during follow-up did not differ between the combination of EVL plus NSBBs and NSBBs alone [125]. These results suggest the importance of NSBBs in preventing EV bleeding.
RCTs comparing carvedilol to EVL (36.4% vs. 35.5%, P=0.857) and carvedilol to the combination of nadolol plus ISMN (51% vs. 43%, P=0.46) did not show any significant difference in rebleeding rate, and the side effects of carvedilol were less than those with the combination of nadolol plus ISMN (1.6% vs. 28.3%, P<0.0001) [126,127]. Therefore, the use of carvedilol to prevent EV rebleeding can be considered, but no studies have compared the combination of EVL plus carvedilol with the combination of EVL plus an NSBBs, which is currently considered to be the primary treatment to prevent rebleeding. Further studies using carvedilol to prevent EV rebleeding are required.
In a meta-analysis of studies about preventing variceal rebleeding by using NSBBs to reduce portal pressure, the risk of variceal rebleeding was significantly reduced (OR, 0.17; 95% CI, 0.09ŌĆō0.33; P=0.0001) when the HVPG was decreased to the target level (reduction in HVPG of Ōēź20% or to Ōēż12 mmHg) compared with the non-responding group [128]. A recent RCT comparing HVPGbased medical therapy with TIPS placement to reduce variceal rebleeding showed lower incidence of rebleeding within 2 years (26% vs. 7%, P=0.002) in the TIPS group, but there was no significant difference in mortality during follow-up between the two groups, and the incidence of HE was lower (8% vs. 18%, P=0.05) in the HVPG-based medical therapy group [129]. Considering that a TIPS is a limited treatment method, HVPG-based medical therapy is a useful way to prevent rebleeding if HVPG measurement is possible. However, because HVPG measurement is invasive, it is not widely practiced in many hospitals.
An RCT comparing TIPS placement with a combination of EVL plus an NSBBs to prevent variceal rebleeding found a lower variceal rebleeding rate in the TIPS group (0% vs. 29%, P=0.001), but the incidence of HE within 1 year in that group was higher (35% vs. 14%, P=0.035). There was no difference in the follow-up mortality rate (32% vs. 26%, P=0.418) between the two groups [130]. Therefore, the use of TIPS is not recommended as a primary treatment for the prevention of variceal rebleeding, and it should instead be considered a rescue therapy for patients with primary treatment failure [131]. In addition, liver transplantation is considered a rescue therapy for patients with recurrent variceal rebleeding because it exhibits good long-term results [132,133].
[Recommendations]
1. In patients with acute esophageal variceal bleeding, treatment to prevent variceal rebleeding is recommended. (A1)
2. The combination of endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL) plus NSBBs is recommended as the primary treatment for esophageal variceal bleeding. (A1) If the combination treatment is difficult to perform, use of a NSBBs or EVL alone is recommended. (A1)
3. If primary treatment for esophageal variceal rebleeding fails, TIPS placement should be considered as a rescue therapy. (B1)
4. Liver transplantation might be considered in patients with recurrent variceal rebleeding. (B1)
Gastric varices are enlarged submucosal veins of the stomach that cause critical upper gastrointestinal bleeding. GVs occur in approximately 20% of patients with portal hypertension, and the bleeding rate in 2 years is known to be 25% [134]. The incidence of gastric varices is lower than that of EVs, but their rebleeding rate and mortality rate are higher because they cause severe bleeding [134-136].
Gastric varices are classified as gastroesophageal varices (GOV) or isolated gastric varices (IGV) depending on their location and relation to any EVs (Fig. 1). GOVs are classified by whether they extend along the lesser curvature (GOV1) or the gastric fundus (GOV2). IGV are classified as varices located in the fundus (IGV1) and those in any other region, i.e., stomach or duodenum (IGV2) [134]. The incidence of GOV1s is about 74%.
The risk factors for gastric variceal bleeding are location (IGV1>GOV2>GOV1), variceal size, redness, and severe liver dysfunction [26,47,93,137-139].
To prevent bleeding from GOV1s, follow the guidelines for the prevention of EV bleeding. In a Korean study of 85 patients with GOV1s, the GOV1s also disappeared when EVs were eliminated by EVL (64.7%) [140]. For GOV2s and IGV1s, EVO, balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration (BRTO), and vascular plug-assisted retrograde transvenous obliteration (PARTO) can be considered to prevent bleeding [141,142]. NSBBs are non-invasive and can be used because they can reduce other side effects in patients with cirrhosis.
One randomized study reported the prevention of first gastric variceal bleeding. It enrolled 89 patients with GOV2s or IGV1s larger than 10 mm [141]. The effects of EVO (cyanoacrylate), an NSBB, and simple observation were compared. For the prevention of gastric variceal bleeding, EVO (10%) was superior to an NSBB (38%) and simple observation (53%) [141]. The survival rate of the EVO group (93%) was higher than that of the simple observation group (73%), but it did not differ from that of the NSBB group (83%). In a meta-analysis of patients with a high risk of gastric variceal bleeding, BRTO was effective in preventing gastric variceal bleeding (clinical success rate, 97.3%) [142]. In a recent study of 73 patients, PARTO was found to be a safe procedure without serious side effects that effectively prevented gastric variceal bleeding (Fig. 2) [143,144].
Bleeding from gastric varices is less common than from EVs; however, the risks of rebleeding or varix-related death are much higher in patients bleeding from gastric varices. The gastric varices that bleed are generally large and have high blood flow in the channel, which makes massive bleeding common in patients with large gastric varices [134,145,146]. Gastric varices exhibit unique characteristics and have a greater variety of sizes, forms, locations, and collateral vessels than EVs. An individualized approach might be needed because few well-controlled clinical trials have tested treatments for gastric variceal bleeding. Until sufficient evidence accumulates, clinicians should seek the best option for each patient based on the patientŌĆÖs general condition and bleeding patterns and the clinicianŌĆÖs medical resources and expertise [145].
Urgent endoscopic examination, within 12 to 24 hours, is necessary when a patient is suspected to have active bleeding from gastric varices. Endoscopic examination can visualize the bleeding sites and directly enable proper hemostatic treatments [47,147].
EVO achieves hemostasis and induces variceal eradication by an intravariceal injection of tissue adhesive agents (cyanoacrylates). Active or recent bleeding from fundic varices (GOV2s, IGV1s) or GOV1s can be managed with EVO. Special care is needed to prevent complications from the adhesive agents, such as ocular injury, damage to endoscopic devices, or the impaction of an injection needle into a varix [148]. Medical personnel are advised to wear goggles during the procedure. The working channel of a scope can be occluded by adhesive agent that spills during the procedure, so it can be helpful to flush the channel with olive oil in advance. To inject the sticky mixture quickly, a large needle is generally used (21 G or 22 G). The injection site is determined based on the direction of blood flow inside the varix. Because the intravariceal pressure is usually concentrated in the most protruding part of the varix, avoid that site if possible. The injection needle should be long enough to pass through the thick gastric wall (5 mm or longer). 2-N-butyl cyanoacrylate, which is the most commonly used agent in Korea, is used as a 1:1 mixture with lipiodol to delay the polymerization reaction. About 1 mL of mixture is used in each session, and the injection can be repeated until hemostasis is achieved. The initial volume and ratio of the mixture can be adjusted to accommodate the variceal size, intravariceal blood flow, and bleeding pattern (active or stabilized). If the bleeding is severe or the variceal size is large, the volume of the mixture can be increased to 2 mL at a time. As soon as the injection is finished, 1 mL of distilled water or saline should be pushed into the catheter to ensure that the mixture remaining in the catheter is injected into the varix. Then, the needle should be retracted quickly to prevent intravariceal impaction of the needle. The success rate of EVO for hemostasis was 91ŌĆō97%, and the rebleeding rate was 17ŌĆō49% in patients with active gastric variceal bleeding [149-153]. The common complications following EVO are systemic embolism, infection, fever, gastric perforation, gastric ulcer, and peritonitis [154].
As with EVs, EVL is frequently performed for GOV1 bleeding. EVL for gastric varices showed an initial hemostasis rate of 80ŌĆō90% and a rebleeding rate of 14ŌĆō56% in patients with GOV1s [140,155-158]. However, it should be noted that the depth and size of gastric varices differ from those of EVs. Ligation might not be adequate due to the thick gastric mucosa. Gastric ulcers, where the bands fall off, will expose submucosal varices directly to gastric acid and food materials. This situation could increase the risk of massive bleeding from the ulcers [154,155,158,159]. In patients with fundal variceal bleeding, the effect or safety of EVL has not been fully explored. In a small randomized trial, EVL showed a significantly higher rebleeding rate than EVO in patients with IGV1 bleeding (83.3% vs. 7.7%, P=0.003) [155].
Radiologic intervention is one useful hemostatic therapy for the management of bleeding from gastric varices. Sufficient consultation with interventional radiologists is needed in advance. Imaging tests, such as computed tomography (CT), should be performed before the procedure to confirm that the collateral veins are accessible and that no contraindications to the procedure are present.
TIPS placement is a procedure that robustly decompresses portal hypertension by making a bypass between the hepatic vein and the portal vein. In small non-randomized trials, both TIPS and EVO achieved a hemostasis rate of more than 90%. Complications, such as HE and stent occlusion, and medical costs were higher with the TIPS than with EVO [160,161]. However, TIPS placement is a useful rescue therapy when initial hemostasis fails [162-164]. The success rate of TIPS in controlling bleeding as a rescue therapy is 90ŌĆō100%, with a rebleeding rate of 16ŌĆō40% [162-166]. Moreover, since non-covered stents have been replaced by covered stents, the occlusion and stenosis rates have decreased to 8% [167,168]. HE can be prevented by decreasing the stent diameter. In a randomized study, the incidence rates of HE within 2 years were 43% and 27% in patients with a conventional stent (10 mm) and those with a smaller one (8 mm), respectively (P=0.03) [168]. TIPS is contraindicated in patients with heart failure or severe pulmonary hypertension because it can abruptly increase preload to the heart. It is difficult to perform the procedure in patients with main portal vein thrombosis. When a cyst, abscess, or mass is blocking the accessible tract in the liver or the intrahepatic bile ducts are markedly dilated, it is difficult to perform TIPS [169].
RTO obliterates gastric varices by infusing a sclerosant or embolic agent in a retrograde manner through a gastrorenal shunt. An accessible shunt should be confirmed by CT prior to the procedure. After occluding the shunt with a balloon catheter, a sclerosant, such as ethanolamine oleate or sodium tetradecyl sulfate, is infused into the gastric varices [170,171]. In a recent, large, retrospective study, the technical success rate of BRTO was 95% [172]. Another multicenter study, in which 23% of patients had GOV1s, had a technical success rate of 97% [173]. However, the EVs recurred or became aggravated in 20ŌĆō41% of patients after the procedure [172,173]. A recent meta-analysis also showed favorable results. The technical success and major complication rates of BRTO were 96.4% and 2.6%, respectively. The clinical success rate, defined as no recurrence of gastric varices or complete obliteration of varices on subsequent imaging, was 97.3% [142].
If a shunt is too large for balloon catheter occlusion, BRTO is not possible. Moreover, BRTO requires that patients retain the balloon catheter for several hours, until the sclerosing agent has hardened in the varices. In rare cases, the balloon can rupture during the procedure, and a systemic embolism of the sclerosing agent can occur. Therefore, a novel intervention, PARTO, was recently developed. PARTO uses a vascular plug with or without coils instead of a balloon and uses a gelatin sponge as the embolic agent [143]. A multicenter prospective study showed that complete thrombosis of gastric varices and shunts was achieved in 98.6% of patients. No recurrent variceal bleeding or development of HE occurred during follow-up. Moreover, 40% of patients showed improvement in their Child-Pugh scores [144]. Thus, PARTO is a noteworthy treatment that can replace BRTO in patients with gastric varices and a gastrorenal shunt. However, more data on the long-term efficacy and safety of PARTO are needed.
In patients with cirrhosis and acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding, a restrictive blood transfusion strategy (with a target range for the post-transfusion hemoglobin level of 7 to 9 g/dL) and antibiotic prophylaxis improved survival [83,174]. Although patients enrolled in the studies were small, the same transfusion strategy can be recommended for those with gastric variceal bleeding. The beneficial effects of vasoactive agents (terlipressin, octreotide, somatostatin) have not been fully proved in patients with gastric variceal bleeding, either. However, considering their ability to decrease portal hypertension, their use in patients with bleeding from gastric varices can be recommended [91,158,175,176].
GOV1s, which are an extended type of EV, develop along the lesser curvature and receive blood from the left gastric vein. When EVs are eradicated by endoscopic treatments, the gastric varices also concomitantly disappear in 60ŌĆō65% of patients [134,140]. Because of their close relationship in pathophysiology, the management of bleeding from cardiac varices (GOV1s) is similar to that for EV bleeding [177]. However, it should be noted that sufficient ligation can be difficult for gastric varices because of their large size and deeper location. Furthermore, subsequent post-ligation ulcers might be exposed to gastric acid or food material [154,155,158,159]. According to small clinical trials and observational studies, EVO produces more favorable outcomes than EVL. The initial hemostasis rates with EVO and EVL in patients with GOV1 bleeding were 85ŌĆō100% and 80ŌĆō90%, respectively. The rebleeding rates following EVO and EVL were 3ŌĆō26% and 14ŌĆō56%, respectively [140,155-158]. However, most of those trials were small; the evidence needed to recommend one of these treatments over the other remains insufficient [140,155,157,158,178]. Therefore, clinicians may choose either EVO or EVL based on their expertise, available medical resources, and the variceal condition (size or extent).
GOV2s are a type of gastric varix that extends from EVs toward the fundus. IGV1s are varices localized in the fundus in the absence of EVs [134]. Both GOV2s and IGV1s are usually called gastric fundic varices. Unlike EVs, fundic varices are supplied with blood from the posterior gastric vein or short gastric vein [179,180]. Bleeding from the fundus usually occurs in a stage of large varix. Management of fundic variceal bleeding can be difficult because massive or recurrent bleeding is frequently accompanied. Moreover, collateral shunts or blood circulation around the fundic varices are very diverse. Therefore, it is difficult to apply simple or uniform treatments for fundic variceal bleeding [181]. Urgent endoscopic examination is always needed in patients with suspicious fundic variceal bleeding in order to direct visualization of bleeding sites and to apply immediate treatments. EVO is one of the most commonly performed in patients with bleeding from fundic varices [182] EVO achieved initial hemostasis more often than EVL (OR, 4.44; 95% CI, 1.14ŌĆō17.3). In particular, the rebleeding rate following EVO was significantly lower than that following EVL in patients with IGV1s (OR, 0.06; 95% CI, 0.01ŌĆō0.58) [183]. TIPS placement and EVO are both effective treatments to control bleeding, with a hemostasis rate of more than 90%. Because of complications such as HE, stent occlusion, and higher cost, TIPS placement over EVO is not recommended as a first-line treatment [160,161]. However, TIPS placement is an effective rescue therapy when endoscopic therapy fails. The hemostasis rate of TIPS in a rescue setting is 90ŌĆō100% [162-166]. BRTO also achieved a high hemostasis rate (more than 90%) [184-186]. However, BRTO showed a significantly lower rebleeding risk (OR, 0.27; 95% CI, 0.09ŌĆō0.81) and a lower risk of HE (OR, 0.05; 95% CI, 0.02ŌĆō0.13) than TIPS [186]. Improvement in liver function was also demonstrated following BRTO [187]. However, all those results are based on mostly small retrospective studies.
In a small prospective study, BRTO and EVO had similar hemostasis and technical success rates. However, the rebleeding rate was significantly lower in the BRTO group than the EVO group (15.4% vs. 71.4%, P<0.01) [188]. These results should be interpreted carefully, however, because BRTO was performed only in patients without active bleeding; all the patients with active bleeding were treated with EVO.
In summary, current data suggest that EVO, TIPS, BRTO, or (theoretically) PARTO can be used as the initial treatment for patients bleeding from fundic varices. Because of a lack of evidence, treatments should be chosen based on individual situations in consideration of patientsŌĆÖ safety and the applicability of each therapy in the relevant medical facility.
Currently, PPIs are used in many patients to prevent ulcer bleeding following endoscopic treatments. However, their effectiveness and duration of treatment have not been fully explored. Long-term use of PPI can increase risk of infection and subsequently cause spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and HE [79]. However, a recent retrospective study showed that PPI use decreased the rebleeding risk following EVO (OR, 0.554; 95% CI, 0.352ŌĆō0.873) [189].
A TIPS can be urgently placed when endoscopic treatments fail. The hemostasis rate with rescue TIPS was 90ŌĆō96% in patients with gastric varices, which is comparable to that with EV bleeding [162,163]. In a few small studies, BRTO also showed comparable outcomes in patients who failed to achieve initial hemostasis. BRTO can be considered as a rescue therapy when a patient was hemodynamically stabilized and has an accompanying gastrorenal shunt [184,186]. As a bridging therapy, a balloon tamponade can be applied to control massive bleeding until rescue therapy is ready [109].
[Recommendations]
1. In p atient s with gas tric variceal b le e ding, gener al management, such as prophylactic antibiotics, restrictive transfusion, and vasoactive agents, can be provided as they are for esophageal variceal bleeding. (B1)
2. Gastric varices extending from EVs along the lesser curvature (GOV1s) can be treated with either EVO or EVL, depending on the size and location of the bleeding varix. (B1)
3. In patients with bleeding from fundic varices (GOV2s, IGV1s), EVO should be considered first. (A1) Retrograde transvenous obliteration (BRTO or PARTO) or TIPS can be used depending on the bleeding status (active or stabilized) and the presence of an accessible shunt. (B1)
4. A PPI can be used following endoscopic treatments to prevent post-procedure ulcer bleeding. (B2)
5. Retrograde transvenous obliteration (BRTO or PARTO) or TIPS should be considered as a rescue therapy when endoscopic treatments fail. (B1)
6. Until a rescue therapy is ready, a balloon tamponade can be applied as a bridging therapy. (B2)
GOV1s can be managed in the same way as EVs to prevent rebleeding. The eradication of concurrent EVs with EVL and an NSBB can be used if the EVs are medium to large in diameter. Gastric varices subsequently disappeared in 65% of patients when EVs were controlled [140]. The rebleeding rate from GOV1s following eradication of EVs was 16ŌĆō42% [155,156]. Esophageal EVL can be performed simultaneously with or after treatments for gastric varices. In terms of gastric varices, EVO showed a significantly lower rebleeding rate than EVL in patients bleeding from GOV1s (OR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.16ŌĆō0.94) [155,158,183]. However, those studies included only a small number of patients. In a retrospective Korean study, EVO showed beneficial outcomes, with lower 1-year rebleeding rate (3.6% vs. 30.8%, P=0.004) and bleeding-related mortality rate (5% vs. 22%, P=0.05) than EVL [140]. In a different small study, TIPS placement showed a significantly lower rebleeding rate than EVO (21% vs. 65%, P<0.02) [190]. However, it is difficult to draw conclusions from that study alone because its rebleeding rate following EVO was relatively higher than previous reports. If an accessible gastrorenal shunt is identified, BRTO or PARTO might be considered. Unfortunately, evidence to support those interventions in patients with GOV1 bleeding is very limited [173,191].
In patients bleeding from fundic varices (GOV2s or IGV1s), the only predictor for rebleeding following EVO was variceal size (F3). The use of NSBBs failed to decrease the rebleeding rate [192]. In an RCT, eradication of gastric varices with repeated EVO lowered the rebleeding rate significantly compared with NSBBs (10% vs. 44%, P=0.004) [193]. There were no differences in rebleeding (54% vs. 47%, P=0.609) or bleeding-related mortality (42% vs. 47%, P=0.766) between EVO alone and EVO plus an NSBB, respectively [194]. Therefore, use of an NSBB is not recommended to prevent recurrent bleeding from fundic varices. However, NSBBs should be considered if patients have significant portal hypertension or other proven indications, such as large EVs [47]. Clinical trials comparing the rebleeding rates after repeated EVO and TIPS or BRTO are scarce. In a small randomized study of patients with GOV2 bleeding, there was no significant difference in the rebleeding rate between EVO repeated every 4 weeks and TIPS placement (16% vs. 0%, P>0.05) [190]. However, TIPS placement was associated with a higher incidence of complications than EVO [161]. In a meta-analysis, BRTO (7.4%) showed a much lower rebleeding rate than TIPS (22.8%) (OR, 0.27; 95% CI, 0.09ŌĆō0.81) [186]. For GOV2s, treatment of the accompanying EVs can be performed with or after the treatment of fundic varices, according to the guidelines for treating EVs (Fig. 3).
[Recommendations]
1. In patients with remnant or recurrent GOV1s following initial treatments, repeated EVO or EVL can be performed to prevent rebleeding. (B2)
2. In patients with remnant or recurrent fundic varices (GOV2s, IGV1s), EVO or RTO (BRTO or PARTO) can be performed. (B2) If there is no accessible shunt or if complications related to severe portal hypertension (recurrent bleeding from EVs, refractory ascites, or hydrothorax) are not controlled, a TIPS can be placed. (B2)
In cirrhosis, variceal bleeding at sites other than the stomach and esophagus is very rare, and there are no established treatment guidelines. The most common locations are the rectum, duodenum, and postoperative stomach. A multi-disciplinary approach involving an endoscopist, interventional radiologists, and surgeons should be used to account for the vascular supply. EVO, BRTO, PARTO, TIPS, the coil inserting method, and the like can all be used [195].
Although the incidence of portal hypertensive gastropathy bleeding in cirrhosis is not high, some patients experience poor quality of life due to chronic bleeding and the associated iron-deficiency anemia and repeated transfusions [196,197]. Portal hypertensive gastropathy is diagnosed when gastric mucosal changes cause a snake-skin appearance or mosaic pattern on endoscopy in patients with portal hypertension [198-200]. When gastric mucosal changes alone are found, it is diagnosed as a mild form. When red or dark brown viscous changes are found along with changes in the gastric mucosa, it is considered to be severe (Fig. 4) [30]. Severe portal hypertensive gastropathy causes more chronic bleeding than the mild form [201].
Portal hypertensive gastropathy is associated with portal hypertension and causes gastric mucosal changes in the stomach and body, and 30% of patients with gastric antral vascular ectasia (watermelon stomach) also have portal hypertension. It is unclear whether portal hypertension is involved in the development of gastric antral vascular ectasia. Gastric antral vascular ectasia causes dilated vessels with fibrin thrombi and fibromuscular hyperplasia of the lamina propria [202].
In chronic bleeding caused by portal hypertensive gastropathy, the goal of treatment is lowering the portal pressure with NSBBs, vasoconstrictors, or a TIPS [203,204]. In cases with active bleeding, endoscopic treatment with argon plasma coagulation can be used. In addition, iron supplementation is recommended [205].
HE occurs in more than 10% of all cases of cirrhosis and is a critical complication that seriously reduces the quality of life [206]. Because HE can cause serious losses not just for individuals, but also socioeconomically, preventive therapy is of paramount importance. However, because the pathophysiological factors in the development of HE and biomarkers to predict the occurrence of HE have not been sufficiently identified, there are no standardized criteria for diagnosing, classifying, or evaluating the treatment response to HE. It is imperative that those criteria be established in Korea. In particular, quality-of-life assessments and diet and exercise education for patients with HE are clinically important and need to be actively developed.
HE is a neuropsychiatric syndrome caused by hepatic dysfunction that manifests as various neurologic and psychiatric abnormalities [207-209]. Clinically, it is classified into overt and covert encephalopathy. Overt HE (OHE) is defined as the occurrence of disorientation, flapping tremor, or asterixis (Table 3). Covert HE (CHE) includes minimal encephalopathy in which cognitive impairment cannot be identified without a cognitive function test and West-Haven criteria grade 1 HE, which means mild cognitive or behavioral change without disorientation [210]. The prevalence of HE is reported to be 10ŌĆō14% of cirrhotic patients and 16ŌĆō21% of patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis [206,211]. In Korea, HE was found in 16ŌĆō21% of hepatitis B virusŌĆōrelated decompensated liver cirrhosis patients [212]. Moreover, 20% of cirrhotic patients admitted to the emergency department were reported to have HE [213].
HE is classified according to the underlying liver disease, clinical course, precipitating factors, and severity of neurologic symptoms [209]. By underlying liver disease, HE is subdivided into three groups: from acute liver failure, from portosystemic bypass or shunting, and from portal hypertension caused by chronic liver disease. HE caused by portal hypertension is classified as episodic, recurrent (more than two times per year), and persistent HE (no fully recovery from behavioral change). When classified by the precipitating factors, HE is divided into precipitated and spontaneous types. Precipitating factors include gastrointestinal bleeding, uremia, sedatives, diuretics, protein overload, infection, constipation, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalance. The severity of HE is classified using the West-Haven criteria (Table 3).
HE presents with a wide range of clinical patterns, from minimal HE (MHE), in which cognitive impairment cannot be identified without a cognitive function test, to OHE, which is easily detected based solely on symptoms and does not require a cognitive function test. As HE progresses, symptoms such as personality changes, indifference, anxiety, and irritability appear and can reduce sleep quality and quality of life [214]. In some patients, increased muscle tension, hyperreactivity, and the Babinski reflex are present, and they are rarely accompanied by seizures [215,216]. The flapping tremor, a phenomenon in which hand tremors are caused by incongruity in the tension of various muscles resulting from hyperextension of the wrist as the fingers are spread apart, is a common symptom in the early and middle phases of OHE.
The severity of HE is classified using the West-Haven criteria and the Glasgow Coma Scale [207], with the former used as the basic diagnostic criteria. However, due to their large number of subjective factors, the West-Haven criteria suffer from significant interobserver deviation, which makes it difficult to diagnose the first stage (grade 1) of HE in a clinical setting. Therefore, MHE and stage 1 HE are classified as CHE (Table 3) [217]. The International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN) defines the onset of disorientation or flapping tremor as the start of OHE [218].
HE requires differentiation from underlying brain diseases, such as cerebral hemorrhage and edema, that can accompany cognitive dysfunction. It should also be differentiated from substance abuse, alcoholism, hyponatremia, and psychiatric illnesses. In chronic alcoholics in particular, it can be difficult to differentiate HE from other alcohol-related neurological diseases. For example, Korsakoff syndrome, which is caused by a thiamine deficiency induced by long-term drinking, is characterized by symptoms such as anterograde amnesia and decreased word memory [219], and WernickeŌĆÖs encephalopathy is marked by eye movement paralysis, gaze-induced nystagmus, and gait disturbances, in addition to memory lapses [220]. Delirium caused by withdrawal from alcohol also needs to be differentiated from HE. Delirium that results from alcohol withdrawal is characterized by an increased heart rate, cold sweats, loud shouting, and a harsh and repetitive tremor [221]. A differential diagnosis is required for acute hyponatremia, hypoglycemia, and metabolic alkalosis because each can present with symptoms similar to those of HE [222]. The differential diagnosis for hyponatremia requires particular caution because its symptoms are very similar to those of HE, and hyponatremia itself can lead to HE [223]. Subdural hematoma can also present with symptoms similar to those of HE and should be carefully differentiated. Cases of subdural hematoma are commonly accompanied by other neurological symptoms, such as hemiplegia. Encephalitis often presents with symptoms such as headache, fever, vomiting, and stiff neck, but a differential diagnosis is required because those symptoms are not always clear and can be accompanied by sleepiness, drowsiness, and unconsciousness. In cases of dementia, the symptoms appear relatively gradually in most cases, whereas alcohol-related dementia often includes violent tendencies caused by frontal lobe damage, as well as the inability to remember recent events [224].
OHE can be diagnosed based solely on clinical symptoms, but other diseases that can cause cognitive dysfunction should still be ruled out. Brain CT and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are helpful for differentiating neuropsychological abnormalities caused by underlying brain diseases, such as intracranial hemorrhage [225]. Because the risk of cerebral hemorrhage is about five times higher in patients with liver cirrhosis than in healthy people, brain CT or MRI should be performed if a brain lesion is suspected [226]. Brain MRI, in particular, is helpful for diagnosing HE, in which brain edema is associated with nonspecific symptoms such as headache and vomiting, when acute liver failure is suspected [225]. On T1-weighted MRI, an increased signal in the basal ganglia is commonly observed, but those changes lack the sensitivity and specificity required to diagnose HE [227].
If the diagnosis of HE is difficult, neurophysiological or neuropsychological tests can also be performed. In HE, a characteristic, slow triphasic wave is observed during electroencephalography (EEG) [228]. This slow triphasic wave is an overall periodic waveform in the bilateral frontal lobes that demonstrates bilateral synchronization and is often accompanied by slow background activity; it is usually seen in phase 2 or 3 HE and disappears in comatose patients [225,229]. Once a slow triphasic wave has developed, the clinical outcome is reportedly very poor [230]. In recent studies, the decrease in EEG amplitude in patients with OHE was associated with the severity of HE [231].
The brainstem auditory-evoked-potential test is sensitive for the diagnosis of CHE [226,227,232]. Patients with liver cirrhosis accompanied by CHE exhibit conduction time delays (IŌĆōV latency) from the auditory nerve to the midbrain and conduction time delays (IIIŌĆōV latency) from the pontine to the midbrain on the brain auditory-evoked-potential test. It is also known that the risk of developing OHE is increased when abnormal findings are observed on the brain auditory-evoked-potentials test [227]. However, in a study using the cortical auditory-evoked-potential test, the N200 latency was increased in patients with HE [233]. Therefore, the diagnosis of HE cannot be made using EEG alone; further research is required to determine the usefulness of evoked-potential EEG in the diagnosis and prognosis of HE.
The venous blood ammonia level is not proportional to the degree of HE and has no association with its prognosis [234]. The metabolism of ammonia is greatly influenced by various organs, such as the kidneys, muscles, brain, and bowel, as well as the liver [235]. However, repeated measurements of ammonia concentrations can help to determine a treatmentŌĆÖs effects [235,236]. If patients with suspected OHE have normal ammonia concentrations, attention should be paid to the differential diagnosis to look for other diseases [234]. There are various methods of measuring ammonia concentrations, such as those involving the venous or arterial blood or plasma. Because the normal range varies depending on the specific measurement method, a suitable reference value should be used. Although the partial pressure of ammonia gas in arterial blood is thought to be closely related to both the neurophysiological test results and the ammonia concentration in the bloodŌĆōbrain barrier in patients with HE, additional studies are needed to determine the clinical usefulness of that value [237]. Regarding other serum markers, some studies have reported increases in the serum S100╬▓ concentration that were proportional to the cognitive function test results in HE patients [238].
[Recommendations]
1. To confirm the diagnosis of OHE, other diseases that can cause cognitive impairment must first be ruled out, and the diagnosis must be made based on clinical symptoms. (A1)
2. HE is classified as either OHE, which can be diagnosed using only symptoms, or CHE, which requires a cognitive function test. (B1)
3. In patients with suspected HE, imaging tests, including a brain MRI or a neurophysiological test, can be performed to rule out other diseases that can cause cognitive impairment .(B2)
4. Venous blood ammonia levels are not proportional to the degree of HE and are not associated with its prognosis (A1). However, if patients with suspected HE show normal ammonia concentrations, differentiation from other diseases is required. (B1)
The goals of treatment are as follows: 1) prevention of secondary damage caused by decreased consciousness and normalization of the patientŌĆÖs state of consciousness, 2) elimination of social and economic restrictions by preventing recurrence, and 3) improvement of patient prognosis and quality of life. Therefore, appropriate supportive care should be provided to prevent secondary damage (e.g., fall-related injuries or aspiration pneumonia) from an altered consciousness. Furthermore, the precipitating factors should be identified and managed appropriately as soon as possible, and treatments should be initiated using medications that can decrease or eliminate the production of ammonia, the major pathogenic material.
The precipitating factor can be identified in 80ŌĆō90% of patients with HE [239]. In many cases, HE can be improved simply by eliminating the precipitating factor; therefore, identifying and promptly managing the precipitating factors is required [240]. The currently known precipitating factors of HE and the corresponding diagnostic tests and treatments are shown in Table 4. According to reports from patients in the Republic of Korea [241,242], gastrointestinal bleeding, infection, dehydration by paracentesis, and constipation were the major precipitating factors.
The primary treatment for HE is nonabsorbable disaccharides such as lactulose (╬▓-galactosido-fructose) or lactitol (╬▓-galactoside sorbitol), which lead to recovery in 70ŌĆō90% of HE patients [217]. Therapeutic mechanisms involve the reduction of intestinal pH by the production of acetic and lactic acids (via bacterial degradation of lactulose). Another potential mechanism is the ability of the nonabsorbable disaccharides to increase the count of lactobacillus, which do not produce ammonia. Furthermore, nonabsorbable disaccharides convert ammonia to ammonium, rendering it less absorbable, and they also produce an osmotic laxative effect that flushes the ammonia out [93,217]. Based on many clinical studies and their low cost, nonabsorbable disaccharides are recommended as an initial therapeutic opition [209,240]. Uribe et al. [243] found that a 20% lactitol enema had higher efficacy in improving symptoms than a tap water enema (100% vs. 20%, P=0.0037) and that the overall response rate to nonabsorbable disaccharidesŌĆōbased therapy was 82.5%. According to a systematic review and meta-analysis [244], lactulose or lactitol was more effective in improving symptoms than placebo, with a RR of 0.62 (95% CI, 0.46ŌĆō0.84), This finding was reproduced in another recent study [245], which found an RR of 0.63 (95% CI, 0.53ŌĆō0.74). When overt HE occurs, 30ŌĆō45 mL of lactulose (20ŌĆō30 g) every 1ŌĆō2 hours should be administered orally until the patient is having at least 2 bowel movements a day. An equivalent daily dose of lactitol is 67ŌĆō100 g [246]. Thereafter, the dose should be titrated to achieve two to three soft stools per day. If patients are unable to take medications orally, administration via nasogastric tube might be tried. If patients have severe HE (West-Haven criteria of grade 3 or more) or are unable to take medications orally or via nasogastric tube, an enema of 300 mL lactulose and 700 mL water can be performed 3ŌĆō4 times per day until clinical improvement is noted [240,243,247,248]. In this situation, the enema solution should be retained in the intestine for at least 30 minutes [93].
Rifaximin, a rifamycin derivative, maintains high concentration levels in the intestine because it is not absorbed, and it remains in an active form until it is excreted.
It inhibits bacterial RNA synthesis by binding to bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, and it has broad antimicrobial activity against aerobic and anaerobic gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria [93]. So far, several studies have shown that rifaximin has a positive effect in managing HE [242,249-251]. Several RCTs with small sample sizes have assessed the effect of rifaximin as a first-line regimen for OHE. A meta-analysis of those RCTs found that rifaximin had a therapeutic effect similar to that of lactulose or lactitol [249,251-254]. Furthermore, in a recent RCT, patients treated with a combination of rifaximin and lactulose showed a better recovery from HE within 10 days (76% vs. 44%, P=0.004) and shorter hospital stays (5.8 vs. 8.2 days, P=0.001) than those treated with lactulose alone [255]. The maximum dose is 1,200 mg/day, which might limit its use in cases of severe HE (West-Haven criteria of grade 3 or more) because of the need for oral administration [93].
Neomycin and metronidazole are also poorly absorbed by the intestine, affect urea-producing bacteria, and reduce the generation of ammonia, which improves HE [93]. However, they are not recommended for the management of HE because of their side effects, such as intestinal malabsorption, nephrotoxicity, and ototoxicity for neomycin and peripheral neuropathy for metronidazole [209,240,256].
Because ornithine and aspartate are important substrates used to metabolize ammonia to urea and glutamine, the administration of LOLA can lower plasma ammonia concentrations, with produces improvements in HE [93,257]. For patients with West-Haven criteria grade 1ŌĆō2 HE, intravenous LOLA can lower the number connection test (NCT)-A time and plasma ammonia concentrations more effectively than placebo [258]. According to a recent RCT, patients treated with the combination of lactulose and intravenous LOLA (30 g/day) had a lower grade of HE within 1ŌĆō4 days of treatment, with an OR of 2.06ŌĆō3.04 and a shorter duration until symptom recovery (1.92 vs. 2.50 days, P=0.002), compared with those who received lactulose alone [259]. Oral LOLA can lower the NCT-A time and plasma ammonia concentrations; [260,261] however, further studies are required to assess its efficacy in managing OHE [257].
Among cirrhotic patients, the capacity for glycogen storage in the liver decreases along with the reduced liver parenchyme. Therefore, catabolism becomes predominant because protein is required for gluconeogenesis. Because BCAAs, such as valine, leucine, and isoleucine, are absorbed in the peripheral tissue, patients with cirrhosis have a lower concentration of the BCAAs and a higher concentration of the aromatic amino acids in the blood compared with healthy people. Thus, BCAA supplementation inhibits proteolysis and decreases the influx of toxic materials via the blood-brain barrier. Furthermore, it plays an important role in muscle metabolism, leading to glutamine production that is useful for detoxifying ammonia [262,263]. According to recent meta-analyses [264-266], oral BCAAs might be beneficial in managing OHE and should be used as an ancillary pharmacological option. However, intravenous BCAAs have no effect on episodic HE [209,240,267].
Because albumin has great anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, it might be helpful in improving the overall survival time of patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis [268-270]. According to recent research in patients with West-Haven criteria grade Ōēź2 HE [271], those treated with a combination of lactulose and intravenous albumin (1.5 g/kg/day) showed a better recovery rate within 10 days than those treated with lactulose alone (75% vs. 53.3%, P=0.03) (Table 5).
In addition, polyethylene glycol (PEG), an osmotic laxative, might be tried. Its postulated mechanism of action is flushing ammonia out of the gut, like the nonabsorbable disaccharides [240]. A single RCT comparing PEG (4 liters over 4 hours via oral administration or nasogastric tube) to lactulose only showed it to be superior in terms of clinical improvement over a 24-hour period, documented by a greater decrement in the HE scoring algorithm (Δ 1.5 vs. Δ 0.7, P=0.002) and a shorter median time to resolution (1 day vs. 2 days, P=0.01) [272]. However, further studies are required to assess its efficacy and safety.
Flumazenil, an antagonist of the benzodiazepine receptor, might improve consciousness among patients with severe HE; however, its effect is temporary, and survival time is not improved [273]. Therefore, it is not recommended as a first-line regimen. Nonetheless, it can be used in patients with HE caused by benzodiazepine. Levocarnitine or sodium benzoate might be effective in managing HE because they can lower plasma ammonia concentrations [274,275].
Patient with acute liver failure and HE can be considered for liver transplantation because of their poor prognosis [93]. In cases of recurrent OHE, the severity is associated with its overall prognosis [276], and the overall survival rate after an episode of OHE was 42% and 23% at 1 and 3 years, respectively [277]. Therefore, liver transplantation should be considered for such patients. Furthermore, liver transplantation is also indicated in patients with severe HE who do not respond to the above medical treatments.
[Recommendations]
1. Precipitating factors of HE include gastrointestinal bleeding, infection, constipation, infection, excessive intake of protein, dehydration, renal function disorder, electrolyte imbalance, psychoactive medication, and acute hepatic injury. So first, those factors should be recognized and managed. (A1)
2. To manage acute episodic over t HE, non-absorbable disaccharides (e.g., lactulose, lactitol) are recommended. Enema is recommended in severe HE (West Haven criteria grade Ōēź3) or a clinical situation in which oral intake is inappropriate. (A1)
3. Rifaximin might be combined with non -absorbable disaccharides to treat patients with HE. (B1)
4. Oral BCAA and intravenous LOLA or albumin can be used additionally. (B2)
5. Liver transplantation is indicated in patients with severe HE who do not respond to the medical treatments. (A1)
Among patients with OHE, 50ŌĆō70% will experience a recurrence within 1-year, so secondary prevention for OHE should be started after the first event. As the first-line therapy, nonabsorbable disaccharides (lactulose [278,279], lactutol [280]) should be used. A dose of 30ŌĆō60 mL of lactulose, allowing 2ŌĆō3 stools per day, in patients who recovered from acute episodes of OHE significantly reduced the recurrence of OHE (19.6%) compared with the control group (46.8%) [278]. In cases of lactulose/lactitol intolerance, rifaximin can be used as single therapy (400 mg tid or 550 mg bid) [281]. According to a case-control study that included decompensated liver cirrhosis patients, a median 2 years of rifaximin therapy significantly lowered the recurrence of OHE compared with the control group (31.5% vs. 47%, P=0.034) [281].
A prospective RCT by Bass et al. [282] found that 6-months of rifaximin therapy significantly lowered the recurrence of OHE compared with the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.42; 95% CI, 0.28ŌĆō0.64); about 91% of that study population used lactulose concomitantly. Non-absorbable disaccharide and rifaximin combination therapy can reduce the recurrence of OHE more than each single therapy [240,282], and it is therefore recommended for recurrent OHE. These medical treatments can effectively prevent OHE recurrence and improve the survival times of patients with OHE [281,283]. Long-term treatment with rifaximin raised concerns about the risk of Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) infection, but recent studies found that C. difficile infection was not increased by rifaximin treatment compared with the control group [283-285].
Long-term oral BCAA treatment is recommended for patients whose oral diet is insufficient because it can improve symptoms and reduce the recurrence of OHE [266,286]. In a meta-analysis of 16 RCTs, oral BCAA reduced the recurrence of OHE (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.61ŌĆō0.88), but the overall survival time did not differ between the two groups [266].
LOLA can reduce the recurrence of HE. In an RCT including 150 patients, oral LOLA (6 g three times per day) for 6 months significantly reduced the recurrence of OHE (HR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.17ŌĆō0.87) [287]. Nonetheless, recent meta-analyses have shown that oral LOLA was not more effective than lactulose or rifaximin for OHE prevention [287,288].
In patients with intractable ascites, intravenous albumin infusion can prevent OHE. A recent prospective RCT showed that long-term intravenous albumin (40 g per week) infusion significantly lowered the risk of grade 3 or 4 OHE (HR, 0.48; 95% CI, 0.37ŌĆō0.63) and improved overall survival times (HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.40ŌĆō0.95) [269].
A structured educational intervention has been reported to improve patient adherence to prophylactic therapy and reduce readmission with OHE [289]. According to an RCT of 39 patients with a history of OHE, a 15-minute educational session reduced the risk of OHE-related hospitalization (HR, 0.14; 95% CI, 0.02ŌĆō0.77) [269]. The education of patients and caregivers should include 1) the effects and potential side effects (e.g., diarrhea) of the prescribed medication (lactulose, rifaximin, and so on), 2) the importance of adherence, 3) early symptoms and signs of recurring OHE, and 4) actions to be taken if a recurrence begins [209].
Nutritional deficits and subsequent sarcopenia are known to increase complications, including HE [290,291], and lower the overall survival times of cirrhotic patients [292-294]. Therefore, adequate assessment and intervention for nutritional status are recommended. Because most decompensated cirrhotic patients are malnourished, daily energy intake should be 35ŌĆō40 kcal/kg, and protein intake should be 1.2ŌĆō1.5 g/kg. Long-term protein restriction should be avoided because it can induce protein catabolism, hepatic dysfunction, and sarcopenia [295].
To take in enough energy, small frequent meals (4ŌĆō6 times per day including a night snack) improve the long-term prognosis for liver cirrhosis patients while preventing sarcopenia [296], but the direct effect that small meals and a night snack has on OHE prevention has not been fully established.
Exercise can improve the long-term outcomes of cirrhotic patients [297,298]. In particular, cirrhotic patients usually have decreased skeletal muscle volume [291] because hyperammonemia hinders the synthesis of skeletal muscles [299,300]. An adequate exercise program can prevent muscle loss [301], enhance effective ammonia metabolism, and prevent OHE recurrence. However, exercise can temporarily increase the portal pressure in OHE patients [297,298], and it could increase the risk of a fall or fracture in malnourished patients. Therefore, adequate nutritional support should precede exercise therapy (Fig. 5).
[Recommendations]
1. A nonabsorbable disaccharide (lactulose, lactitol) or rifaximin, as single or combined therapy, is recommended for the prevention of overt HE recurrence. (A1)
2. Oral branched-chain amino acid or oral LOLA supplementation can prevent the recurrence of overt HE. (B1)
3. Adequate education of patients and caregivers at the time of discharge is needed to reduce the recurrence of overt HE. (B1)
4. Nutritional assessment and management are needed for decompensated liver cirrhosis patients who experienced overt HE. (B1) Long-term protein restriction should be avoided, and adequate energy and protein intakes are necessary. (B1)
CHE is regarded as the preclinical stage of OHE, and it includes West-Haven criteria grade 1 and MHE, which is the mildest form of HE [210]. It is difficult to diagnose CHE it because it can be diagnosed only by psychometric or neurophysiologic examination and is without definite clinical manifestations, such as disorientation or asterixis. Furthermore, it is difficult to clinically distinguish MHE and grade 1 HE. Therefore, MHE and grade 1 HE from the West-Haven criteria are often defined as a single syndrome called CHE. Because the concept of CHE was initiated by ISHEN in 2011, most previous studies have been done on MHE; little research has been done on CHE, including West-Haven criteria grade 1 HE [210].
The prevalence of MHE is 22ŌĆō78% of patients with liver cirrhosis, although the rate can differ depending on the diagnostic method [226,302-308]. The prevalence of MHE is related to prior episodes of OHE, age, severity of liver disease, and the presence of EVs [309]. In a study using the psychometric HE score (PHES) in a single institution in Korea, MHE was seen in 25.6% of patients with cirrhosis, including 20.2% of those in Child-Pugh A, 42.9% in Child-Pugh B, and 60% in Child-Pugh C [310].
Patients with CHE have impaired cognitive functions such as attention, executive functions, visuospatial perception, psychomotor speed, and reaction times [311]. Those impaired cognitive functions interfere with daily functioning, such as social interactions, alertness, emotional behavior, sleep, home management, and recreation, and lower the quality of life [214,304,312].
Patients with CHE are at risk of falls and fractures [313,314], and their poor cognitive performance increases the risk that they will lose their jobs [315]. Therefore, CHE increases the burden on both individual patients and society. CHE is regarded as the preclinical stage of OHE because of the increased risk of progression to OHE [226,302], and CHE is associated with worsened survival times [316,317]. However, it is difficult to distinguish whether the shortened survival is caused by CHE or hepatic dysfunction.
To diagnose CHE, the patient must have 1) a disease that can lead to CHE, such as liver cirrhosis or a portosystemic shunt, 2) no other neurological disease, 3) no neurological manifestation such as disorientation or asterixis, and 4) abnormal cognitive or neurophysiologic functioning.
One of the paper and pencil tests, PHES, consists of five tests (digit symbol test, NCT-A, NCT-B, serial dotting, and line tracing) that measure attention, psychomotor speed, visual perception, and visuo-spatial orientation [318]. The PHES has been widely used to diagnose CHE and has a sensitivity of 96% and a specificity of 100% [319]. It was developed in Germany and has been validated in several countries, including Korea [310,319-324]. It is recommended that at least two of the NCT-A, NCT-B, block design test, and digit symbol test be performed if the full PHES cannot be used due to copyright issues or in places where the PHES has not been validated [208].
The Korean paper and pencil test (KPPT) to evaluate MHE in Korean patients with liver cirrhosis was developed with the support of the Korean Association for the Study of the Liver [325,326]. The KPPT consists of six tests: NCT-A, NCT-B, digit span test (DST), symbol digit modality test (SDMT), word list memory test, and Medical College of Georgia Complex figures. The KPPT short version is configured to be relatively simple to use and contains the NCT-A, NCT-B, DST, and SDMT. A recent prospective multicenter study validated the KPPT short version in Korean patients with liver cirrhosis [325]. The KPPT is available at http://encephalopathy.or.kr/inspection [326].
The ICT is a computerized test that evaluates attention, response inhibition, and working memory [306,327]. In the ICT, the subject is instructed to respond to alternating patterns of the letters X and Y, called the target. Non-alternating presentations of the letters X and Y, called lures, are randomly planted within the sequence of letters. This test evaluates the response times of the subjects and the response rate to the target and lures. The sensitivity and specificity of the ICT are 87% and 77%, respectively, and it is highly reproducible [327]. However, it has not been validated for Korean patients.
The Stroop test evaluates psychomotor speed and cognitive flexibility [328] using two components (the ŌĆ£offŌĆØ and ŌĆ£onŌĆØ states). In the ŌĆ£offŌĆØ state, subjects match the color of the symbol. In the ŌĆ£onŌĆØ state, subjects match the color of the word when the color of the word and the meaning of the word are incongruent, which evaluates response inhibition.
The computer-based Stroop test shows a sensitivity of 89.1% and a specificity of 82.1% when using the paper and pencil test as a standard test [329]. A recent prospective multicenter study in the US showed that Stroop test had high sensitivity and acceptable inter-center agreement [330]. In addition, the Stroop test has good testŌĆōretest reliability, and it has the advantage that it can be easily administered using a smartphone. A Korean Stroop test was developed, and a recent study showed that the Korean Stroop test is valid for diagnosing MHE (area under the curve, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.66ŌĆō0.83, P<0.001) [331]. The Korean Stroop test is available at http://encephalopathy.or.kr/inspection [326].
EEG is a test that reflects cerebral cortical neuronal activity. In patients with CHE, a quantitative EEG analysis shows an increase in the relative power of the ╬Ė band and a decrease in the mean dominant frequency [332]. However, EEG can be affected by various conditions that can affect cortical function. In addition, it requires a technician and a neurologist and is associated with both interobserver and intraobserver variability.
CFF measures the frequency at which light begins to flicker noticeably. CFF is highly correlated with paper and pencil testing [333]. In a meta-analysis of nine studies using CFF, the sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing CHE were 61% and 79%, respectively [334]. However, it is not applicable to patients with red-green blindness or Korean patients with cirrhosis because it has not been validated in Korea.
The animal naming test (ANT) is a semantic fluency test that consists of listing the names of as many animals as possible in 1 minute. In a prospective study conducted in Italy, the sensitivity and specificity of the ANT for diagnosing CHE were 78% and 63%, respectively, when the cut-off was less than 15, and the ANT was a significant predictor for the development of OHE [307]. In a recent prospective study in Germany, the sensitivity and specificity were 31% and 98%, respectively, when the cut-off was less than 15, and they suggested 23 as a cut-off to increase sensitivity [335]. Nabi et al. [336] reported that a combination of age, sex, and the responses to 4 Sickness Impact Profile (SIP) questions that are highly related to CHE identified patients with CHE with more than 80% sensitivity. However, that test needs to be validated further. Some studies reported that serum cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-6, IL-17a, interferon-╬│ [337-339] and 3-nitrotyrosin [340,341], are associated with CHE. However, further studies are needed on the pathophysiology of CHE and the role of the markers in CHE.
CHE has no clinical signs of HE. It can show abnormalities in cognitive functions in various fields, but each field is not reduced to the same extent. In addition, because one test cannot judge the abnormality in all fields and agreement is poor between tests [342,343], a combination of least two tests is recommended for a diagnosis of CHE [210]. For multicenter studies, a paper and pencil test and one computerized or neurophysiologic test are recommended for a CHE diagnosis. A single institution can use one test that has been validated locally [209].
Because CHE decreases patient quality of life, increases socioeconomic burden, and hastens mortality, it might be necessary to test and diagnose all patients at risk. However, that would increase costs. Therefore, it is advisable to perform a diagnostic test in patients with a history recent of falls or traffic accidents and patients who report a low quality of life or complaints about daily living, such as those who complain of sleep disturbance or a loss of concentration or memory [209,344].
Because most patients with CHE are diagnosed at an outpatient clinic, the screening tests should be performable without any special tools and with high sensitivity, such as the four questions from SIP, the ANT, and the Stroop test using a smartphone.
Most studies about treating CHE were performed in a small number of patients with a short duration of treatment. In addition, most studies have focused on improving cognitive function and quality of life; studies are still needed on extending survival and reducing readmissions or the development of OHE.
As with OHE, it is known that nitrogenous substances, especially ammonia, play a major role in CHE. Therefore, treatments can be given to reduce ammonia. The most studied treatment is lactulose, which showed a marked improvement in cognitive function and quality of life [304,345] and decreased the development of OHE [345], compared with the placebo.
Probiotics alter the gut microbiome and inhibit ammonia production in the intestine, thereby improving cognitive function and decreasing the development of OHE [346-348]. However, studies on the effects of probiotics in patients with CHE have low evidence levels [349]. Additional studies are needed to determine the beneficial probiotic species and optimal doses. Rifaximin and nonabsorbable antibiotics also improved cognitive function and quality of life [305] and improved driving ability [350]. However, rifaximin failed to establish non-inferiority over lactulose in non-inferiority studies [351], and lactulose treatment is more cost-effective than rifaximin therapy [350]. Therefore, further studies on the role of rifaximin in the treatment of CHE are warranted. Although LOLA [352], BCAA [353], acetyl L-carnitine [354,355], and nutrition therapy [308] have been reported to improve cognitive function, there is still a lack of evidence for those treatments.
HRQoL in patients with cirrhosis is lower than that of patients with chronic liver disease without cirrhosis. The HRQoL of cirrhotic patients with HE is particularly low [356]. Patients with HE suffer from various degrees of altered consciousness, personality changes, impaired intellectual functioning, and neuromuscular dysfunction. Although HE is not immediately life-threatening, it can greatly interfere with a patientŌĆÖs functioning, social interactions, and sense of well-being [357]. The occurrence of HE is associated with various complications that can also adversely affect HRQoL. Therefore, the independent effect of HE on HRQoL is not easily measured. Because patients with OHE are unaware of their disease (anosognosia) [358], alterations in their behavior and abilities are more easily recognized by the people living with them than by the patients themselves. The presence of OHE negatively affects both mental and physical functioning, whereas MHE mainly has negative effects on mental health. Several studies have shown that the HRQoL of patients with MHE is lower than that of patients without HE [312,359-362]. Therefore, we suggest that patients with cirrhosis should be screened for the early detection and treatment of HE to improve their HRQoL.
HRQoL is measured using self-administered, standardized questionnaires in which patients report their health status. The questionnaires are classified as generic and disease-specific [363]. Because generic questionnaires provide an overview of HRQoL, usually taking into account the physical, mental, and social aspects of a patientŌĆÖs health status, generic questionnaires have the advantage of depicting the relative impacts of different diseases. However, generic questionnaires have the disadvantage of insensitivity to clinically important changes. Thus, generic questionnaires are often combined with disease-specific questionnaires. The most widely used generic questionnaires for measuring HRQoL are the SIP, Nottingham Health Profile (NHP), and Medical Outcomes Study Short Form-36 (SF-36) [364]. The SIP consists of 136 items that measure 12 domains. It requires several minutes to complete, and patients with cognitive dysfunctions sometimes fail to complete it [365]. The NHP measures distress and is useful in patients with moderate or severe disability, but it is not very sensitive to mild disability [366]. The SF-36 is applicable to a wide range of patients, from those with a severe disability to the general population. The SF-36 is easy to complete and has high sensitivity, which makes it the best and most widely used scale in clinical practice. It contains 36 questions that are split into eight domains and provides a physical component summary (PCS) and a mental component summary (MCS) (Supplementary Table 1) [367].
Disease-specific questionnaires have been developed for a variety of chronic diseases, such as renal failure, heart failure, liver cirrhosis, diabetes, and osteoarticular diseases, that greatly affect the HRQoL of patients. Liver-disease-specific questionnaires include the Chronic Liver Disease Questionnaire (CLDQ), Liver Disease Quality of Life (LDQOL), Short Form Liver Disease Quality of Life (SF-LDQOL), and Liver Disease Symptom Index 2.0 (LDSI). The CLDQ comprises 29 questions split into six domains, with domain scores and an overall score presented as 1ŌĆō7 scales. Higher scores on the CLDQ represent better HRQoL. The CLDQ is short, easily applicable, and correlates with the severity of liver disease [368]. The LDQOL uses the SF-36 and adds 12 liver-specific scales comprising 75 questions. All scales are scored from 0ŌĆō100, with higher scores representing better HRQoL [369]. The SF-LDQOL uses the SF-36 and adds 36 Likert questionnaires; it is also scored from 1ŌĆō100 [370]. The LDSI uses 18 items to measure the impact and severity of a patientŌĆÖs liver disease on daily activities in nine areas (Supplementary Table 2) [371].
Although there is a large consensus about the direct and profound effect that HE has on HRQoL, most studies have focused on MHE [208,372,373]. A small study about the HRQoL of patients with and without HE compared 18 patients experiencing OHE with 57 patients without a previous episode. Patients with a previous episode of OHE had significantly low SF-36 PCS and MCS scores. However, patients with MHE were affected in only one domain, physical functioning, of the SF-36 [374]. One study of 160 cirrhotic patients undergoing liver transplantation found that patients with MHE or OHE had a lower MCS than patients without HE [357].
Cognitive impairment of patients with HE mainly affects areas that require multiple and complicated functions, such as attention, visuospatial abilities, psychomotor speed, balance, and coordination, rather than language or general intellect. In other words, patients can perform daily activities such as wearing clothes or using the toilet, but their overall planning or cognitive function and exercise performance might suffer [318]. Because driving a vehicle requires comprehensive performance and a strategic way of thinking, patients with MHE require attention while driving [375-378]. Cirrhotic patients engaged in professions that required sustained attention and motor coordination are more severely affected by MHE than those with jobs that require mainly verbal abilities. In an outpatient cohort with cirrhosis, up to 60% of blue collar workers lost their jobs, versus only 20% of white collar workers [236].
A disruption of normal sleep-wake patterns is another early sign of HE [379], and regular sleep is a key indicator of perceived health status. Sleep disturbances are included as relevant items in the assessment of HRQoL in the NHP questionnaire, and sleep disturbances in patients with HE negatively affect HRQoL [380]. Patients with MHE report a decrease in the quality of their sleep and in their physical and mental HRQoL [214,381].
Psychological status and a patientŌĆÖs mood can affect the course of a disease and treatment response, and depression affects social functioning, physical abilities, and health status [382]. Cirrhotic patients suffer not only from liver disease itself, but also from decreased quality of life in the form of poor work performance and an increased risk of accidents. Therefore, there is a need for extensive social attention and research on public social support systems and economic support for cirrhotic patients.
Although many studies have aimed at improving HE, relatively few studies have aimed at a significant improvement in the HRQoL of patients with HE [383]. Prasad et al. [304] first investigated the effect of treatment-related improvements in cognitive function on HRQoL. Patients with MHE treated with lactulose for 3 months showed a significant improvement in their HRQoL on several SIP subscores, particularly in emotional behavior, mobility, sleep/rest, and recreation and pastimes. In an 8-week study of rifaximin therapy in patients with MHE, the patients showed significantly improved scores in both neuro-psychometric performance and the SIP [305]. Another study reported that rifaximin therapy to prevent a recurrence in patients with HE favorably affected HRQoL as measured by CLDQ scores [384]. Treating OHE patients with oral LOLA [385] and MHE patients with acetyl-L-carnitine [354] also improved HRQoL. However, a 60-day course of probiotic yogurt supplementation had no significant effects on HRQoL in 25 patients with cirrhosis [346].
To date, insufficient studies have been done to establish an association between improved HRQoL and treatments for OHE and MHE. Considering that 10% or more of cirrhotic patients have HE, and 50% of cirrhotic patients with MHE who have not been treated can progress to OHE within 4ŌĆō24 months [386], it is necessary to change the paradigm of treatment to improve the HRQoL of patients.
[Recommendations]
1. Active diagnosis and treatment of HE improves patientŌĆÖs health-related quality of life. (A1)
2. Health-related quality of life in patients with HE is assessed by self-administered, standardized questionnaires and can be measured using either generic or disease-specific questionnaires. (B2)
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
KASL Committee for Revision of the Clinical Practice Guidelines for Liver Cirrhosis: Varices, hepatic encephalopathy, and related complications: Jae Young Jang (Committee Chair, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine), Sang Gyune Kim (Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine), Yeon Seok Seo (Korea University College of Medicine), Moon Young Kim (Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine), Beom Kyung Kim (Yonsei University College of Medicine), Byung Seok Kim (Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine), Sung Eun Kim (Hallym University College of Medicine), Ki Tae Suk (Hallym University College of Medicine), Do Seon Song (The Catholic University College of Medicine), Jae Jun Shim (Kyung Hee University College of Medicine), Seung Kak Shin (Gachon University College of Medicine), Yun Bin Lee (Seoul National University College of Medicine), Eun Sun Jang (Seoul National University College of Medicine), Dae Won Jun (Hanyang University College of Medicine).
FOOTNOTES
AuthorsŌĆÖ contributions
Jae Young Jang (Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine): Introduction Writing and Guidelines General Management
Sang Gyune Kim (Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine): Manuscript writing for introduction of HE
Yeon Seok Seo (Korea University College of Medicine): Manuscript writing for introduction of varices part, surveillance of varices, preventing the formation and progression of EVs
Moon Young Kim (Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine): Guidelines editing and manuscript organization
Beom Kyung Kim (Yonsei University College of Medicine): Manuscript writing for management of overt HE
Byung Seok Kim (Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine): Manuscript writing for prevention of first EVs bleeding
Sung Eun Kim (Hallym University College of Medicine): Manuscript writing for HE and health-related quality of life
Ki Tae Suk (Hallym University College of Medicine): Manuscript writing for definition of gastric varices and prevention of primary bleeding, other variceal bleeding and portal hypertensive gastropathy
Do Seon Song (The Catholic University College of Medicine): Manuscript writing for covert HE
Jae Jun Shim (Kyung Hee University College of Medicine): Manuscript writing for management of bleeding from gastric varices and prevention of rebleeding
Seung Kak Shin (Gachon University College of Medicine): Manuscript writing for prevention of EVs rebleeding
Yun Bin Lee (Seoul National University College of Medicine): Manuscript writing for diagnosis and management of acute EVs bleeding
Eun Sun Jang (Seoul National University College of Medicine): Manuscript writing for definition of HE, prevention of overt HE
Dae Won Jun (Hanyang University College of Medicine): Manuscript writing for diagnosis of HE
Conflicts of Interest
Jae Young Jang: Received grants from Yuhan; received honoraria from BMS, Gilead, Dong-A ST, Yuhan, and Bukwang
Sang Gyune Kim: Received grants from GE healthcare, Samsung Medison, BMS, Samil, Ildong; received honoraria from BMS, MSD, Gilead, Dong-A ST, Daewoog; consulted Samsung Medison
Yeon Seok Seo: Received honoraria from Yuhan, Bukwang, Samjin, Gilead, Dong-A ST, Samil, Deawoong, Chongkundang, Abbvie, MSD
Moon Young Kim: Received grants from Samjin, Yuhan, Bukwang; received honoraria from BMS, Gilead, Dong-A ST, Yuhan, Daewoong
Beom Kyung Kim: Received honoraria from Samil, Dong-A ST, Yuhan, Celltrion, Deawoong, BMS, Chongkundang
Byung Seok Kim: Received grants from Gilead, Abbvie, MSD, Dong-A ST, Daewoong, Ildong, Chongkundang; received honoraria from Gilead, BMS, Abbvie, Yuhan SK chemical
Sung Eun Kim: Received grants from Daewoong
Ki Tae Suk: Nothing to disclose.
Do Seon Song: Received grants from Alfa Wassermann Jae Jun Shim: Received grants from Samil; received honoraria from MSD, Yuhan; consulted Gilead
Seung Kak Shin: Nothing to disclose.
Yun Bin Lee: Nothing to disclose.
Eun Sun Jang: Received honoraria from Chongkundang
Dae Won Jun: Received grants from Yuhan, BMS, Gilead, Dong-A ST, Hanwha, Samil, Diagen; received honoraria from Yuhan, BMS, Gilead, Dong-A ST, Hawha, Daewoong
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
Supplementary material is available at Clinical and Molecular Hepatology website (http://www.e-cmh.org).
Supplementary┬ĀTable┬Ā1.
Generic questionnaire assessing health-related quality of life
Supplementary┬ĀTable┬Ā2.
Disease specific questionnaires for health-related quality of life in chronic liver disease patients
Figure┬Ā1.
Classification of gastric varices. PV, portal vein; LGV, left gastric vein; SV, splenic vein; GOV, gastroesophageal varices; PGV, posterior gastric vein; SGV, short gastric vein; IGV, isolated gastric varices; GEV, gastric epiploic vein.
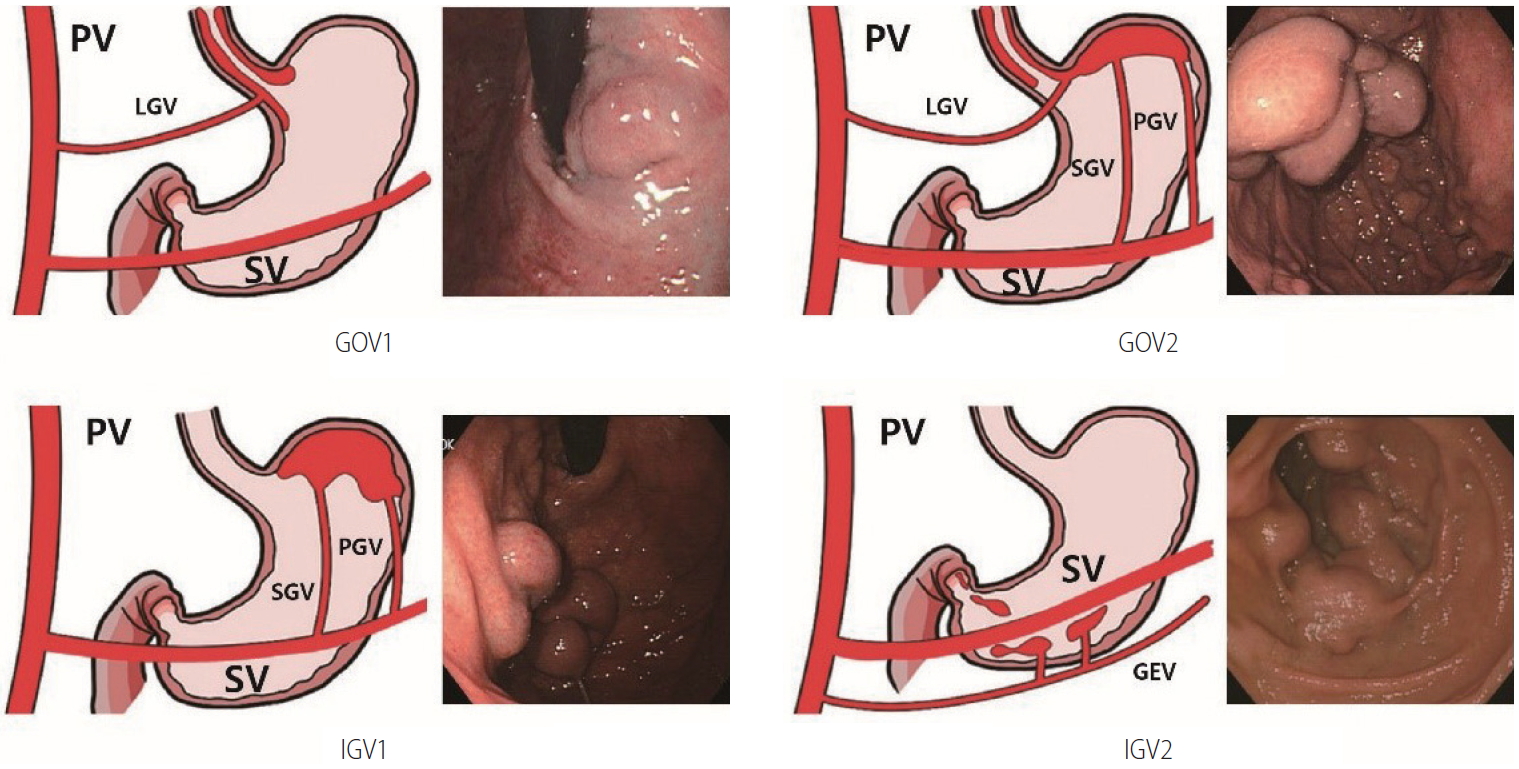
Figure┬Ā2.
The prevention of initial variceal bleeding. UGI, upper gastrointestinal; EV, esophageal varix; GV, gastric varix; GOV, gastroesophageal varix; IGV, isolated gastric varix; NSBB, non-selective beta blocker; EVL, endoscopic variceal ligation; RTO, retrograde transvenous obliteration; EVO, endoscopic variceal obturation.
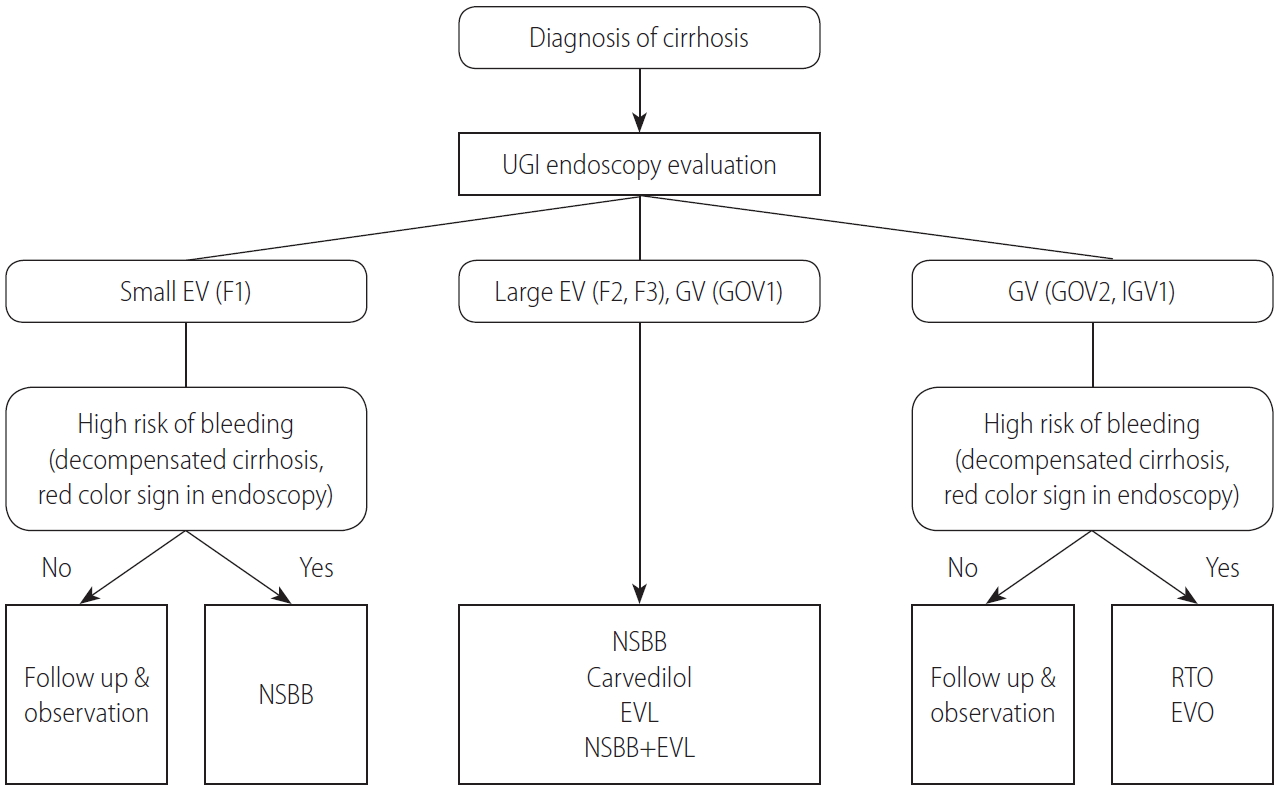
Figure┬Ā3.
The treatment of acute variceal bleeding and prevention of variceal rebleeding. UGI, upper gastrointestinal; EV, esophageal varix; GOV, gastroesophageal varix; IGV, isolated gastric varix; EVL, endoscopic variceal ligation; EVO, endoscopic variceal obturation; RTO, retrograde transvenous obliteration; TIPS, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; NSBB, non-selective beta blocker.
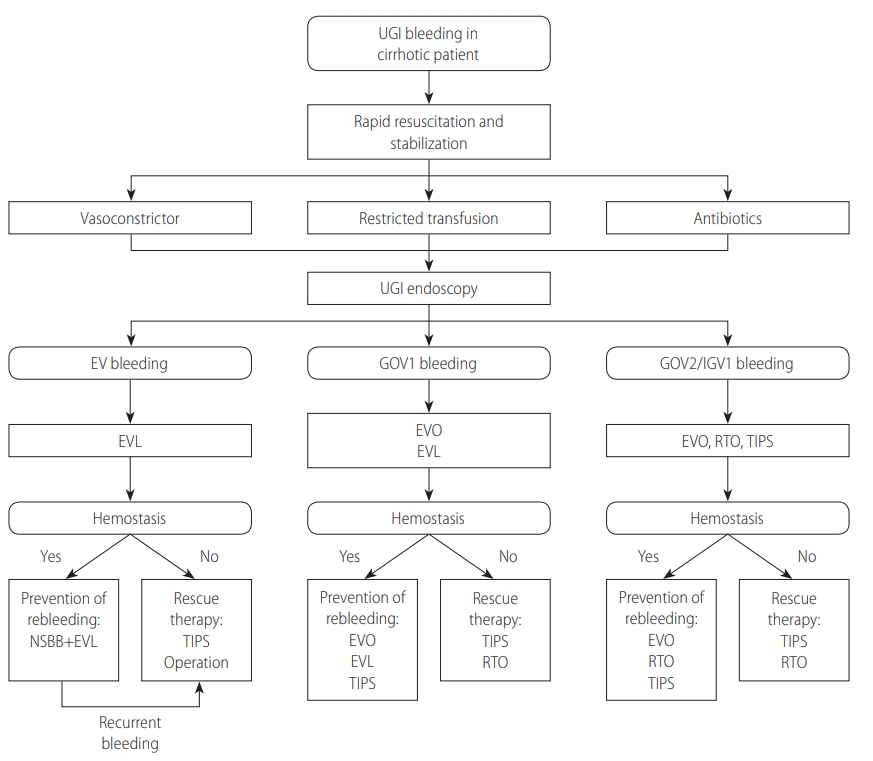
Figure┬Ā5.
The treatment and prevention of recurrence of hepatic encephalopathy. P.O., per oral; BCAA, branched-chain amino acid; IV LOLA, intravenous L-ornithine-L-aspartate.
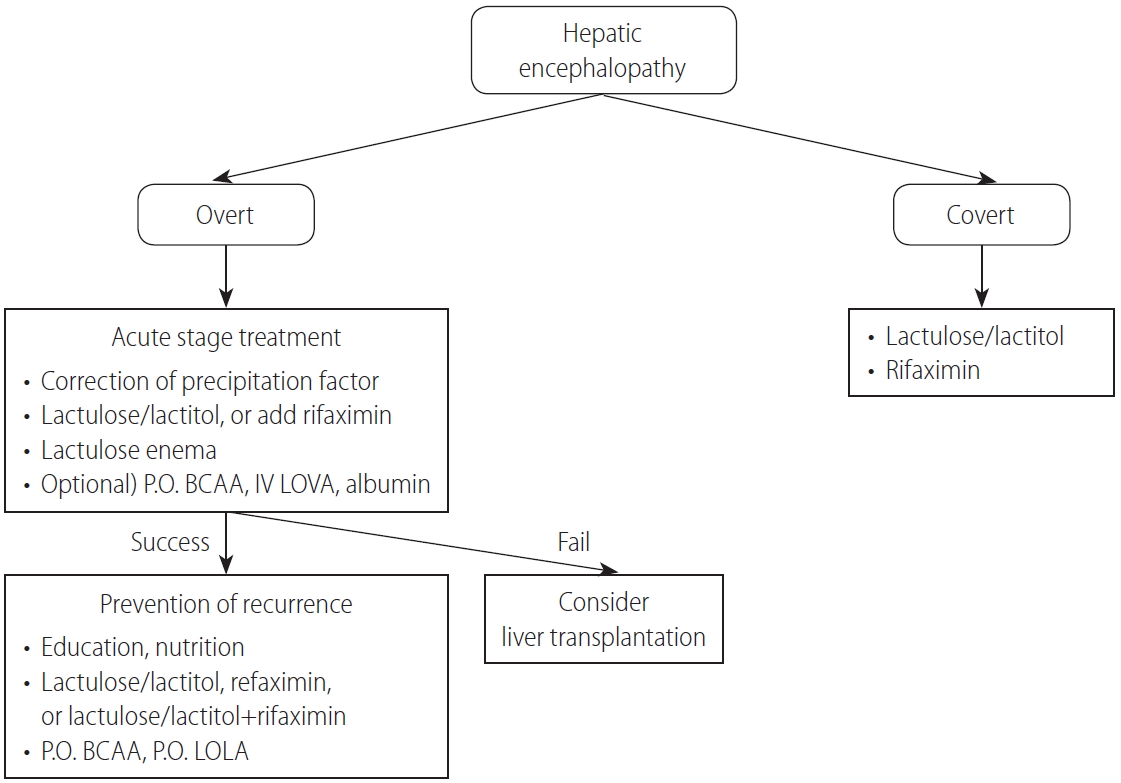
Table┬Ā1.
Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE)
Of the quality levels of evidence, we excluded ŌĆ£very low quality (D),ŌĆØ which was originally included in the GRADE system, for convenience. (Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008;336:924-926.)
Table┬Ā2.
Vasoactive agents used in the management of acute variceal bleeding
Table┬Ā3.
Definition and classification of hepatic encephalopathy
Table┬Ā4.
Diagnostic tests to identify the precipitating factors of hepatic encephalopathy and their treatments
Table┬Ā5.
Pharmacological options for managing overt hepatic encephalopathy
Abbreviations
ANT
animal naming test
BCAAs
branched-chain amino acids
BRTO
balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration
cACLD
compensated advanced chronic liver disease
CFF
critical flicker frequency
CHE
covert hepatic encephalopathy
CI
confidence interval
CLDQ
Chronic Liver Disease Questionnaire
CPG
clinical practice guideline
CT
computed tomography
DST
digit span test
EEG
electroencephalography
EIS
endoscopic injection sclerotherapy
EVL
endoscopic variceal ligation
EVO
endoscopic variceal obturation
EVs
esophageal varices
GOV
gastroesophageal varices
GRADE
Grading of Recommendations
HE
hepatic encephalopathy
HR
hazard ratio
HRQoL
health-related quality of life
HVPG
hepatic venous pressure gradient
ICT
inhibitory control test
IGV
isolated gastric varices
IL
interleukin
ISHEN
International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism
ISMN
isosorbide-5-mononitrate
KASL
the Korean Association for the Study of the Liver
KPPT
Korean paper and pencil test
LDQoL
Liver Disease Quality of Life
LDSI
Liver Disease Symptom Index
LOLA
L-ornithine-L-aspartate
MCS
mental component summary
MHE
minimal hepatic encephalopathy
MRI
magnetic resonance imaging
NCT
number connection test
NHP
Nottingham Health Profile
NSBBs
nonselective beta-blockers
OHE
overt hepatic encephalopathy
OR
odds ratio
PARTO
vascular plug-assisted retrograde transvenous obliteration
PCS
physical component summary
PEG
polyethylene glycol
PHES
psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score
PPI
proton pump inhibitor
PRBC
packed red blood cell
RCTs
randomized controlled trials
RR
relative risk
SDMT
symbol digit modality test
SF-36
Medical Outcomes Study Short Form-36
SF-LDQOL
Short Form Liver Disease Quality of Life
SIP
Sickness Impact Profile
SVR
sustained virologic response
TIPS
transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
REFERENCES
1. DŌĆÖAmico G, Pasta L, Morabito A, DŌĆÖAmico M, Caltagirone M, Malizia G, et al. Competing risks and prognostic stages of cirrhosis: a 25-year inception cohort study of 494 patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014;39:1180-1193.


2. Kovalak M, Lake J, Mattek N, Eisen G, Lieberman D, Zaman A. Endoscopic screening for varices in cirrhotic patients: data from a national endoscopic database. Gastrointest Endosc 2007;65:82-88.


3. Iwakiri Y, Groszmann RJ. The hyperdynamic circulation of chronic liver diseases: from the patient to the molecule. Hepatology 2006;43(2 Suppl 1):S121-S131.


4. Garc├Ła-Pag├Īn JC, Gracia-Sancho J, Bosch J. Functional aspects on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension in cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2012;57:458-461.


5. Abraldes JG, Iwakiri Y, Loureiro-Silva M, Haq O, Sessa WC, Groszmann RJ. Mild increases in portal pressure upregulate vascular endothelial growth factor and endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the intestinal microcirculatory bed, leading to a hyperdynamic state. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2006;290:G980-G987.


6. Groszmann RJ, Garcia-Tsao G, Bosch J, Grace ND, Burroughs AK, Planas R, et al. Beta-blockers to prevent gastroesophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2254-2261.


7. Merli M, Nicolini G, Angeloni S, Rinaldi V, De Santis A, Merkel C, et al. Incidence and natural history of small esophageal varices in cirrhotic patients. J Hepatol 2003;38:266-272.


8. North Italian Endoscopic Club for the Study and Treatment of Esophageal Varices. Prediction of the first variceal hemorrhage in patients with cirrhosis of the liver and esophageal varices. A prospective multicenter study. N Engl J Med 1988;319:983-989.


9. McCormick PA, OŌĆÖKeefe C. Improving prognosis following a first variceal haemorrhage over four decades. Gut 2001;49:682-685.



10. Carbonell N, Pauwels A, Serfaty L, Fourdan O, L├®vy VG, Poupon R. Improved survival after variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis over the past two decades. Hepatology 2004;40:652-659.


11. Seo YS, Park SY, Kim MY, Kim JH, Park JY, Yim HJ, et al. Lack of difference among terlipressin, somatostatin, and octreotide in the control of acute gastroesophageal variceal hemorrhage. Hepatology 2014;60:954-963.


12. Villanueva C, Piqueras M, Aracil C, G├│mez C, L├│pez-Balaguer JM, Gonzalez B, et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing ligation and sclerotherapy as emergency endoscopic treatment added to somatostatin in acute variceal bleeding. J Hepatol 2006;45:560-567.


13. Reverter E, Tandon P, Augustin S, Turon F, Casu S, Bastiampillai R, et al. A MELD-based model to determine risk of mortality among patients with acute variceal bleeding. Gastroenterology 2014;146:412-419 e3.


14. Kim YD, Cheon GJ, Kim MY, Suk KT, Baik SK, Kim DJ. Changes in the clinical outcomes of variceal bleeding in cirrhotic patients: a 10-year experience in gangwon province, South Korea. Gut Liver 2012;6:476-481.




17. Bedossa P, Darg├©re D, Paradis V. Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003;38:1449-1457.


18. Regev A, Berho M, Jeffers LJ, Milikowski C, Molina EG, Pyrsopoulos NT, et al. Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol 2002;97:2614-2618.


19. Intraobserver and interobserver variations in liver biopsy interpretation in patients with chronic hepatitis C. The French METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology 1994;20(1 Pt 1):15-20.


20. Marcellin P, Gane E, Buti M, Afdhal N, Sievert W, Jacobson IM, et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B: a 5-year open-label follow-up study. Lancet 2013;381:468-475.


21. Chang TT, Liaw YF, Wu SS, Schiff E, Han KH, Lai CL, et al. Long-term entecavir therapy results in the reversal of fibrosis/cirrhosis and continued histological improvement in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2010;52:886-893.


22. Krogsgaard K, Gluud C, Henriksen JH, Christoffersen P. Correlation between liver morphology and portal pressure in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 1984;4:699-703.


23. van Leeuwen DJ, Howe SC, Scheuer PJ, Sherlock S. Portal hypertension in chronic hepatitis: relationship to morphological changes. Gut 1990;31:339-343.



24. European Association For The Study Of The Liver; European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2012;56:908-943.


25. Rinella ME, Sanyal AJ. NAFLD in 2014: genetics, diagnostics and therapeutic advances in NAFLD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;12:65-66.




26. de Franchis R; Baveno VI Faculty. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension. J Hepatol 2015;63:743-752.


27. Augustin S, Pons M, Maurice JB, Bureau C, Stefanescu H, Ney M, et al. Expanding the Baveno VI criteria for the screening of varices in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease. Hepatology 2017;66:1980-1988.


28. Maurice JB, Brodkin E, Arnold F, Navaratnam A, Paine H, Khawar S, et al. Validation of the Baveno VI criteria to identify low risk cirrhotic patients not requiring endoscopic surveillance for varices. J Hepatol 2016;65:899-905.


29. Lee HA, Kim SU, Seo YS, Lee YS, Kang SH, Jung YK, et al. Prediction of the varices needing treatment with non-invasive tests in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease. Liver Int 2019;39:1071-1079.


30. de Franchis R. Updating consensus in portal hypertension: report of the Baveno III Consensus Workshop on definitions, methodology and therapeutic strategies in portal hypertension. J Hepatol 2000;33:846-852.


31. Grace ND, Groszmann RJ, Garcia-Tsao G, Burroughs AK, Pagliaro L, Makuch RW, et al. Portal hypertension and variceal bleeding: an AASLD single topic symposium. Hepatology 1998;28:868-880.


32. de Franchis R, Pascal JP, Ancona E, Burroughs AK, Henderson M, Fleig W, et al. Definitions, methodology and therapeutic strategies in portal hypertension. A Consensus Development Workshop, Baveno, Lake Maggiore, Italy, April 5 and 6, 1990. J Hepatol 1992;15:256-261.


33. Beppu K, Inokuchi K, Koyanagi N, Nakayama S, Sakata H, Kitano S, et al. Prediction of variceal hemorrhage by esophageal endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 1981;27:213-218.


34. Pockros PJ, Hamzeh FM, Martin P, Lentz E, Zhou X, Govindarajan S, et al. Histologic outcomes in hepatitis C-infected patients with varying degrees of virologic response to interferon-based treatments. Hepatology 2010;52:1193-1200.


35. Promrat K, Kleiner DE, Niemeier HM, Jackvony E, Kearns M, Wands JR, et al. Randomized controlled trial testing the effects of weight loss on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010;51:121-129.



36. Bruno S, Crosignani A, Facciotto C, Rossi S, Roffi L, Redaelli A, et al. Sustained virologic response prevents the development of esophageal varices in compensated, Child-Pugh class A hepatitis C virus-induced cirrhosis. A 12-year prospective follow-up study. Hepatology 2010;51:2069-2076.


37. Di Marco V, Calvaruso V, Ferraro D, Bavetta MG, Cabibbo G, Conte E, et al. Effects of eradicating hepatitis C virus infection in patients with cirrhosis differ with stage of portal hypertension. Gastroenterology 2016;151:130-139 e2.


38. DŌĆÖAmbrosio R, Aghemo A, Rumi MG, Primignani M, DellŌĆÖEra A, Lampertico P, et al. The course of esophageal varices in patients with hepatitis C cirrhosis responding to interferon/ribavirin therapy. Antivir Ther 2011;16:677-684.


39. Lens S, Alvarado-Tapias E, Mari├▒o Z, Londo├▒o MC, LLop E, Martinez J, et al. Effects of all-oral anti-viral therapy on HVPG and systemic hemodynamics in patients with hepatitis C virus-associated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2017;153:1273-1283 e1.


40. Merkel C, Marin R, Angeli P, Zanella P, Felder M, Bernardinello E, et al. A placebo-controlled clinical trial of nadolol in the prophylaxis of growth of small esophageal varices in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2004;127:476-484.


41. Sarin SK, Mishra SR, Sharma P, Sharma BC, Kumar A. Early primary prophylaxis with beta-blockers does not prevent the growth of small esophageal varices in cirrhosis: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatol Int 2013;7:248-256.



42. Qi XS, Bao YX, Bai M, Xu WD, Dai JN, Guo XZ. Nonselective beta-blockers in cirrhotic patients with no or small varices: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:3100-3108.



43. Bhardwaj A, Kedarisetty CK, Vashishtha C, Bhadoria AS, Jindal A, Kumar G, et al. Carvedilol delays the progression of small oesophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis: a randomised placebocontrolled trial. Gut 2017;66:1838-1843.


44. Kim SG, Kim TY, Sohn JH, Um SH, Seo YS, Baik SK, et al. A randomized, multi-center, open-label study to evaluate the efficacy of carvedilol vs. propranolol to reduce portal pressure in patients with liver cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 2016;111:1582-1590.



45. Garcia-Tsao G, Sanyal AJ, Grace ND, Carey W; Practice Guidelines Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2007;46:922-938.


46. Zoli M, Merkel C, Magalotti D, Gueli C, Grimaldi M, Gatta A, et al. Natural history of cirrhotic patients with small esophageal varices: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol 2000;95:503-508.


47. Garcia-Tsao G, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, Bosch J. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology 2017;65:310-335.


48. DŌĆÖAmico G, Pagliaro L, Bosch J. Pharmacological treatment of portal hypertension: an evidence-based approach. Semin Liver Dis 1999;19:475-505.



49. Pagliaro L, DŌĆÖAmico G, S├Črensen TI, Lebrec D, Burroughs AK, Morabito A, et al. Prevention of first bleeding in cirrhosis. A meta-analysis of randomized trials of nonsurgical treatment. Ann Intern Med 1992;117:59-70.


50. Gluud LL, Klingenberg S, Nikolova D, Gluud C. Banding ligation versus beta-blockers as primary prophylaxis in esophageal varices: systematic review of randomized trials. Am J Gastroenterol 2007;102:2842-2848 quiz 2841, 2849.


51. Li L, Yu C, Li Y. Endoscopic band ligation versus pharmacological therapy for variceal bleeding in cirrhosis: a meta-analysis. Can J Gastroenterol 2011;25:147-155.




52. Khuroo MS, Khuroo NS, Farahat KL, Khuroo YS, Sofi AA, Dahab ST. Meta-analysis: endoscopic variceal ligation for primary prophylaxis of oesophageal variceal bleeding. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005;21:347-361.


53. De BK, Das D, Sen S, Biswas PK, Mandal SK, Majumdar D, et al. Acute and 7-day portal pressure response to carvedilol and propranolol in cirrhotics. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2002;17:183-189.


54. Ba├▒ares R, Moitinho E, Piqueras B, Casado M, Garc├Ła-Pag├Īn JC, de Diego A, et al. Carvedilol, a new nonselective beta-blocker with intrinsic anti- alpha1-adrenergic activity, has a greater portal hypotensive effect than propranolol in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 1999;30:79-83.


55. Ba├▒ares R, Moitinho E, Matilla A, Garc├Ła-Pag├Īn JC, Lampreave JL, Piera C, et al. Randomized comparison of long-term carvedilol and propranolol administration in the treatment of portal hypertension in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2002;36:1367-1373.


56. Tripathi D, Ferguson JW, Kochar N, Leithead JA, Therapondos G, McAvoy NC, et al. Randomized controlled trial of carvedilol versus variceal band ligation for the prevention of the first variceal bleed. Hepatology 2009;50:825-833.


57. Shah HA, Azam Z, Rauf J, Abid S, Hamid S, Jafri W, et al. Carvedilol vs. esophageal variceal band ligation in the primary prophylaxis of variceal hemorrhage: a multicentre randomized controlled trial. J Hepatol 2014;60:757-764.


58. Abd ElRahim AY, Fouad R, Khairy M, Elsharkawy A, Fathalah W, Khatamish H, et al. Efficacy of carvedilol versus propranolol versus variceal band ligation for primary prevention of variceal bleeding. Hepatol Int 2018;12:75-82.



59. Sarin SK, Wadhawan M, Agarwal SR, Tyagi P, Sharma BC. Endoscopic variceal ligation plus propranolol versus endoscopic variceal ligation alone in primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol 2005;100:797-804.


60. Bonilha DQ, Lenz L, Correia LM, Rodrigues RA, de Paulo GA, Ferrari AP, et al. Propranolol associated with endoscopic band ligation reduces recurrence of esophageal varices for primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding: a randomized-controlled trial. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;27:84-90.


61. Lo GH, Chen WC, Wang HM, Lee CC. Controlled trial of ligation plus nadolol versus nadolol alone for the prevention of first variceal bleeding. Hepatology 2010;52:230-237.


62. Gheorghe C, Gheorghe L, Iacob S, Iacob R, Popescu I. Primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in cirrhotics awaiting liver transplantation. Hepatogastroenterology 2006;53:552-557.

63. Sharma M, Singh S, Desai V, Shah VH, Kamath PS, Murad MH, et al. Comparison of therapies for primary prevention of esophageal variceal bleeding: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Hepatology 2019;69:1657-1675.


64. Angelico M, Carli L, Piat C, Gentile S, Capocaccia L. Effects of isosorbide-5-mononitrate compared with propranolol on first bleeding and long-term survival in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1997;113:1632-1639.


65. Lui HF, Stanley AJ, Forrest EH, Jalan R, Hislop WS, Mills PR, et al. Primary prophylaxis of variceal hemorrhage: a randomized controlled trial comparing band ligation, propranolol, and isosorbide mononitrate. Gastroenterology 2002;123:735-744.


66. Garc├Ła-Pag├Īn JC, Morillas R, Ba├▒ares R, Albillos A, Villanueva C, Vila C, et al. Propranolol plus placebo versus propranolol plus isosorbide-5-mononitrate in the prevention of a first variceal bleed: a double-blind RCT. Hepatology 2003;37:1260-1266.


67. Mi├▒ano C, Garcia-Tsao G. Clinical pharmacology of portal hypertension. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2010;39:681-695.



68. Lebrec D, Vinel JP, Dupas JL. Complications of portal hypertension in adults: a French consensus. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005;17:403-410.


69. Abraczinskas DR, Ookubo R, Grace ND, Groszmann RJ, Bosch J, Garcia-Tsao G, et al. Propranolol for the prevention of first esophageal variceal hemorrhage: a lifetime commitment? Hepatology 2001;34:1096-1102.


70. Serst├® T, Melot C, Francoz C, Durand F, Rautou PE, Valla D, et al. Deleterious effects of beta-blockers on survival in patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites. Hepatology 2010;52:1017-1022.


71. Serst├® T, Francoz C, Durand F, Rautou PE, Melot C, Valla D, et al. Beta-blockers cause paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction in patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites: a cross-over study. J Hepatol 2011;55:794-799.


72. Mandorfer M, Bota S, Schwabl P, Bucsics T, Pfisterer N, Kruzik M, et al. Nonselective ╬▓ blockers increase risk for hepatorenal syndrome and death in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Gastroenterology 2014;146:1680-1690 e1.


73. Leithead JA, Rajoriya N, Tehami N, Hodson J, Gunson BK, Tripathi D, et al. Non-selective ╬▓-blockers are associated with improved survival in patients with ascites listed for liver transplantation. Gut 2015;64:1111-1119.


74. Bossen L, Krag A, Vilstrup H, Watson H, Jepsen P. Nonselective ╬▓-blockers do not affect mortality in cirrhosis patients with ascites: post Hoc analysis of three randomized controlled trials with 1198 patients. Hepatology 2016;63:1968-1976.


75. Madsen BS, Nielsen KF, Fialla AD, Krag A. Keep the sick from harm in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: dose of beta blockers matters. J Hepatol 2016;64:1455-1456.


76. Shaheen NJ, Stuart E, Schmitz SM, Mitchell KL, Fried MW, Zacks S, et al. Pantoprazole reduces the size of postbanding ulcers after variceal band ligation: a randomized, controlled trial. Hepatology 2005;41:588-594.


77. Boo GB, Oh JC, Lee BJ, Lee DM, Kim YD, Park CG, et al. The effect of proton pump inhibitor on healing of post-esophageal variceal ligation ulcers. Korean J Gastroenterol 2008;51:232-240.

78. Kang SH, Yim HJ, Kim SY, Suh SJ, Hyun JJ, Jung SW, et al. Proton pump inhibitor therapy is associated with reduction of early bleeding risk after prophylactic endoscopic variceal band ligation: a retrospective cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e2903.



79. Dam G, Vilstrup H, Watson H, Jepsen P. Proton pump inhibitors as a risk factor for hepatic encephalopathy and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhosis with ascites. Hepatology 2016;64:1265-1272.


80. Tsai CF, Chen MH, Wang YP, Chu CJ, Huang YH, Lin HC, et al. Proton pump inhibitors increase risk for hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis in a population study. Gastroenterology 2017;152:134-141.


81. Goel GA, Deshpande A, Lopez R, Hall GS, van Duin D, Carey WD. Increased rate of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis among cirrhotic patients receiving pharmacologic acid suppression. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;10:422-427.


82. Hwang JH, Shergill AK, Acosta RD, Chandrasekhara V, Chathadi KV, Decker GA, et al. The role of endoscopy in the management of variceal hemorrhage. Gastrointest Endosc 2014;80:221-227.


83. Villanueva C, Colomo A, Bosch A, Concepci├│n M, Hernandez-Gea V, Aracil C, et al. Transfusion strategies for acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding. N Engl J Med 2013;368:11-21.


84. Castaneda B, Morales J, Lionetti R, Moitinho E, Andreu V, P├®rezDel-Pulgar S, et al. Effects of blood volume restitution following a portal hypertensive-related bleeding in anesthetized cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 2001;33:821-825.


85. Bosch J, Thabut D, Bendtsen F, DŌĆÖAmico G, Albillos A, Gonz├Īlez Abraldes J, et al. Recombinant factor VIIa for upper gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis: a randomized, double-blind trial. Gastroenterology 2004;127:1123-1130.


86. Bosch J, Thabut D, Albillos A, Carbonell N, Spicak J, Massard J, et al. Recombinant factor VIIa for variceal bleeding in patients with advanced cirrhosis: a randomized, controlled trial. Hepatology 2008;47:1604-1614.


87. Bernard B, Grang├® JD, Khac EN, Amiot X, Opolon P, Poynard T. Antibiotic prophylaxis for the prevention of bacterial infections in cirrhotic patients with gastrointestinal bleeding: a meta-analysis. Hepatology 1999;29:1655-1661.


88. Chavez-Tapia NC, Barrientos-Gutierrez T, Tellez-Avila F, SoaresWeiser K, Mendez-Sanchez N, Gluud C, et al. Meta-analysis: antibiotic prophylaxis for cirrhotic patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding - an updated Cochrane review. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2011;34:509-518.


89. Tandon P, Abraldes JG, Keough A, Bastiampillai R, Jayakumar S, Carbonneau M, et al. Risk of bacterial infection in patients with cirrhosis and acute variceal hemorrhage, based on Child-Pugh class, and effects of antibiotics. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;13:1189-1196 e2.


90. Fern├Īndez J, Ruiz del Arbol L, G├│mez C, Durandez R, Serradilla R, Guarner C, et al. Norfloxacin vs ceftriaxone in the prophylaxis of infections in patients with advanced cirrhosis and hemorrhage. Gastroenterology 2006;131:1049-1056 quiz 1285.


91. Wells M, Chande N, Adams P, Beaton M, Levstik M, Boyce E, et al. Meta-analysis: vasoactive medications for the management of acute variceal bleeds. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2012;35:1267-1278.


92. Ioannou G, Doust J, Rockey DC. Terlipressin for acute esophageal variceal hemorrhage. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003;(1):CD002147.



93. Suk KT, Baik SK, Yoon JH, Cheong JY, Paik YH, Lee CH, et al. Revision and update on clinical practice guideline for liver cirrhosis. Korean J Hepatol 2012;18:1-21.




94. Sol├Ā E, Lens S, Guevara M, Mart├Łn-Llah├Ł M, Fagundes C, Pereira G, et al. Hyponatremia in patients treated with terlipressin for severe gastrointestinal bleeding due to portal hypertension. Hepatology 2010;52:1783-1790.


95. Hashizume M, Ohta M, Ueno K, Tanoue K, Kitano S, Sugimachi K. Endoscopic ligation of esophageal varices compared with injection sclerotherapy: a prospective randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc 1993;39:123-126.


96. Lo GH, Lai KH, Cheng JS, Hwu JH, Chang CF, Chen SM, et al. A prospective, randomized trial of sclerotherapy versus ligation in the management of bleeding esophageal varices. Hepatology 1995;22:466-471.


97. Laine L, Cook D. Endoscopic ligation compared with sclerotherapy for treatment of esophageal variceal bleeding. A meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 1995;123:280-287.


98. Lo GH, Lai KH, Cheng JS, Lin CK, Huang JS, Hsu PI, et al. Emergency banding ligation versus sclerotherapy for the control of active bleeding from esophageal varices. Hepatology 1997;25:1101-1104.


99. Stiegmann GV, Goff JS, Michaletz-Onody PA, Korula J, Lieberman D, Saeed ZA, et al. Endoscopic sclerotherapy as compared with endoscopic ligation for bleeding esophageal varices. N Engl J Med 1992;326:1527-1532.


100. Dai C, Liu WX, Jiang M, Sun MJ. Endoscopic variceal ligation compared with endoscopic injection sclerotherapy for treatment of esophageal variceal hemorrhage: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:2534-2541.



101. Hsu YC, Chung CS, Tseng CH, Lin TL, Liou JM, Wu MS, et al. Delayed endoscopy as a risk factor for in-hospital mortality in cirrhotic patients with acute variceal hemorrhage. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;24:1294-1299.


102. Chen PH, Chen WC, Hou MC, Liu TT, Chang CJ, Liao WC, et al. Delayed endoscopy increases re-bleeding and mortality in patients with hematemesis and active esophageal variceal bleeding: a cohort study. J Hepatol 2012;57:1207-1213.


103. Monescillo A, Mart├Łnez-Lagares F, Ruiz-del-Arbol L, Sierra A, Guevara C, Jim├®nez E, et al. Influence of portal hypertension and its early decompression by TIPS placement on the outcome of variceal bleeding. Hepatology 2004;40:793-801.


104. Garc├Ła-Pag├Īn JC, Caca K, Bureau C, Laleman W, Appenrodt B, Luca A, et al. Early use of TIPS in patients with cirrhosis and variceal bleeding. N Engl J Med 2010;362:2370-2379.


105. Rudler M, Cluzel P, Corvec TL, Benosman H, Rousseau G, Poynard T, et al. Early-TIPSS placement prevents rebleeding in high-risk patients with variceal bleeding, without improving survival. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014;40:1074-1080.


106. Ibrahim M, El-Mikkawy A, Abdel Hamid M, Abdalla H, Lemmers A, Mostafa I, et al. Early application of haemostatic powder added to standard management for oesophagogastric variceal bleeding: a randomised trial. Gut 2019;68:844-853.



107. de Franchis R; Baveno V Faculty. Revising consensus in portal hypertension: report of the Baveno V consensus workshop on methodology of diagnosis and therapy in portal hypertension. J Hepatol 2010;53:762-768.


108. Azoulay D, Castaing D, Majno P, Saliba F, Ichaï P, Smail A, et al. Salvage transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for uncontrolled variceal bleeding in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2001;35:590-597.


109. Pan├®s J, Ter├®s J, Bosch J, Rod├®s J. Efficacy of balloon tamponade in treatment of bleeding gastric and esophageal varices. Results in 151 consecutive episodes. Dig Dis Sci 1988;33:454-459.



110. Ter├®s J, Cecilia A, Bordas JM, Rimola A, Bru C, Rod├®s J. Esophageal tamponade for bleeding varices. Controlled trial between the Sengstaken-Blakemore tube and the Linton-Nachlas tube. Gastroenterology 1978;75:566-569.


111. Haq I, Tripathi D. Recent advances in the management of variceal bleeding. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf) 2017;5:113-126.




112. Escorsell ├Ć, Pavel O, C├Īrdenas A, Morillas R, Llop E, Villanueva C, et al. Esophageal balloon tamponade versus esophageal stent in controlling acute refractory variceal bleeding: a multicenter randomized, controlled trial. Hepatology 2016;63:1957-1967.


113. Lebrec D, Poynard T, Bernuau J, Bercoff E, Nouel O, Capron JP, et al. A randomized controlled study of propranolol for prevention of recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis: a final report. Hepatology 1984;4:355-358.


114. Garden OJ, Mills PR, Birnie GG, Murray GD, Carter DC. Propranolol in the prevention of recurrent variceal hemorrhage in cirrhotic patients. A controlled trial. Gastroenterology 1990;98:185-190.


115. Colombo M, de Franchis R, Tommasini M, Sangiovanni A, Dioguardi N. Beta-blockade prevents recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding in well-compensated patients with alcoholic cirrhosis: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Hepatology 1989;9:433-438.


116. Garc├Ła-Pag├Īn JC, Feu F, Bosch J, Rod├®s J. Propranolol compared with propranolol plus isosorbide-5-mononitrate for portal hypertension in cirrhosis. A randomized controlled study. Ann Intern Med 1991;114:869-873.


117. Gournay J, Masliah C, Martin T, Perrin D, Galmiche JP. Isosorbide mononitrate and propranolol compared with propranolol alone for the prevention of variceal rebleeding. Hepatology 2000;31:1239-1245.


118. Cheung J, Zeman M, van Zanten SV, Tandon P. Systematic review: secondary prevention with band ligation, pharmacotherapy or combination therapy after bleeding from oesophageal varices. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2009;30:577-588.


119. Ding SH, Liu J, Wang JP. Efficacy of beta-adrenergic blocker plus 5-isosorbide mononitrate and endoscopic band ligation for prophylaxis of esophageal variceal rebleeding: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2009;15:2151-2155.



120. Lo GH, Chen WC, Lin CK, Tsai WL, Chan HH, Chen TA, et al. Improved survival in patients receiving medical therapy as compared with banding ligation for the prevention of esophageal variceal rebleeding. Hepatology 2008;48:580-587.


121. Lo GH, Lai KH, Cheng JS, Chen MH, Huang HC, Hsu PI, et al. Endoscopic variceal ligation plus nadolol and sucralfate compared with ligation alone for the prevention of variceal rebleeding: a prospective, randomized trial. Hepatology 2000;32:461-465.


122. de la Pe├▒a J, Brullet E, Sanchez-Hern├Īndez E, Rivero M, Vergara M, Martin-Lorente JL, et al. Variceal ligation plus nadolol compared with ligation for prophylaxis of variceal rebleeding: a multicenter trial. Hepatology 2005;41:572-578.


123. Gonzalez R, Zamora J, Gomez-Camarero J, Molinero LM, Ba├▒ares R, Albillos A. Meta-analysis: combination endoscopic and drug therapy to prevent variceal rebleeding in cirrhosis. Ann Intern Med 2008;149:109-122.


124. Ravipati M, Katragadda S, Swaminathan PD, Molnar J, Zarling E. Pharmacotherapy plus endoscopic intervention is more effective than pharmacotherapy or endoscopy alone in the secondary prevention of esophageal variceal bleeding: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Gastrointest Endosc 2009;70:658-664 e5.


125. Puente A, Hern├Īndez-Gea V, Graupera I, Roque M, Colomo A, Poca M, et al. Drugs plus ligation to prevent rebleeding in cirrhosis: an updated systematic review. Liver Int 2014;34:823-833.


126. Stanley AJ, Dickson S, Hayes PC, Forrest EH, Mills PR, Tripathi D, et al. Multicentre randomised controlled study comparing carvedilol with variceal band ligation in the prevention of variceal rebleeding. J Hepatol 2014;61:1014-1019.


127. Lo GH, Chen WC, Wang HM, Yu HC. Randomized, controlled trial of carvedilol versus nadolol plus isosorbide mononitrate for the prevention of variceal rebleeding. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;27:1681-1687.


128. DŌĆÖAmico G, Garcia-Pagan JC, Luca A, Bosch J. Hepatic vein pressure gradient reduction and prevention of variceal bleeding in cirrhosis: a systematic review. Gastroenterology 2006;131:1611-1624.


129. Sauerbruch T, Mengel M, Dollinger M, Zipprich A, R├Čssle M, Panther E, et al. Prevention of rebleeding from esophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis receiving small-diameter stents versus hemodynamically controlled medical therapy. Gastroenterology 2015;149:660-668 e1.


130. Holster IL, Tjwa ET, Moelker A, Wils A, Hansen BE, Vermeijden JR, et al. Covered transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic therapy + ╬▓-blocker for prevention of variceal rebleeding. Hepatology 2016;63:581-589.


131. Boyer TD, Haskal ZJ; American Association for the Study of Liver Disease. The role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the management of portal hypertension. Hepatology 2005;41:386-400.


132. Henderson JM. Salvage therapies for refractory variceal hemorrhage. Clin Liver Dis 2001;5:709-725.


133. Kawaoka T, Takahashi S, Aikata H, Azakami T, Saneto H, Takaki S, et al. Beneficial effects of living-donor liver transplantation on esophageal varices. J Gastroenterol 2008;43:982-989.



134. Sarin SK, Lahoti D, Saxena SP, Murthy NS, Makwana UK. Prevalence, classification and natural history of gastric varices: a long-term follow-up study in 568 portal hypertension patients. Hepatology 1992;16:1343-1349.


135. de Franchis R, Primignani M. Natural history of portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Liver Dis 2001;5:645-663.


136. Sarin SK. Long-term follow-up of gastric variceal sclerotherapy: an eleven-year experience. Gastrointest Endosc 1997;46:8-14.


137. Kim T, Shijo H, Kokawa H, Tokumitsu H, Kubara K, Ota K, et al. Risk factors for hemorrhage from gastric fundal varices. Hepatology 1997;25:307-312.


138. Lee CH, Lee JH, Choi YS, Paik SW, Sinn DH, Lee CY, et al. Natural history of gastric varices and risk factors for bleeding. Korean J Hepatol 2008;14:331-341.



139. Jakab SS, Garcia-Tsao G. Screening and surveillance of varices in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;17:26-29.



140. Park SW, Seo YS, Lee HA, Park SJ, Kim TH, Lee JM, et al. Changes in cardiac varices and their clinical significance after eradication of esophageal varices by band ligation. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;2016:2198163.




141. Mishra SR, Sharma BC, Kumar A, Sarin SK. Primary prophylaxis of gastric variceal bleeding comparing cyanoacrylate injection and beta-blockers: a randomized controlled trial. J Hepatol 2011;54:1161-1167.


142. Park JK, Saab S, Kee ST, Busuttil RW, Kim HJ, Durazo F, et al. Balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration (BRTO) for treatment of gastric varices: review and meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci 2015;60:1543-1553.



143. Gwon DI, Ko GY, Yoon HK, Sung KB, Kim JH, Shin JH, et al. Gastric varices and hepatic encephalopathy: treatment with vascular plug and gelatin sponge-assisted retrograde transvenous obliteration--a primary report. Radiology 2013;268:281-287.


144. Gwon DI, Kim YH, Ko GY, Kim JW, Ko HK, Kim JH, et al. Vascular plug-assisted retrograde transvenous obliteration for the treatment of gastric varices and hepatic encephalopathy: a prospective multicenter study. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2015;26:1589-1595.


145. Ryan BM, Stockbrugger RW, Ryan JM. A pathophysiologic, gastroenterologic, and radiologic approach to the management of gastric varices. Gastroenterology 2004;126:1175-1189.


146. Thakeb F, Salem SA, Abdallah M, el Batanouny M. Endoscopic diagnosis of gastric varices. Endoscopy 1994;26:287-291.



147. Tripathi D, Stanley AJ, Hayes PC, Patch D, Millson C, Mehrzad H, et al. U.K. guidelines on the management of variceal haemorrhage in cirrhotic patients. Gut 2015;64:1680-1704.



148. Kapoor A, Dharel N, Sanyal AJ. Endoscopic diagnosis and therapy in gastroesophageal variceal bleeding. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 2015;25:491-507.



149. Akahoshi T, Hashizume M, Shimabukuro R, Tanoue K, Tomikawa M, Okita K, et al. Long-term results of endoscopic Histoacryl injection sclerotherapy for gastric variceal bleeding: a 10-year experience. Surgery 2002;131(1 Suppl):S176-S181.


150. Kim JW, Baik SK, Kim KH, Kim HJ, Jo KW, Hong JH, et al. Effect of endoscopic sclerotherapy using N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate in patients with gastric variceal bleeding. Korean J Hepatol 2006;12:394-403.

151. Paik CN, Kim SW, Lee IS, Park JM, Cho YK, Choi MG, et al. The therapeutic effect of cyanoacrylate on gastric variceal bleeding and factors related to clinical outcome. J Clin Gastroenterol 2008;42:916-922.


152. Jun CH, Kim KR, Yoon JH, Koh HR, Choi WS, Cho KM, et al. Clinical outcomes of gastric variceal obliteration using N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate in patients with acute gastric variceal hemorrhage. Korean J Intern Med 2014;29:437-444.




153. Lee HA, Chang JM, Goh HG, Kim TH, Lee YS, Suh SJ, et al. Prognosis of patients with gastric variceal bleeding after endoscopic variceal obturation according to the type of varices. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;31:211-217.


155. Tan PC, Hou MC, Lin HC, Liu TT, Lee FY, Chang FY, et al. A randomized trial of endoscopic treatment of acute gastric variceal hemorrhage: N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate injection versus band ligation. Hepatology 2006;43:690-697.


156. El Amin H, Abdel Baky L, Sayed Z, Abdel Mohsen E, Eid K, Fouad Y, et al. A randomized trial of endoscopic variceal ligation versus cyanoacrylate injection for treatment of bleeding junctional varices. Trop Gastroenterol 2010;31:279-284.

157. Lo GH, Lin CW, Perng DS, Chang CY, Lee CT, Hsu CY, et al. A retrospective comparative study of histoacryl injection and banding ligation in the treatment of acute type 1 gastric variceal hemorrhage. Scand J Gastroenterol 2013;48:1198-1204.


158. Cales P, Masliah C, Bernard B, Garnier PP, Silvain C, SzostakTalbodec N, et al. Early administration of vapreotide for variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 2001;344:23-28.


159. Lo GH, Lai KH. Is endoscopic ligation therapy with large detachable snares and elastic bands really safe and effective? Gastrointest Endosc 2003;57:438-439 author reply 439-440.


160. Mahadeva S, Bellamy MC, Kessel D, Davies MH, Millson CE. Cost-effectiveness of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate (histoacryl) glue injections versus transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the management of acute gastric variceal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol 2003;98:2688-2693.


161. Procaccini NJ, Al-Osaimi AM, Northup P, Argo C, Caldwell SH. Endoscopic cyanoacrylate versus transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for gastric variceal bleeding: a single-center U.S. analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 2009;70:881-887.


162. Chau TN, Patch D, Chan YW, Nagral A, Dick R, Burroughs AK. ŌĆ£SalvageŌĆØ transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: gastric fundal compared with esophageal variceal bleeding. Gastroenterology 1998;114:981-987.


163. Barange K, Peron JM, Imani K, Otal P, Payen JL, Rousseau H, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the treatment of refractory bleeding from ruptured gastric varices. Hepatology 1999;30:1139-1143.


164. Sahagun G, Benner KG, Saxon R, Barton RE, Rabkin J, Keller FS, et al. Outcome of 100 patients after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for variceal hemorrhage. Am J Gastroenterol 1997;92:1444-1452.

165. Sanyal AJ, Freedman AM, Luketic VA, Purdum PP, Shiffman ML, Tisnado J, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts for patients with active variceal hemorrhage unresponsive to sclerotherapy. Gastroenterology 1996;111:138-146.


166. Stanley AJ, Jalan R, Ireland HM, Redhead DN, Bouchier IA, Hayes PC. A comparison between gastric and oesophageal variceal haemorrhage treated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunt (TIPSS). Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997;11:171-176.


167. Barrio J, Ripoll C, Ba├▒ares R, Echenagusia A, Catalina MV, Cam├║├▒ez F, et al. Comparison of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt dysfunction in PTFE-covered stent-grafts versus bare stents. Eur J Radiol 2005;55:120-124.


168. Wang Q, Lv Y, Bai M, Wang Z, Liu H, He C, et al. Eight millimetre covered TIPS does not compromise shunt function but reduces hepatic encephalopathy in preventing variceal rebleeding. J Hepatol 2017;67:508-516.


169. Colombato L. The role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) in the management of portal hypertension. J Clin Gastroenterol 2007;41 Suppl 3:S344-S351.


170. Kanagawa H, Mima S, Kouyama H, Gotoh K, Uchida T, Okuda K. Treatment of gastric fundal varices by balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1996;11:51-58.


171. Chu HH, Kim M, Kim HC, Lee JH, Jae HJ, Chung JW. Long-term outcomes of balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration for the treatment of gastric varices: a comparison of ethanolamine oleate and sodium tetradecyl sulfate. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2018;41:578-586.



172. Imai Y, Nakazawa M, Ando S, Sugawara K, Mochida S. Long-term outcome of 154 patients receiving balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration for gastric fundal varices. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;31:1844-1850.


173. Jang SY, Kim GH, Park SY, Cho CM, Tak WY, Kim JH, et al. Clinical outcomes of balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration for the treatment of gastric variceal hemorrhage in Korean patients with liver cirrhosis: a retrospective multicenter study. Clin Mol Hepatol 2012;18:368-374.




174. Chavez-Tapia NC, Barrientos-Gutierrez T, Tellez-Avila FI, SoaresWeiser K, Uribe M. Antibiotic prophylaxis for cirrhotic patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010;(9):CD002907.



175. Besson I, Ingrand P, Person B, Boutroux D, Heresbach D, Bernard P, et al. Sclerotherapy with or without octreotide for acute variceal bleeding. N Engl J Med 1995;333:555-560.


176. Zuberi BF, Baloch Q. Comparison of endoscopic variceal sclerotherapy alone and in combination with octreotide in controlling acute variceal hemorrhage and early rebleeding in patients with low-risk cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 2000;95:768-771.


177. Henry Z, Uppal D, Saad W, Caldwell S. Gastric and ectopic varices. Clin Liver Dis 2014;18:371-388.


178. R├Łos Castellanos E, Seron P, Gisbert JP, Bonfill Cosp X. Endoscopic injection of cyanoacrylate glue versus other endoscopic procedures for acute bleeding gastric varices in people with portal hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015;(5):CD010180.


179. Watanabe K, Kimura K, Matsutani S, Ohto M, Okuda K. Portal hemodynamics in patients with gastric varices. A study in 230 patients with esophageal and/or gastric varices using portal vein catheterization. Gastroenterology 1988;95:434-440.


180. Saad WE. Vascular anatomy and the morphologic and hemodynamic classifications of gastric varices and spontaneous portosystemic shunts relevant to the BRTO procedure. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol 2013;16:60-100.


181. Maruyama H, Okugawa H, Yoshizumi H, Kobayashi S, Yokosuka O. Hemodynamic features of gastrorenal shunt: a Doppler study in cirrhotic patients with gastric fundal varices. Acad Radiol 2008;15:1148-1154.


182. Kim MY, Um SH, Baik SK, Seo YS, Park SY, Lee JI, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of gastric variceal bleeding: retrospective Korean multicenter data. Clin Mol Hepatol 2013;19:36-44.




183. Qiao W, Ren Y, Bai Y, Liu S, Zhang Q, Zhi F. Cyanoacrylate injection versus band ligation in the endoscopic management of acute gastric variceal bleeding: meta-analysis of randomized, controlled studies based on the PRISMA statement. Medicine (Baltimore) 2015;94:e1725.



184. Choi YH, Yoon CJ, Park JH, Chung JW, Kwon JW, Choi GM. Balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration for gastric variceal bleeding: its feasibility compared with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Korean J Radiol 2003;4:109-116.



185. Sabri SS, Abi-Jaoudeh N, Swee W, Saad WE, Turba UC, Caldwell SH, et al. Short-term rebleeding rates for isolated gastric varices managed by transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2014;25:355-361.


186. Wang YB, Zhang JY, Gong JP, Zhang F, Zhao Y. Balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration versus transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for treatment of gastric varices due to portal hypertension: a meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;31:727-733.


187. Gimm G, Chang Y, Kim HC, Shin A, Cho EJ, Lee JH, et al. Balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration versus transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for the management of gastric variceal bleeding. Gut Liver 2018;12:704-713.




188. Hong CH, Kim HJ, Park JH, Park DI, Cho YK, Sohn CI, et al. Treatment of patients with gastric variceal hemorrhage: endoscopic N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate injection versus balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;24:372-378.


189. Kim KR, Jun CH, Cho KM, Wi JW, Park SY, Cho SB, et al. Can proton pump inhibitors reduce rebleeding following Histoacryl sclerotherapy for gastric variceal hemorrhage? Korean J Intern Med 2015;30:593-601.




190. Lo GH, Liang HL, Chen WC, Chen MH, Lai KH, Hsu PI, et al. A prospective, randomized controlled trial of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus cyanoacrylate injection in the prevention of gastric variceal rebleeding. Endoscopy 2007;39:679-685.


191. Ninoi T, Nishida N, Kaminou T, Sakai Y, Kitayama T, Hamuro M, et al. Balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration of gastric varices with gastrorenal shunt: long-term follow-up in 78 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2005;184:1340-1346.


192. Wu CY, Yeh HZ, Chen GH. Pharmacologic efficacy in gastric variceal rebleeding and survival: including multivariate analysis. J Clin Gastroenterol 2002;35:127-132.


193. Mishra SR, Chander Sharma B, Kumar A, Sarin SK. Endoscopic cyanoacrylate injection versus beta-blocker for secondary prophylaxis of gastric variceal bleed: a randomised controlled trial. Gut 2010;59:729-735.


194. Hung HH, Chang CJ, Hou MC, Liao WC, Chan CC, Huang HC, et al. Efficacy of non-selective ╬▓-blockers as adjunct to endoscopic prophylactic treatment for gastric variceal bleeding: a randomized controlled trial. J Hepatol 2012;56:1025-1032.


196. Primignani M, Carpinelli L, Preatoni P, Battaglia G, Carta A, Prada A, et al. Natural history of portal hypertensive gastropathy in patients with liver cirrhosis. The New Italian Endoscopic Club for the study and treatment of esophageal varices (NIEC). Gastroenterology 2000;119:181-187.


197. DŌĆÖAmico G, Montalbano L, Traina M, Pisa R, Menozzi M, Span├▓ C, et al. Natural history of congestive gastropathy in cirrhosis. The Liver Study Group of V. Cervello Hospital. Gastroenterology 1990;99:1558-1564.


198. Spina GP, Arcidiacono R, Bosch J, Pagliaro L, Burroughs AK, Santambrogio R, et al. Gastric endoscopic features in portal hypertension: final report of a consensus conference, Milan, Italy, September 19, 1992. J Hepatol 1994;21:461-467.


199. Zardi EM, Ghittoni G, Margiotta D, Viera FT, Di Matteo F, Rossi S. Portal hypertensive gastropathy in cirrhotics without varices: a case-control study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;27:91-96.


200. Choe WH. Portal hypertensive gastropathy and gastric antral vascular ectasia. Korean J Gastroenterol 2010;56:186-191.


201. Kim MY, Choi H, Baik SK, Yea CJ, Won CS, Byun JW, et al. Portal hypertensive gastropathy: correlation with portal hypertension and prognosis in cirrhosis. Dig Dis Sci 2010;55:3561-3567.



202. Patwardhan VR, Cardenas A. Review article: the management of portal hypertensive gastropathy and gastric antral vascular ectasia in cirrhosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014;40:354-362.


203. Zhou Y, Qiao L, Wu J, Hu H, Xu C. Comparison of the efficacy of octreotide, vasopressin, and omeprazole in the control of acute bleeding in patients with portal hypertensive gastropathy: a controlled study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2002;17:973-979.


204. Kamath PS, Lacerda M, Ahlquist DA, McKusick MA, Andrews JC, Nagorney DA. Gastric mucosal responses to intrahepatic portosystemic shunting in patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2000;118:905-911.


205. P├®rez-Ayuso RM, Piqu├® JM, Bosch J, Pan├®s J, Gonz├Īlez A, P├®rez R, et al. Propranolol in prevention of recurrent bleeding from severe portal hypertensive gastropathy in cirrhosis. Lancet 1991;337:1431-1434.


206. Jepsen P, Ott P, Andersen PK, S├Ėrensen HT, Vilstrup H. Clinical course of alcoholic liver cirrhosis: a Danish population-based cohort study. Hepatology 2010;51:1675-1682.


207. Blei AT, C├│rdoba J; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of G. Hepatic Encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:1968-1976.


208. Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, Tarter R, Weissenborn K, Blei AT. Hepatic encephalopathy--definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology 2002;35:716-721.


209. Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology 2014;60:715-735.


210. Bajaj JS, Cordoba J, Mullen KD, Amodio P, Shawcross DL, Butterworth RF, et al. Review article: the design of clinical trials in hepatic encephalopathy--an International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN) consensus statement. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2011;33:739-747.



211. Saunders JB, Walters JR, Davies AP, Paton A. A 20-year prospective study of cirrhosis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981;282:263-266.



212. Jang JW, Choi JY, Kim YS, Yoo JJ, Woo HY, Choi SK, et al. Effects of virologic response to treatment on short- and long-term outcomes of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection and decompensated cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018;16:1954-1963.


213. Jeong JH, Park IS, Kim DH, Kim SC, Kang C, Lee SH, et al. CLIFSOFA score and SIRS are independent prognostic factors in patients with hepatic encephalopathy due to alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e3935.



214. Labenz C, Baron JS, Toenges G, Schattenberg JM, Nagel M, Sprinzl MF, et al. Prospective evaluation of the impact of covert hepatic encephalopathy on quality of life and sleep in cirrhotic patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2018;48:313-321.


215. Delanty N, French JA, Labar DR, Pedley TA, Rowan AJ. Status epilepticus arising de novo in hospitalized patients: an analysis of 41 patients. Seizure 2001;10:116-119.


216. Prabhakar S, Bhatia R. Management of agitation and convulsions in hepatic encephalopathy. Indian J Gastroenterol 2003;22 Suppl 2:S54-S58.

217. Ferenci P, Herneth A, Steindl P. Newer approaches to therapy of hepatic encephalopathy. Semin Liver Dis 1996;16:329-338.



218. Bajaj JS, Wade JB, Sanyal AJ. Spectrum of neurocognitive impairment in cirrhosis: implications for the assessment of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2009;50:2014-2021.


220. Krieger D, Krieger S, Jansen O, Gass P, Theilmann L, Lichtnecker H. Manganese and chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet 1995;346:270-274.


221. Davidson EA, Solomon P. The differentiation of delirium tremens from impending hepatic coma. J Ment Sci 1958;104:326-333.


222. James IM, Sampson D, Nashat S, Williams HS, Garassini M. Effect of induced metabolic alkalosis in hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet 1969;2:1106-1108.


223. Yun BC, Kim WR. Hyponatremia in hepatic encephalopathy: an accomplice or innocent bystander? Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:1390-1391.



224. Ito S, Sakakibara R, Yoshiyama Y, Hattori T. Senile portosystemic hepatic encephalopathy as a treatable dementia-like syndrome. J Neurol 2004;251:1015-1016.



225. Sutter R, Kaplan PW. Uncovering clinical and radiological associations of triphasic waves in acute encephalopathy: a case-control study. Eur J Neurol 2014;21:660-666.


226. Romero-G├│mez M, Boza F, Garc├Ła-Valdecasas MS, Garc├Ła E, Aguilar-Reina J. Subclinical hepatic encephalopathy predicts the development of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:2718-2723.


227. Amodio P, Montagnese S. Clinical neurophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy. J Clin Exp Hepatol 2015;5(Suppl 1):S60-S68.



228. Van der Rijt CC, Schalm SW, De Groot GH, De Vlieger M. Objective measurement of hepatic encephalopathy by means of automated EEG analysis. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1984;57:423-426.


229. Marchetti P, DŌĆÖAvanzo C, Orsato R, Montagnese S, Schiff S, Kaplan PW, et al. Electroencephalography in patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2011;141:1680-1689 e1-e2.


230. Ficker DM, Westmoreland BF, Sharbrough FW. Epileptiform abnormalities in hepatic encephalopathy. J Clin Neurophysiol 1997;14:230-234.


231. Olesen SS, Gram M, Jackson CD, Halliday E, Sandberg TH, Drewes AM, et al. Electroencephalogram variability in patients with cirrhosis associates with the presence and severity of hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 2016;65:517-523.


232. Sawhney IM, Verma PK, Dhiman RK, Chopra JS, Sharma A, Chawla YK, et al. Visual and auditory evoked responses in acute severe hepatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1997;12:554-559.


233. Moon JH, Jun DW, Yum MK, Lee KN, Lee HL, Lee OY, et al. Prolonged N200 is the early neurophysiologic change in the patient with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Scand J Gastroenterol 2014;49:604-610.


235. Tapper EB, Jiang ZG, Patwardhan VR. Refining the ammonia hypothesis: a physiology-driven approach to the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Mayo Clin Proc 2015;90:646-658.


236. Rose CF. Ammonia-lowering strategies for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2012;92:321-331.


237. Kramer L, Tribl B, Gendo A, Zauner C, Schneider B, Ferenci P, et al. Partial pressure of ammonia versus ammonia in hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2000;31:30-34.


238. Saleh A, Kamel L, Ghali A, Ismail A, El Khayat H. Serum levels of astroglial S100-beta and neuron-specific enolase in hepatic encephalopathy patients. East Mediterr Health J 2007;13:1114-1123.



239. Fessel JM, Conn HO. Analysis of the causes and prevention of hepatic coma. Gastroenterology 1972;62:191.
240. Acharya C, Bajaj JS. Current management of hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol 2018;113:1600-1612.



241. Hong SI, Hong KP, Lee SH. Clinical observations of hepatic encephalopathy. J Korean Acad Fam Med 1991;12:58-64.
242. Paik YH, Lee KS, Han KH, Song KH, Kim MH, Moon BS, et al. Comparison of rifaximin and lactulose for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a prospective randomized study. Yonsei Med J 2005;46:399-407.



243. Uribe M, Campollo O, Vargas F, Ravelli GP, Mundo F, Zapata L, et al. Acidifying enemas (lactitol and lactose) vs. nonacidifying enemas (tap water) to treat acute portal-systemic encephalopathy: a double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Hepatology 1987;7:639-643.


244. Als-Nielsen B, Gluud LL, Gluud C. Nonabsorbable disaccharides for hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004;(2):CD003044.


245. Gluud LL, Vilstrup H, Morgan MY. Nonabsorbable disaccharides for hepatic encephalopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2016;64:908-922.


246. Morgan MY, Hawley KE. Lactitol vs. lactulose in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients: a double-blind, randomized trial. Hepatology 1987;7:1278-1284.


248. Uribe M, Berthier JM, Lewis H, Mata JM, Sierra JG, Garc├Ła-Ramos G, et al. Lactose enemas plus placebo tablets vs. neomycin tablets plus starch enemas in acute portal systemic encephalopathy. A double-blind randomized controlled study. Gastroenterology 1981;81:101-106.


249. Bucci L, Palmieri GC. Double-blind, double-dummy comparison between treatment with rifaximin and lactulose in patients with medium to severe degree hepatic encephalopathy. Curr Med Res Opin 1993;13:109-118.


250. Patidar KR, Bajaj JS. Antibiotics for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2013;28:307-312.




251. Mas A, Rod├®s J, Sunyer L, Rodrigo L, Planas R, Vargas V, et al. Comparison of rifaximin and lactitol in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy: results of a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, controlled clinical trial. J Hepatol 2003;38:51-58.


252. Fera G, Agostinacchio F, Nigro M, Schiraldi O, Ferrieri A. Rifaximin in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Eur J Clin Res 1993;4:57-66.
253. Massa P, Vallerino E, Dodero M. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy with rifaximin: double blind, double dummy study versus lactulose. Eur J Clin Res 1993;4:7-18.
254. Kimer N, Krag A, M├Ėller S, Bendtsen F, Gluud LL. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the effects of rifaximin in hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014;40:123-132.


255. Sharma BC, Sharma P, Lunia MK, Srivastava S, Goyal R, Sarin SK. A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial comparing rifaximin plus lactulose with lactulose alone in treatment of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol 2013;108:1458-1463.



256. Phongsamran PV, Kim JW, Cupo Abbott J, Rosenblatt A. Pharmacotherapy for hepatic encephalopathy. Drugs 2010;70:1131-1148.


257. Butterworth RF, Kircheis G, Hilger N, McPhail MJW. Efficacy of l-ornithine l-aspartate for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy and hyperammonemia in cirrhosis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Exp Hepatol 2018;8:301-313.



258. Kircheis G, Nilius R, Held C, Berndt H, Buchner M, G├Črtelmeyer R, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of L-ornithine-L-aspartate infusions in patients with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy: results of a placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Hepatology 1997;25:1351-1360.


259. Sidhu SS, Sharma BC, Goyal O, Kishore H, Kaur N. L-ornithine L-aspartate in bouts of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2018;67:700-710.


260. Stauch S, Kircheis G, Adler G, Beckh K, Ditschuneit H, G├Črtelmeyer R, et al. Oral L-ornithine-L-aspartate therapy of chronic hepatic encephalopathy: results of a placebo-controlled double-blind study. J Hepatol 1998;28:856-864.


261. Poo JL, G├│ngora J, S├Īnchez-Avila F, Aguilar-Castillo S, Garc├ŁaRamos G, Fern├Īndez-Zertuche M, et al. Efficacy of oral L-ornithine-L-aspartate in cirrhotic patients with hyperammonemic hepatic encephalopathy. Results of a randomized, lactulose-controlled study. Ann Hepatol 2006;5:281-288.


262. Song KH, Kim MS, Han KH, Lee KS, Chon CY, Moon YM, et al. Prospective study on efficacy of oral supplement of branched-chain amino acid granules on the nutritional status of the cirrhotics. Korean J Hepatol 2001;7:432-438.
263. Leise MD, Poterucha JJ, Kamath PS, Kim WR. Management of hepatic encephalopathy in the hospital. Mayo Clin Proc 2014;89:241-253.



264. Gluud LL, Dam G, Borre M, Les I, Cordoba J, Marchesini G, et al. Lactulose, rifaximin or branched chain amino acids for hepatic encephalopathy: what is the evidence? Metab Brain Dis 2013;28:221-225.



265. Gluud LL, Dam G, Borre M, Les I, Cordoba J, Marchesini G, et al. Oral branched-chain amino acids have a beneficial effect on manifestations of hepatic encephalopathy in a systematic review with meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. J Nutr 2013;143:1263-1268.



266. Gluud LL, Dam G, Les I, Marchesini G, Borre M, Aagaard NK, et al. Branched-chain amino acids for people with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017;5:CD001939.



267. Naylor CD, OŌĆÖRourke K, Detsky AS, Baker JP. Parenteral nutrition with branched-chain amino acids in hepatic encephalopathy. A meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 1989;97:1033-1042.


268. Sort P, Navasa M, Arroyo V, Aldeguer X, Planas R, Ruiz-del-Arbol L, et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. N Engl J Med 1999;341:403-409.


269. Caraceni P, Riggio O, Angeli P, Alessandria C, Neri S, Foschi FG, et al. Long-term albumin administration in decompensated cirrhosis (ANSWER): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet 2018;391:2417-2429.


270. Sim├│n-Talero M, Garc├Ła-Mart├Łnez R, Torrens M, Augustin S, G├│mez S, Pereira G, et al. Effects of intravenous albumin in patients with cirrhosis and episodic hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized double-blind study. J Hepatol 2013;59:1184-1192.


271. Sharma BC, Singh J, Srivastava S, Sangam A, Mantri AK, Trehanpati N, et al. Randomized controlled trial comparing lactulose plus albumin versus lactulose alone for treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;32:1234-1239.


272. Rahimi RS, Singal AG, Cuthbert JA, Rockey DC. Lactulose vs polyethylene glycol 3350--electrolyte solution for treatment of overt hepatic encephalopathy: the HELP randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 2014;174:1727-1733.



273. Goulenok C, Bernard B, Cadranel JF, Thabut D, Di Martino V, Opolon P, et al. Flumazenil vs. placebo in hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a meta-analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002;16:361-372.


274. Malaguarnera M, Pistone G, Elvira R, Leotta C, Scarpello L, Liborio R. Effects of L-carnitine in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. World J Gastroenterol 2005;11:7197-7202.



275. Sushma S, Dasarathy S, Tandon RK, Jain S, Gupta S, Bhist MS. Sodium benzoate in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy: a double-blind randomized trial. Hepatology 1992;16:138-144.


276. Stewart CA, Malinchoc M, Kim WR, Kamath PS. Hepatic encephalopathy as a predictor of survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Liver Transpl 2007;13:1366-1371.


277. Bustamante J, Rimola A, Ventura PJ, Navasa M, Cirera I, Reggiardo V, et al. Prognostic significance of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol 1999;30:890-895.


278. Sharma BC, Sharma P, Agrawal A, Sarin SK. Secondary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy: an open-label randomized controlled trial of lactulose versus placebo. Gastroenterology 2009;137:885-891 891.e1.


279. Als-Nielsen B, Gluud LL, Gluud C. Non-absorbable disaccharides for hepatic encephalopathy: systematic review of randomised trials. BMJ 2004;328:1046.



280. Morgan MY, Hawley KE, Stambuk D. Lactitol versus lactulose in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A double-blind, randomised, cross-over study. J Hepatol 1987;4:236-244.


281. Vlachogiannakos J, Viazis N, Vasianopoulou P, Vafiadis I, Karamanolis DG, Ladas SD. Long-term administration of rifaximin improves the prognosis of patients with decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;28:450-455.


282. Bass NM, Mullen KD, Sanyal A, Poordad F, Neff G, Leevy CB, et al. Rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 2010;362:1071-1081.


283. Mullen KD, Sanyal AJ, Bass NM, Poordad FF, Sheikh MY, Frederick RT, et al. Rifaximin is safe and well tolerated for long-term maintenance of remission from overt hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;12:1390-1397 e2.


284. Kang SH, Lee YB, Lee JH, Nam JY, Chang Y, Cho H, et al. Rifaximin treatment is associated with reduced risk of cirrhotic complications and prolonged overall survival in patients experiencing hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2017;46:845-855.


285. Neff GW, Jones M, Jonas M, Ravinuthala R, Novick D, Kaiser TE, et al. Lack of Clostridium difficile infection in patients treated with rifaximin for hepatic encephalopathy: a retrospective analysis. J Clin Gastroenterol 2013;47:188-192.


286. Park JG, Tak WY, Park SY, Kweon YO, Jang SY, Lee YR, et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) on the progression of advanced liver disease: a Korean nationwide, multicenter, retrospective, observational, cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e6580.



287. Varakanahalli S, Sharma BC, Srivastava S, Sachdeva S, Dahale AS. Secondary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis of liver: a double-blind randomized controlled trial of L-ornithine L-aspartate versus placebo. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018;30:951-958.


288. Goh ET, Stokes CS, Sidhu SS, Vilstrup H, Gluud LL, Morgan MY. L-ornithine L-aspartate for prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy in people with cirrhosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2018;5:CD012410.



289. Garrido M, Turco M, Formentin C, Corrias M, De Rui M, Montagnese S, et al. An educational tool for the prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy. BMJ Open Gastroenterol 2017;4:e000161.



290. Nardelli S, Lattanzi B, Torrisi S, Greco F, Farcomeni A, Gioia S, et al. Sarcopenia is risk factor for development of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt placement. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;15:934-936.


291. Lucero C, Verna EC. The role of sarcopenia and frailty in hepatic encephalopathy management. Clin Liver Dis 2015;19:507-528.


292. Hanai T, Shiraki M, Nishimura K, Ohnishi S, Imai K, Suetsugu A, et al. Sarcopenia impairs prognosis of patients with liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2015;31:193-199.


293. Montano-Loza AJ, Meza-Junco J, Prado CM, Lieffers JR, Baracos VE, Bain VG, et al. Muscle wasting is associated with mortality in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;10:166-173 173.e1.


294. Tandon P, Ney M, Irwin I, Ma MM, Gramlich L, Bain VG, et al. Severe muscle depletion in patients on the liver transplant wait list: its prevalence and independent prognostic value. Liver Transpl 2012;18:1209-1216.


295. European Association of the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines on nutrition in chronic liver disease. J Hepatol 2019;70:172-193.



296. Tsien CD, McCullough AJ, Dasarathy S. Late evening snack: exploiting a period of anabolic opportunity in cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;27:430-441.


297. Berzigotti A, Saran U, Dufour JF. Physical activity and liver diseases. Hepatology 2016;63:1026-1040.


298. Garc├Ła-Pag├Ān JC, Santos C, Barber├Ī JA, Luca A, Roca J, RodriguezRoisin R, et al. Physical exercise increases portal pressure in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Gastroenterology 1996;111:1300-1306.


299. Qiu J, Thapaliya S, Runkana A, Yang Y, Tsien C, Mohan ML, et al. Hyperammonemia in cirrhosis induces transcriptional regulation of myostatin by an NF-╬║B-mediated mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013;110:18162-18167.



300. Nishikawa H, Enomoto H, Ishii A, Iwata Y, Miyamoto Y, Ishii N, et al. Elevated serum myostatin level is associated with worse survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017;8:915-925.



301. Rom├Īn E, Garc├Ła-Galcer├Īn C, Torrades T, Herrera S, Mar├Łn A, Do├▒ate M, et al. Effects of an exercise programme on functional capacity, body composition and risk of falls in patients with cirrhosis: a randomized clinical trial. PLoS One 2016;11:e0151652.



302. Hartmann IJ, Groeneweg M, Quero JC, Beijeman SJ, de Man RA, Hop WC, et al. The prognostic significance of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol 2000;95:2029-2034.


303. Saxena N, Bhatia M, Joshi YK, Garg PK, Dwivedi SN, Tandon RK. Electrophysiological and neuropsychological tests for the diagnosis of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy and prediction of overt encephalopathy. Liver 2002;22:190-197.


304. Prasad S, Dhiman RK, Duseja A, Chawla YK, Sharma A, Agarwal R. Lactulose improves cognitive functions and health-related quality of life in patients with cirrhosis who have minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2007;45:549-559.


305. Sidhu SS, Goyal O, Mishra BP, Sood A, Chhina RS, Soni RK. Rifaximin improves psychometric performance and health-related quality of life in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy (the RIME trial). Am J Gastroenterol 2011;106:307-316.



306. Bajaj JS, Saeian K, Verber MD, Hischke D, Hoffmann RG, Franco J, et al. Inhibitory control test is a simple method to diagnose minimal hepatic encephalopathy and predict development of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol 2007;102:754-760.


307. Campagna F, Montagnese S, Ridola L, Senzolo M, Schiff S, De Rui M, et al. The animal naming test: an easy tool for the assessment of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2017;66:198-208.


308. Maharshi S, Sharma BC, Sachdeva S, Srivastava S, Sharma P. Efficacy of nutritional therapy for patients with cirrhosis and minimal hepatic encephalopathy in a randomized trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;14:454-460 e3; quiz e33.


309. Dhiman RK, Kurmi R, Thumburu KK, Venkataramarao SH, Agarwal R, Duseja A, et al. Diagnosis and prognostic significance of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis of liver. Dig Dis Sci 2010;55:2381-2390.



310. Seo YS, Yim SY, Jung JY, Kim CH, Kim JD, Keum B, et al. Psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score for the detection of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in Korean patients with liver cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;27:1695-1704.


311. Patidar KR, Bajaj JS. Covert and overt hepatic encephalopathy: diagnosis and management. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;13:2048-2061.



312. Groeneweg M, Quero JC, De Bruijn I, Hartmann IJ, Essink-bot ML, Hop WC, et al. Subclinical hepatic encephalopathy impairs daily functioning. Hepatology 1998;28:45-49.


313. Rom├Īn E, C├│rdoba J, Torrens M, Torras X, Villanueva C, Vargas V, et al. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy is associated with falls. Am J Gastroenterol 2011;106:476-482.



314. Soriano G, Rom├Īn E, C├│rdoba J, ens M, Poca M, Torras X, et al. Cognitive dysfunction in cirrhosis is associated with falls: a prospective study. Hepatology 2012;55:1922-1930.


315. Bajaj JS, Wade JB, Gibson DP, Heuman DM, Thacker LR, Sterling RK, et al. The multi-dimensional burden of cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy on patients and caregivers. Am J Gastroenterol 2011;106:1646-1653.




316. Ampuero J, Simón M, Montoliú C, Jover R, Serra MÁ, Córdoba J, et al. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy and critical flicker frequency are associated with survival of patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2015;149:1483-1489.


317. Patidar KR, Thacker LR, Wade JB, Sterling RK, Sanyal AJ, Siddiqui MS, et al. Covert hepatic encephalopathy is independently associated with poor survival and increased risk of hospitalization. Am J Gastroenterol 2014;109:1757-1763.




318. Schomerus H, Hamster W. Neuropsychological aspects of portalsystemic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 1998;13:361-377.


319. Weissenborn K, Ennen JC, Schomerus H, R├╝ckert N, Hecker H. Neuropsychological characterization of hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 2001;34:768-773.


320. Amodio P, Campagna F, Olianas S, Iannizzi P, Mapelli D, Penzo M, et al. Detection of minimal hepatic encephalopathy: normalization and optimization of the Psychometric Hepatic Encephalopathy Score. A neuropsychological and quantified EEG study. J Hepatol 2008;49:346-353.


321. Badea MA, Drug VL, Dranga M, Gavrilescu O, Stefanescu G, Popa I, et al. Diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in a tertiary care center from eastern Romania: validation of the psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score (PHES). Metab Brain Dis 2016;31:1463-1471.



322. Duarte-Rojo A, Estradas J, Hern├Īndez-Ramos R, Ponce-de-Le├│n S, C├│rdoba J, Torre A. Validation of the psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score (PHES) for identifying patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Dig Dis Sci 2011;56:3014-3023.



323. Li SW, Wang K, Yu YQ, Wang HB, Li YH, Xu JM. Psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score for diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in China. World J Gastroenterol 2013;19:8745-8751.



324. Romero-G├│mez M, C├│rdoba J, Jover R, del Olmo JA, Ram├Łrez M, Rey R, et al. Value of the critical flicker frequency in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2007;45:879-885.


325. Jeong JY, Jun DW, Bai D, Kim JY, Sohn JH, Ahn SB, et al. Validation of a paper and pencil test battery for the diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2017;32:1484-1490.



326. HELIOS study group. Integrated diagnostic website for covert hepatic encephalopathy. HELIOS study group web site, <http://encephalopathy.or.kr/inspection>. Assessed 2 Oct 2018.
327. Bajaj JS, Hafeezullah M, Franco J, Varma RR, Hoffmann RG, Knox JF, et al. Inhibitory control test for the diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 2008;135:1591-1600 e1.


328. Bajaj JS, Thacker LR, Heuman DM, Fuchs M, Sterling RK, Sanyal AJ, et al. The stroop smartphone application is a short and valid method to screen for minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2013;58:1122-1132.



329. Bajaj JS, Heuman DM, Sterling RK, Sanyal AJ, Siddiqui M, Matherly S, et al. Validation of encephalApp, smartphone-based stroop test, for the diagnosis of covert hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;13:1828-1835 e1.



330. Allampati S, Duarte-Rojo A, Thacker LR, Patidar KR, White MB, Klair JS, et al. Diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy using stroop encephalApp: a multicenter US-based, Norm-based study. Am J Gastroenterol 2016;111:78-86.



331. Yoon EL, Jun DW, Jeong JY, Kim TY, Song DS, Ahn SB, et al. Validation of Korean stroop test in the screening of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Sci Rep 2019;9:8027.



332. Guerit JM, Amantini A, Fischer C, Kaplan PW, Mecarelli O, Schnitzler A, et al. Neurophysiological investigations of hepatic encephalopathy: ISHEN practice guidelines. Liver Int 2009;29:789-796.


333. Kircheis G, Wettstein M, Timmermann L, Schnitzler A, H├żussinger D. Critical flicker frequency for quantification of low-grade hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2002;35:357-366.


334. Torlot FJ, McPhail MJ, Taylor-Robinson SD. Meta-analysis: the diagnostic accuracy of critical flicker frequency in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2013;37:527-536.



335. Labenz C, Beul L, Toenges G, Schattenberg JM, Nagel M, Sprinzl MF, et al. Validation of the simplified Animal Naming Test as primary screening tool for the diagnosis of covert hepatic encephalopathy. Eur J Intern Med 2019;60:96-100.


336. Nabi E, Thacker LR, Wade JB, Sterling RK, Stravitz RT, Fuchs M, et al. Diagnosis of covert hepatic encephalopathy without specialized tests. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;12:1384-1389 e2.



337. Li W, Li N, Wang R, Li Q, Wu H. Interferon gamma, interleukin-6, and -17a levels were correlated with minimal hepatic encephalopathy in HBV patients. Hepatol Int 2015;9:218-223.



338. Montoliu C, Piedrafita B, Serra MA, del Olmo JA, Urios A, Rodrigo JM, et al. IL-6 and IL-18 in blood may discriminate cirrhotic patients with and without minimal hepatic encephalopathy. J Clin Gastroenterol 2009;43:272-279.


339. Wu H, Li N, Jin R, Meng Q, Chen P, Zhao G, et al. Cytokine levels contribute to the pathogenesis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma via STAT3 activation. Sci Rep 2016;6:18528.




340. Felipo V, Urios A, Valero P, S├Īnchez M, Serra MA, Pareja I, et al. Serum nitrotyrosine and psychometric tests as indicators of impaired fitness to drive in cirrhotic patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Liver Int 2013;33:1478-1489.


341. Montoliu C, Cauli O, Urios A, ElMlili N, Serra MA, Giner-Duran R, et al. 3-nitro-tyrosine as a peripheral biomarker of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with liver cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 2011;106:1629-1637.



342. Montagnese S, Balistreri E, Schiff S, De Rui M, Angeli P, Zanus G, et al. Covert hepatic encephalopathy: agreement and predictive validity of different indices. World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:15756-15762.



343. Montagnese S, Biancardi A, Schiff S, Carraro P, Carl├Ā V, Mannaioni G, et al. Different biochemical correlates for different neuropsychiatric abnormalities in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2011;53:558-566.


344. Henderson PK, Herrera JL. Should we treat minimal/covert hepatic encephalopathy, and with what? Clin Liver Dis 2015;19:487-495.


345. Luo M, Li L, Lu CZ, Cao WK. Clinical efficacy and safety of lactulose for minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;23:1250-1257.


346. Bajaj JS, Saeian K, Christensen KM, Hafeezullah M, Varma RR, Franco J, et al. Probiotic yogurt for the treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol 2008;103:1707-1715.


347. Liu Q, Duan ZP, Ha DK, Bengmark S, Kurtovic J, Riordan SM. Synbiotic modulation of gut flora: effect on minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2004;39:1441-1449.


348. Saab S, Suraweera D, Au J, Saab EG, Alper TS, Tong MJ. Probiotics are helpful in hepatic encephalopathy: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Liver Int 2016;36:986-993.


349. Viramontes H├Črner D, Avery A, Stow R. The effects of probiotics and symbiotics on risk factors for hepatic encephalopathy: a systematic review. J Clin Gastroenterol 2017;51:312-323.


350. Bajaj JS, Pinkerton SD, Sanyal AJ, Heuman DM. Diagnosis and treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy to prevent motor vehicle accidents: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Hepatology 2012;55:1164-1171.



351. Sidhu SS, Goyal O, Parker RA, Kishore H, Sood A. Rifaximin vs. lactulose in treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Liver Int 2016;36:378-385.


352. Mittal VV, Sharma BC, Sharma P, Sarin SK. A randomized controlled trial comparing lactulose, probiotics, and L-ornithine L-aspartate in treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;23:725-732.


353. Les I, Doval E, Garc├Ła-Mart├Łnez R, Planas M, C├Īrdenas G, G├│mez P, et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acids supplementation in patients with cirrhosis and a previous episode of hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized study. Am J Gastroenterol 2011;106:1081-1088.



354. Malaguarnera M, Bella R, Vacante M, Giordano M, Malaguarnera G, Gargante MP, et al. Acetyl-L-carnitine reduces depression and improves quality of life in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Scand J Gastroenterol 2011;46:750-759.


355. Malaguarnera M, Gargante MP, Cristaldi E, Vacante M, Risino C, Cammalleri L, et al. Acetyl-L-carnitine treatment in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Dig Dis Sci 2008;53:3018-3025.



356. Younossi ZM, Boparai N, Price LL, Kiwi ML, McCormick M, Guyatt G, et al. Health-related quality of life in chronic liver disease: the impact of type and severity of disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:2199-2205.


357. Arguedas MR, DeLawrence TG, McGuire BM. Influence of hepatic encephalopathy on health-related quality of life in patients with cirrhosis. Dig Dis Sci 2003;48:1622-1626.


358. Ries ML, Jabbar BM, Schmitz TW, Trivedi MA, Gleason CE, Carlsson CM, et al. Anosognosia in mild cognitive impairment: relationship to activation of cortical midline structures involved in self-appraisal. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2007;13:450-461.



359. Bao ZJ, Qiu DK, Ma X, Fan ZP, Zhang GS, Huang YQ, et al. Assessment of health-related quality of life in Chinese patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. World J Gastroenterol 2007;13:3003-3008.



360. Les I, Doval E, Flavi├Ā M, Jacas C, C├Īrdenas G, Esteban R, et al. Quality of life in cirrhosis is related to potentially treatable factors. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;22:221-227.


361. Schomerus H, Hamster W. Quality of life in cirrhotics with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2001;16:37-41.


362. Wunsch E, Szymanik B, Post M, Marlicz W, Mydłowska M, Milkiewicz P. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy does not impair health-related quality of life in patients with cirrhosis: a prospective study. Liver Int 2011;31:980-984.


363. Patrick DL, Deyo RA. Generic and disease-specific measures in assessing health status and quality of life. Med Care 1989;27:S217-S232.


364. Garratt A, Schmidt L, Mackintosh A, Fitzpatrick R. Quality of life measurement: bibliographic study of patient assessed health outcome measures. BMJ 2002;324:1417.



365. Bergner M, Bobbitt RA, Carter WB, Gilson BS. The sickness impact profile: development and final revision of a health status measure. Med Care 1981;19:787-805.


366. Hunt SM, McEwen J, McKenna SP. Measuring health status: a new tool for clinicians and epidemiologists. J R Coll Gen Pract 1985;35:185-188.


367. Brazier J, Roberts J, Deverill M. The estimation of a preference-based measure of health from the SF-36. J Health Econ 2002;21:271-292.


368. Younossi ZM, Guyatt G, Kiwi M, Boparai N, King D. Development of a disease specific questionnaire to measure health related quality of life in patients with chronic liver disease. Gut 1999;45:295-300.



369. Gralnek IM, Hays RD, Kilbourne A, Rosen HR, Keeffe EB, Artinian L, et al. Development and evaluation of the Liver Disease Quality of Life instrument in persons with advanced, chronic liver disease--the LDQOL 1.0. Am J Gastroenterol 2000;95:3552-3565.


370. Kanwal F, Spiegel BM, Hays RD, Durazo F, Han SB, Saab S, et al. Prospective validation of the short form liver disease quality of life instrument. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2008;28:1088-1101.


371. van der Plas SM, Hansen BE, de Boer JB, Stijnen T, Passchier J, de Man RA, et al. The liver disease symptom index 2.0; validation of a disease-specific questionnaire. Qual Life Res 2004;13:1469-1481.


372. Mullen KD. Review of the final report of the 1998 Working Party on definition, nomenclature and diagnosis of hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007;25 Suppl 1:11-16.


373. Ortiz M, Jacas C, C├│rdoba J. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy: diagnosis, clinical significance and recommendations. J Hepatol 2005;42 Suppl:S45-S53.


374. Moscucci F, Nardelli S, Pentassuglio I, Pasquale C, Ridola L, Merli M, et al. Previous overt hepatic encephalopathy rather than minimal hepatic encephalopathy impairs health-related quality of life in cirrhotic patients. Liver Int 2011;31:1505-1510.


375. Bajaj JS, Ananthakrishnan AN, McGinley EL, Hoffmann RG, Brasel KJ. Deleterious effect of cirrhosis on outcomes after motor vehicle crashes using the nationwide inpatient sample. Am J Gastroenterol 2008;103:1674-1681.


376. Bajaj JS, Hafeezullah M, Hoffmann RG, Saeian K. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a vehicle for accidents and traffic violations. Am J Gastroenterol 2007;102:1903-1909.


377. Marottoli RA, Cooney LM Jr, Wagner R, Doucette J, Tinetti ME. Predictors of automobile crashes and moving violations among elderly drivers. Ann Intern Med 1994;121:842-846.


378. Wein C, Koch H, Popp B, Oehler G, Schauder P. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy impairs fitness to drive. Hepatology 2004;39:739-745.


379. Martino ME, Romero-Vives M, Fern├Īndez-Lorente J, De Vicente E, B├Īrcena R, Gaztelu JM. Sleep electroencephalogram alterations disclose initial stage of encephalopathy. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 2002;24 Suppl D:119-122.

380. Bianchi G, Marchesini G, Nicolino F, Graziani R, Sgarbi D, Loguercio C, et al. Psychological status and depression in patients with liver cirrhosis. Dig Liver Dis 2005;37:593-600.


381. Mostacci B, Ferlisi M, Baldi Antognini A, Sama C, Morelli C, Mondini S, et al. Sleep disturbance and daytime sleepiness in patients with cirrhosis: a case control study. Neurol Sci 2008;29:237-240.



382. Wells KB, Stewart A, Hays RD, Burnam MA, Rogers W, Daniels M, et al. The functioning and well-being of depressed patients. Results from the Medical Outcomes Study. JAMA 1989;262:914-919.


383. Marchesini G, Bianchi G, Amodio P, Salerno F, Merli M, Panella C, et al. Factors associated with poor health-related quality of life of patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2001;120:170-178.


384. Sanyal A, Younossi ZM, Bass NM, Mullen KD, Poordad F, Brown RS, et al. Randomised clinical trial: rifaximin improves health-related quality of life in cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy - a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2011;34:853-861.





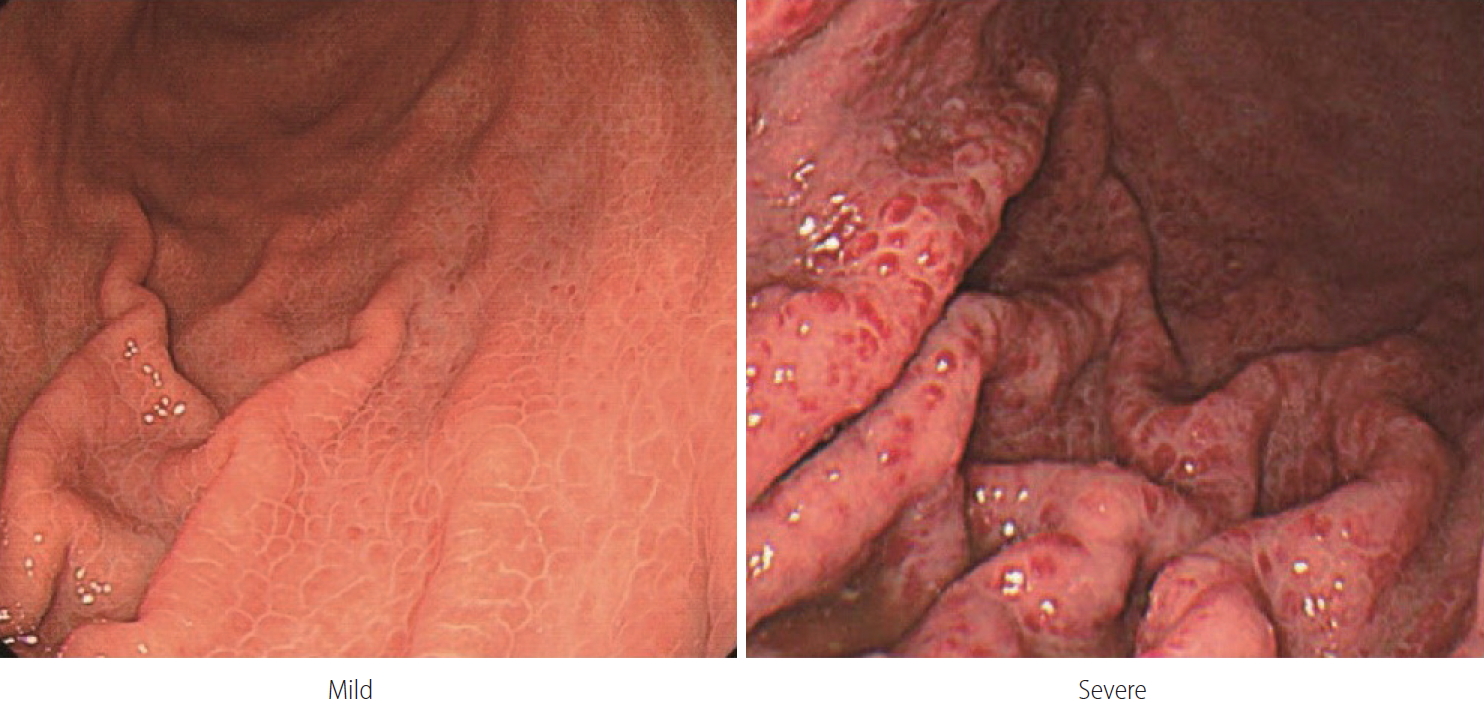
 PDF Links
PDF Links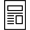 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement1
Supplement1 Print
Print




