| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 25(3); 2019 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
FOOTNOTES
Fuigures and Tables
Figure 1.
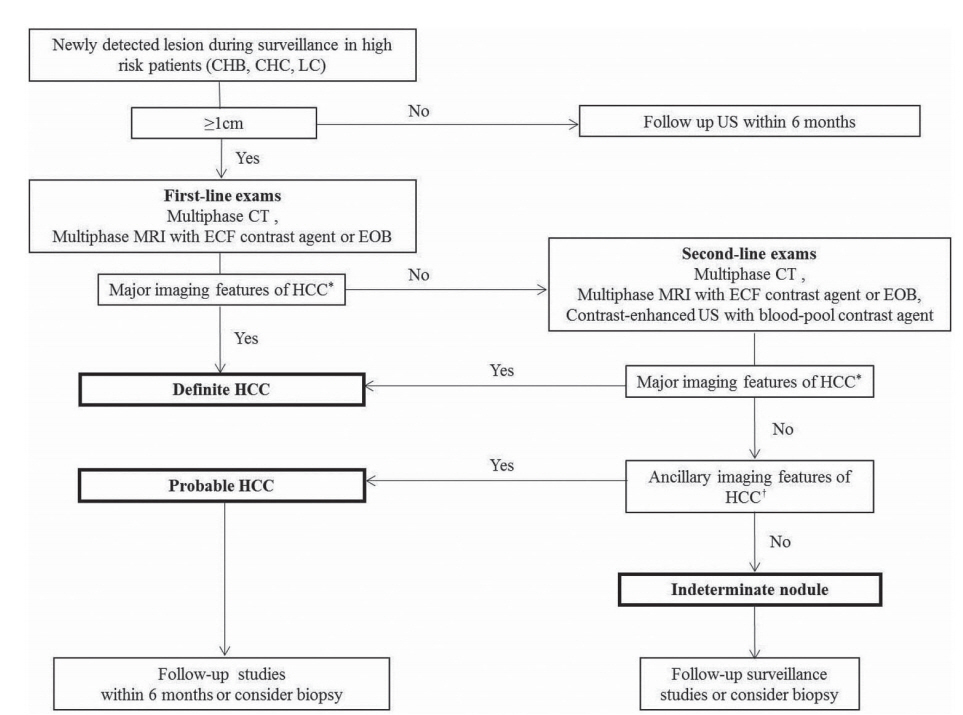
Figure 2.
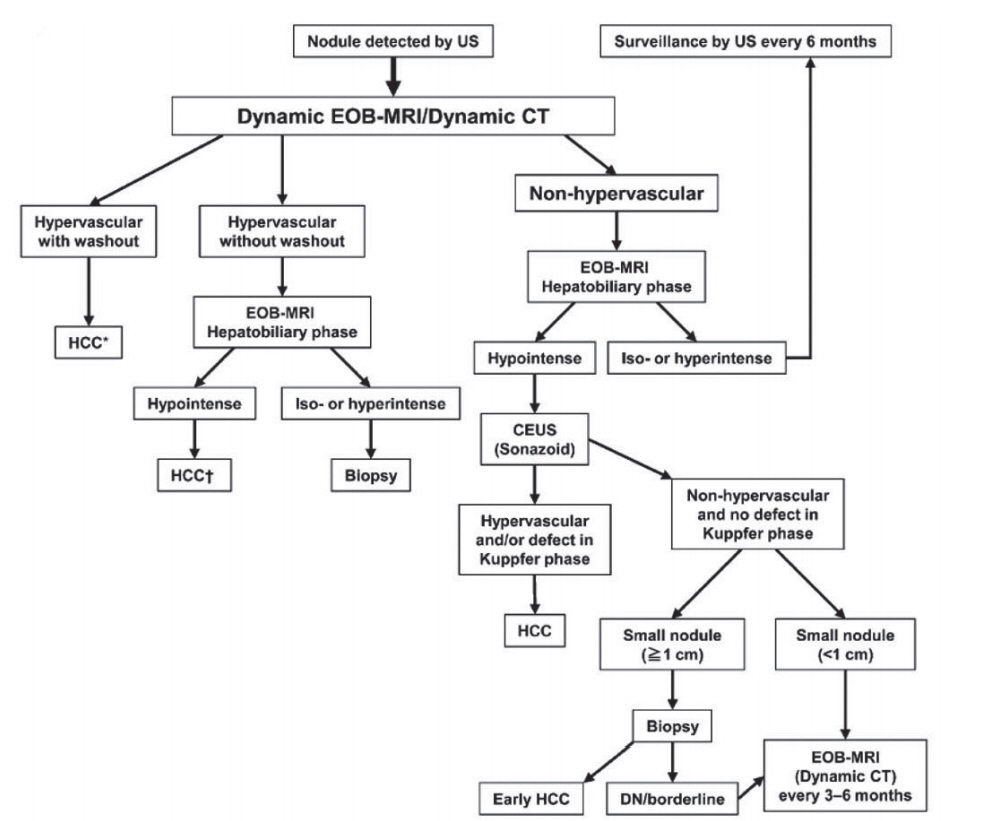
Figure 3.
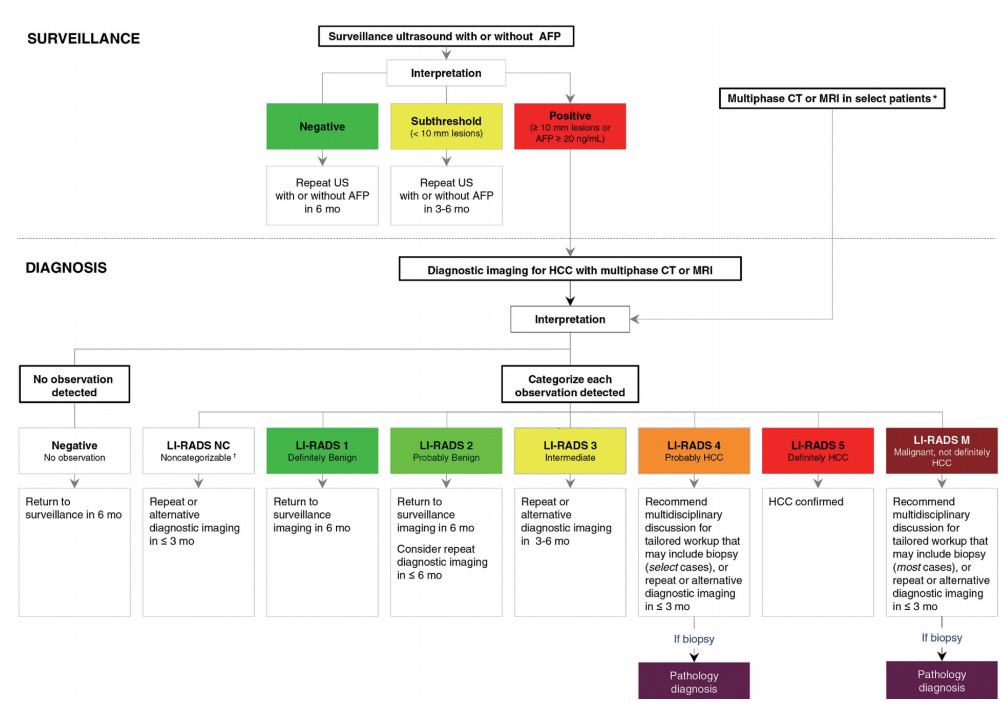
Figure 4.
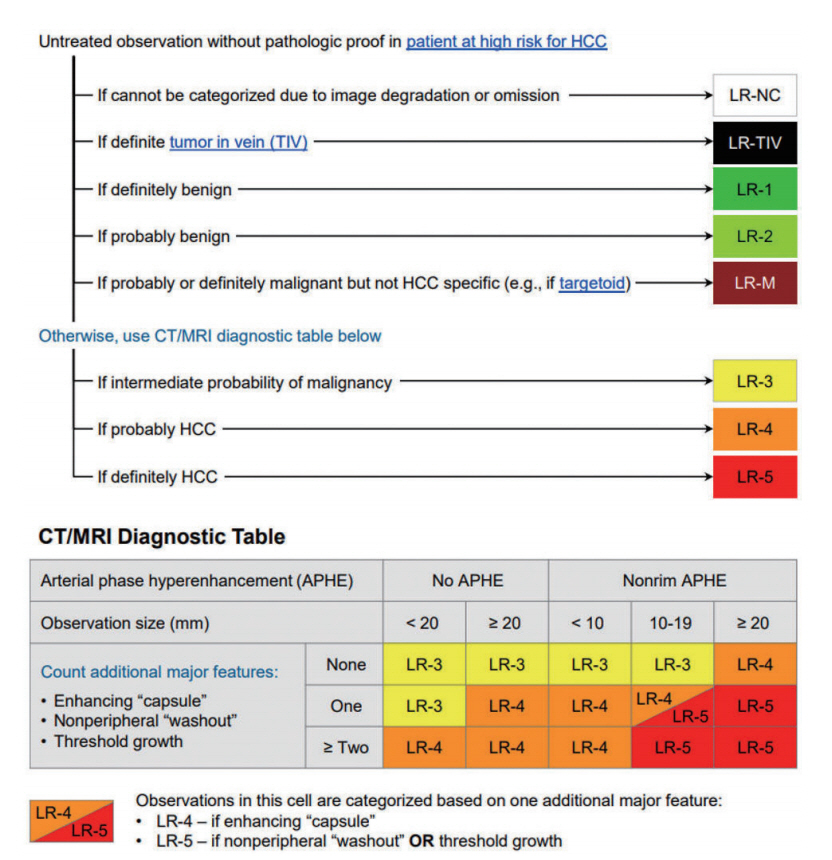
Figure 5.

Table 1.
| Organizations | KLCA-NCC 2018 [13] | APASL 2017 [8] | AASLD 2018 [11] | LI-RADS 2018 [10] | EASL 2018 [12] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target population for surveillance | âĒ Cirrhotic patients with varying etiology | âĒ Cirrhotic patients with varying etiology (HBV, HCV, NASH, genetic hemochromatosis, PBC, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency) | âĒ Cirrhotic patients with varying etiology (hepatitis B, hepatitis C, primary biliary cirrhosis, genetic hemochromatosis, alpha-1-antitrypsin) | âĒ Cirrhotic patients with any etiology | âĒ Cirrhotic patients, Child-Pugh stage A and B |
| âĒ Chronic HBV or HCV carrier | âĒ Noncirrhotic HBV carriers (Asian men >40 y, Asian women >50 y, African/North American blacks, family history of HCC) | âĒ Cirrhotic patients, Child- Pugh stage C awaiting liver transplantation | |||
| âĒ Non-cirrhotic HBV patients (Asian men >40 y, Asian women >50 y, Africans >20 y; family history of HCC) | âĒ Hepatitis B carriers (Asian men >40 y, Asian women > 50 y, all cirrhotic HBV carriers, family history of HCC, African/North American blacks) | âĒ Defers to regional HCC clinical practice guidelines for additional indications in the absence of cirrhosis | âĒ Non-cirrhotic HBV patients at intermediate or high risk of HCC | ||
| âĒ Non-cirrhotic patients with F3 fibrosis, regardless of etiology may be considered based on individual risk assessment | |||||
| Screening and surveillance test | âĒ Ultrasound and AFP measurements every 6 mo | âĒ Ultrasound and AFP measurements every 6 mo | âĒ Ultrasound with/without AFP every 6 mo | âĒ Ultrasound every 6 mo | âĒ Ultrasound every 6 mo |
| âĒ CT or MRI may be used in select patients with a high likelihood of having an inadequate ultrasound | âĒ CT or MRI may be utilized in select patients with a high likelihood of having an inadequate US or with performed but inadequate US | âĒ CT or MRI for patients on waiting list for liver transplantation and when obesity, intestinal gas, and chest wall deformity prevent adequate ultrasound assessment | |||
| âĒ Ultrasound <4 mo interval when a nodule of <1 cm has been detected during surveillance |
KLCA-NCC, Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center; APASL, Asian-Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver; AASLD, Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; LI-RADS, Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System; EASL, European Association for the Study of the Liver; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus; NASH, non alcoholic steatohepatitis; PBC, primary biliary cholangitis; y, years; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; AFP, alpha-fetoprotein; CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; US, ultrasonography; mo, months.
Table 2.
| Organizations | KLCA-NCC 2018 [13] | APASL 2017 [8] | AASLD 2018 [11] | LI-RADS 2018 [10] | EASL 2018 [12] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target population for diagnostic imaging | Patients at risk for HCC with âĨ1 cm nodule on screening/surveillance ultrasound | Patients at risk for HCC with positive screening/surveillance test or clinical suspicion of HCC | Patients at risk for HCC with abnormal results on screening/surveillance test or with clinical suspicions of HCC | âĒ Adult patients with cirrhosis of any cause except vascular disorder or congenital hepatic fibrosis | Patients at risk for HCC with âĨ1 cm nodule on screening/surveillance ultrasound | |||
| âĒ Patients with chronic hepatitis B with or without cirrhosis | ||||||||
| âĒ Patients with current or prior HCC with or without cirrhosis | ||||||||
| âĒ Adult liver transplantation candidates and liver transplant recipients | ||||||||
| Primary imaging modality | CT, MRI using ECCM or HBA | CT, MRI using ECCM or HBA | CT, MRI using ECCM or HBA | âĒ CT, MRI using ECCM or HBA | CT, MRI using ECCM or HBA | |||
| âĒ CEUS | ||||||||
| Secondary imaging modality | CEUS | CEUS (Sonazoid) | None | None | CEUS | |||
| Phases accepted for washout appearance | âĒ ECA: PVP or DP | âĒ ECA: PVP or DP | âĒ ECA: PVP or DP | âĒ ECA: PVP or DP | âĒ ECA: PVP or DP | |||
| âĒ HBA: PVP, DP or hypointensity on HBP | âĒ HBA: PVP | âĒ HBA: PVP | âĒ HBA: PVP | âĒ HBA: PVP | ||||
| Imaging criteria for arterial phase hyperenhancing HCC | âĒ Nodule size >1 cm | âĒ Regardless of size: | Defers to LI-RADS 5 category | âĒ Definitely HCC (LR-5) definition on CT/MRI: | âĒ Nodule size >1 cm | |||
| âĒ APHE and | âĒ APHE and | 1) Nodule size âĨ20 mm | âĒ APHE | |||||
| âĒ Washout | âĒ Washout on PVP or hypointensity on HBP | APHE and one or more of following: | âĒ Washout | |||||
| -Nonperipheral âwashoutâ | ||||||||
| -Enhancing capsule | ||||||||
| -Threshold growth | ||||||||
| 2) Nodule size 10-19 mm | ||||||||
| (1) APHE and | ||||||||
| -Nonperipheral âwashoutâ | ||||||||
| or | ||||||||
| -Threshold growth | ||||||||
| (2) APHE and two or more of the following: | ||||||||
| -Nonperipheral âwashoutâ | ||||||||
| -Enhancing capsule | ||||||||
| -Threshold growth | ||||||||
| âĒ Definitely HCC (LR-5) definition on CEUS: | ||||||||
| -Nodule size âĨ10 mm | ||||||||
| -APHE and | ||||||||
| -Late (>60 s) and mild washout | ||||||||
| Imaging criteria for arterial phase hypo- or isoenhancing HCC | None | Yes | None | None | None | |||
| Imaging criteria for arterial phase hypo- or isoenhancing PROBABLE HCC | Yes | None (but definite HCC diagnosis is possible) | Yes | Yes | None | |||
| Imaging criteria for subcentimeter size HCC | None | Yes | None | None | None | |||
| Exclusion criteria | Yes | None | None | None | None | |||
| When HBA is used, | ||||||||
| -T2 bright SI | ||||||||
| -Targetoid appearance in the DWI orCE-T1WI | ||||||||
| Imaging criteria for HCC tumor in vein | None | None | None | LR-TIV (unequivocal enhancing soft tissue TIV, regardless of visualization of a parenchymal mass) | None | |||
| Ancillary features | Yes | None | Yes | Yes | None | |||
| -To diagnose PROBABLE HCC | -Upgrading (up to LR-4) | |||||||
| -Downgrading | ||||||||
| Categories | âĒ Arterial hyperenhancing HCC | âĒ Arterial hyperenhancing HCC | âĒ Definitely benign (LR-1) | âĒ Definitely benign (LR-1) | Arterial hyperenhancing HCC | |||
| âĒ Probably benign (LR-2) | âĒ Probably benign (LR-2) | |||||||
| âĒ PROBABLE HCC | âĒ Arterial hypo- isoenhancing HCC | âĒ Intermediate (LR-3) | âĒ Intermediate probability of malignancy (LR-3) | |||||
| âĒ Probably HCC (LR-4) | âĒ Probably HCC (LR-4) | |||||||
| âĒ Definitely HCC (LR-5) | âĒ Definitely HCC (LR-5) | |||||||
| âĒ Malignant, not definitely HCC (LR-M) | âĒ Definite tumor in vein (LR-TIV) | |||||||
| âĒ Probably or definitely malignant but not HCC specific (LR-M) | ||||||||
| Staging | mUICC | Do not specify any staging system (multidisciplinary discussion is required) | BCLC | Radiologic T-staging | BCLC | |||
KLCA-NCC, Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center; APASL, Asian-Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver; AASLD, Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; LI-RADS, Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System; EASL, European Association for the Study of the Liver; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; ECCM, extracellular contrast media; HBA, hepatobiliary contrast agent; CEUS, contrast enhanced ultrasound; ECA, extracellular contrast agents; PVP, portal venous phase; DP, delayed phase; HBP, hepatobiliary phase; APHE, arterial phase hyperenhancement; SI, signal intensity; DWI, diffusion weighted image; CE, contrast enhance; TIV, tumor in vein; mUICC, Modified Union for International Cancer Control; BCLC, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer.
Abbreviations
REFERENCES
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- ORCID iDs
-
Jeong Min Lee

https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0561-8777 - Related articles
-
The prime time for management of hepatocellular carcinoma in Hong Kong2023 April;29(2)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



