| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 23(4); 2017 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has been an emerging major health problem, and the most common cause of chronic liver disease in Western countries. Traditionally, liver biopsy has been gold standard method for quantification of hepatic steatosis. However, its invasive nature with potential complication as well as measurement variability are major problem. Thus, various imaging studies have been used for evaluation of hepatic steatosis. Ultrasonography provides fairly good accuracy to detect moderate-to-severe degree hepatic steatosis, but limited accuracy for mild steatosis. Operator-dependency and subjective/qualitative nature of examination are another major drawbacks of ultrasonography. Computed tomography can be considered as an unsuitable imaging modality for evaluation of NAFLD due to potential risk of radiation exposure and limited accuracy in detecting mild steatosis. Both magnetic resonance spectroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging using chemical shift technique provide highly accurate and reproducible diagnostic performance for evaluating NAFLD, and therefore, have been used in many clinical trials as a non-invasive reference of standard method.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is defined as the excessive and abnormal intracellular accumulation of lipid in the liver, primarily in the form of triglycerides [1,2]. NAFLD is a broad spectrum of disease, ranging from simple steatosis to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is characterized by hepatocyte injury, inflammation, and can further progress into more advanced stage of fibrosis/cirrhosis. NASH also increases the risk of liver cancer development as well as death from cardiovascular disease [3-5]. In addition, when NAFLD is not adequately managed, end-stage liver disease as well as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can eventually be developed, and therefore, liver transplantation might be needed for treatment [6-8]. Currently, NAFLD has been the most common cause of chronic liver disease, especially in Western countries, and the estimated prevalence of NAFLD is approximately 30% in the general population [9,10]. NAFLD has been known to be strongly associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia and hypertension, all of that are characteristics of metabolic syndrome, and is considered as hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome nowadays [11-14]. Therefore, NAFLD can be regarded as an emerging major health problem, and early detection and quantitative evaluation of this disease are of crucial importance as early stage of NAFLD is a reversible process, and adequate management of NAFLD in early stage can prevent from progression into more advanced stages including cirrhosis.
Traditionally, liver biopsy has been the gold standard method for the diagnosis and quantification of hepatic steatosis, and the only reliable method for differentiating NASH from simple steatosis [15,16]. However, liver biopsy is an invasive procedure with its own complication such as bleeding as well as procedure related mortality although the morality rate associated with liver biopsy is quite low. Small sample volume of liver parenchyma and reproducibility of assessment among the different pathologists could be another limitation of liver biopsy. Moreover, due to the invasive nature and its potential complication, repeated liver biopsy for monitoring of NAFLD can hardly be possible during the disease course. Therefore, there has been an urgent need to develop reliable non-invasive method for quantitative assessment of NAFLD. Currently, various imaging modalities including ultrasonography (US), computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) have been used to evaluate NAFLD, and each imaging modality has its own pros and cons. In this review, currently used imaging modalities to evaluate NAFLD will be discussed, especially focused on the quantification.
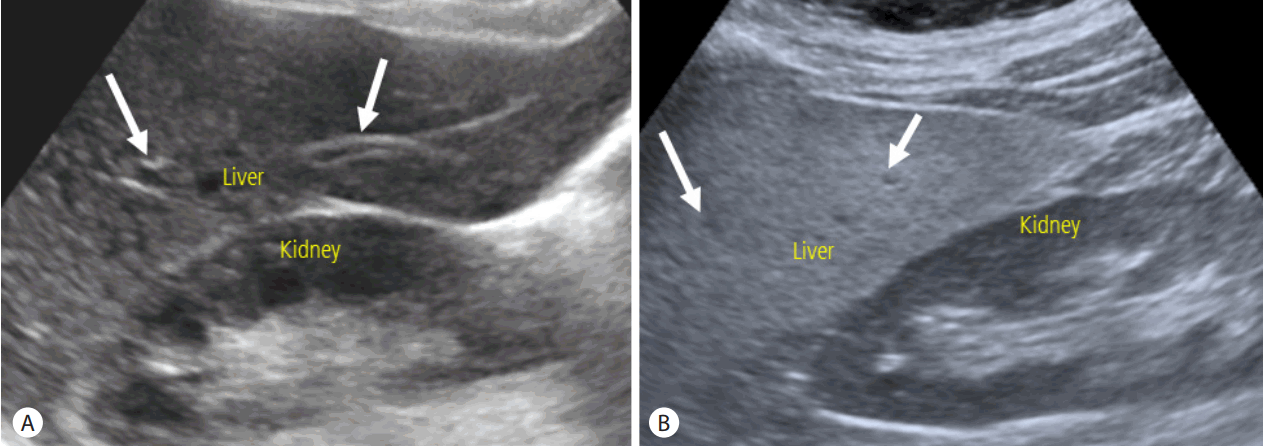
US has several merits over other imaging modalities including CT and MR: US is widely available, and there is no need of radiation exposure in doing US examination. Therefore, US has been widely used as primary imaging modality for the evaluation of liver disease. Evaluation of hepatic steatosis using US is based on the echo change in hepatic parenchyma. As intracellular accumulation of fat vacuoles reflect the ultrasound beam, hepatic steatosis appears as a diffuse increased hepatic parenchymal echogenicity, or ŌĆ£bright liverŌĆØ on US [16]. When liver parenchymal echogenicity is higher than kidney cortex echogenicity, hepatic steatosis is suspected. The assessment of hepatic steatosis using US is typically qualitative nature, and degree of hepatic steatosis is usually determined by the result of visual assessment of hepatic parenchymal echogenicity comparing to the kidney cortex echo, assessment of the degree of ultrasound beam penetration into the deep portion of the liver, and the clarity of blood vessel wall structures in the liver (Fig. 1). The degree of hepatic steatosis is usually graded using four-point scale: normal (grade 0), mild (grade 1), moderate (grade 2) and severe (grade 3) [17-19]. The diagnostic accuracy of US in detecting hepatic steatosis has varied among the different studies, and depends on the exact definition of hepatic steatosis. The presence of concomitant chronic liver disease and fibrosis can also affect the diagnostic performance of US to detect hepatic steatosis, as hepatic fibrosis might also increase the hepatic parenchymal echogenicity [16,20]. US can provides a fair accuracy of detecting the moderate to severe hepatic steatosis (i.e., equal to or more than grade 2 steatosis) with reported sensitivity of about 90% and specificity of about 95% for patients without concomitant chronic liver disease [17,18]. However, regarding the all degree of hepatic steatosis including mild degree, US is not an accurate diagnostic method, and the reported sensitivity and specificity for detecting mild degree hepatic steatosis were ranged from 55.3% to 66.6%, and 77.0% to 93.1%, respectively [18,19,21,22]. Limited diagnostic accuracy for detecting mild degree hepatic steatosis is one of main limitation of US for the evaluation of NAFLD. In addition to limited diagnostic accuracy of detecting mild degree steatosis, qualitative assessment and subjective nature of examination with substantial intra- and inter-observer variability are another major drawbacks of US. The reported intra- and inter-observer agreement were 54.7-67.9% and 47.0-63.7%, respectively, when evaluating the degree of hepatic steatosis with the use of four-point visual grading scale [23]. In addition, the current fourpoint grading scale system might be too simplistic for quantification of hepatic steatosis even though this grading system is currently the most widely used system to evaluate hepatic steatosis in clinical practice.
To overcome aforementioned limitations of US and improve the diagnostic accuracy for evaluating hepatic steatosis, several amendments of US technique have been developed and introduced. One of these amendments is computer-assisted quantitative analysis of ultrasound beam echo amplitude, attenuation and/or texture information [24,25]. Among them, computerized calculation of hepatorenal ratio which is defined as the ratio of the echo intensities of the liver parenchyma and renal cortex has been suggested an accurate method for quantification of hepatic steatosis with the reported accuracy above 90% [26-28]. However, whether hepatorenal ratio is sufficient for the quantitative assessment of hepatic steatosis still remains questionable [29], and several studies have been reported that additional process such as standardization or artificial neural network would be needed to obtain sufficient diagnostic accuracy of the hepatorenal ratio for the quantification of hepatic steatosis [28,30]. In addition, post-processing step after acquisition of US images is inevitably needed to obtain the value of hepatorenal ratio. Recently, acoustic structure quantification (ASQ) which analyses echo amplitude of ultrasound beam and evaluates changes in variance within region of interests has been introduced in clinical practice, and used for the evaluation of diffuse liver disease. Several initial studies using ASQ reported very promising diagnostic accuracy for assessing hepatic steatosis quantitatively both animal and human studies [29,31-33]. However, further studies with large number of patients and prospective design are warranted to validate computer-assisted quantitative analysis of US including hepatorenal ratio and ASQ as a sufficient tool for quantification of hepatic steatosis.
Another recently developed ultrasound based quantification tool for hepatic steatosis is controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) obtained from transient elastography (Fibroscan, Echosens, Paris, France). CAP assesses the degree of ultrasound beam attenuation by the intracellular fat vacuoles at the center frequency of M probe (3.5 MHz), and results are appeared as decibels per meter (dB/m), ranging from 100 to 400 dB/m [34]. After a preliminary study done by Sasso et al. reporting the area under the ROCs (AUROCs) of 0.91, 0.95 and 0.89 for detecting mild, moderate and severe degree steatosis, respectively, with the use of liver biopsy as reference of standard [35], many studies have reported promising accuracy of CAP to evaluate hepatic steatosis quantitatively [34,36-38]. Indeed, a recent meta-analysis has shown AUROCs of 0.85, 0.88, and 0.87 for detecting mild, moderate, and severe degree steatosis, respectively [39]. One of major limitation of CAP could be failure of examination. According to recent studies, failure to obtain CAP value has seen in 6.2-7.7% of cases [38,40], and larger skin capsular distance could be a significant affecting factor for obtaining CAP value [41]. Considering NAFLD is usually associated with obesity as a manifestation of metabolic syndrome, failure to obtain CAP values in obese patients could be an important limitation of this technique.
In summary, US has been used for screening of NAFLD in patients at risk as US is widely available, and there is no need of radiation exposure. Indeed, US can provide fairly good diagnostic accuracy for detecting moderate to severe degree hepatic steatosis. However, limited accuracy for detecting mild degree hepatic steatosis and qualitative, subjective nature of examination with intra-, inter-observer variability are major drawbacks of US. To overcome these limitations, several quantitative parameters obtained from US examination including hepatorenal ratio, ASQ and CAP have been developed, and reported promising results. However, these newly developed quantitative US techniques require further clinical validation.
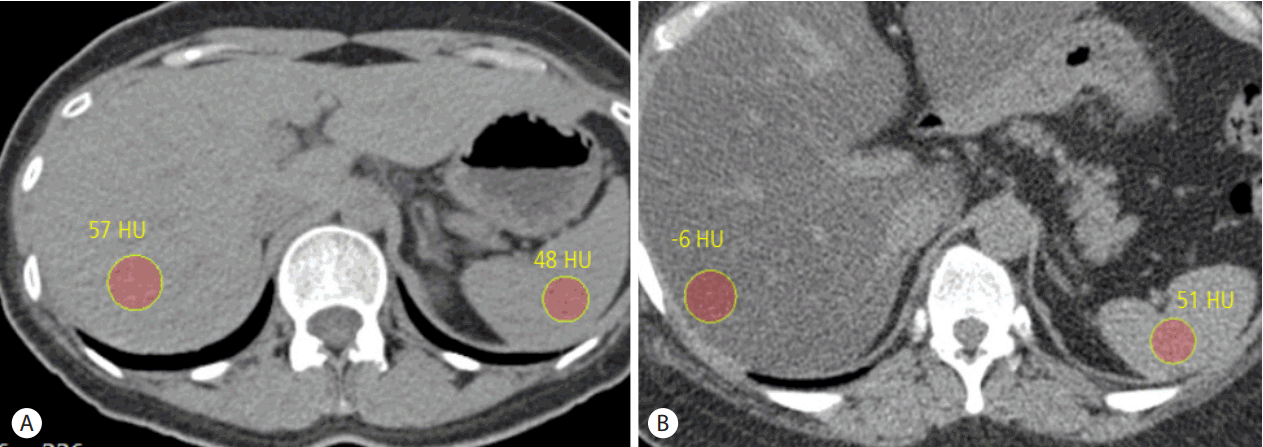
Assessment of hepatic steatosis using CT is based on the measurement of attenuation value of liver parenchyma, expressed as Hounsfield units (HU). Because attenuation value of fat, usually about -100 HU, is much lower than that of soft tissue usually about 30-40 HU, attenuation value of liver parenchyma decreases as hepatic steatosis develops and progresses. Even though several studies reported that contrast enhanced portal venous CT images could be used for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis providing comparable diagnostic accuracy to unenhanced CT scan [42,43], it would be better to use unenhanced CT scan to assess hepatic steatosis as different injection protocol and scan delay can affect attenuation value of liver parenchyma after contrast injection. The measured absolute attenuation value of liver parenchyma on unenhanced CT scan has been known to show a strong correlation with the degree of hepatic steatosis seen on histopathologic examination. However, different CT scanners from different vendors as well as different reconstruction algorithm can affect the absolute attenuation value of liver parenchyma on unenhanced CT scan, and therefore, simple measurement of attenuation value of liver parenchyma on unenhanced CT scan has not been widely used for the assessment of hepatic steatosis [44,45]. Instead of absolute attenuation value of liver parenchyma on unenhanced CT scan, attenuation difference between liver and spleen (CTL-S) on unenhanced CT scan has been the most commonly used quantitative parameter to evaluate hepatic steatosis as potential errors in attenuation value measurement from different CT scanners and different reconstruction algorithm can be avoided by using spleen attenuation as an internal control [16] (Fig. 2). Generally, attenuation value of normal liver parenchyma on unenhanced CT scan is slightly higher than that of spleen. As hepatic steatosis progresses, attenuation value of liver parenchyma decreases, and therefore, CTL-S also decreases. CTL-S has been known to provide fairly accurate diagnostic performance to detect moderate to severe degree hepatic steatosis, and the reported specificity and sensitivity were 100% and 82%, respectively, when cut-off value of CTL-S to detect moderate to severe degree hepatic steatosis was set at -9 [18]. The cut-off CTL-S value to detect moderate to severe degree hepatic steatosis has been varied among the different studies, but is usually around the -10. However, regarding the detection of mild degree hepatic steatosis, CTL-S is not an accurate method, and the limited diagnostic accuracy for detecting mild degree hepatic steatosis is one of major drawback of CT, together with the use of radiation. Beside hepatic steatosis, several factors can also affect the attenuation value of liver parenchyma on unenhanced CT scan. Presence of excessive iron in liver parenchyma in cases of hemochromatosis or hemosiderosis increases the attenuation value of liver parenchyma on unenhanced CT scan. Ingestion of several drugs including amiodarone which contains iodine and accumulates in the liver can also increase the attenuation value of liver parenchyma on unenhanced CT scan [45-47].
Dual energy CT (DECT) which uses two different energy levels can differentiate among several chemical compositions including fat within the tissues, and therefore, has a potential to provide better diagnostic performance to detect hepatic steatosis compared to conventional single energy CT. However, an animal study using DECT reported similar diagnostic performance of DECT to detect hepatic steatosis to that of single energy CT, and failed to prove theoretical advantage of DECT for evaluating hepatic steatosis [48]. Indeed, a human study using DECT for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis reported similar result [49].
Owing to the limited accuracy of CT to detect mild degree hepatic steatosis and to the potential hazard of radiation exposure, CT can be regarded as an unsuitable imaging modality for the evaluation of NAFLD. However, CT may be useful for assessing hepatic steatosis in specific clinical situation. One of these situations is the evaluation for living liver donor candidate. The high spatial resolution of CT is inevitably needed to evaluate donor hepatic vascular anatomy including hepatic artery, portal vein and hepatic vein after contrast injection. In this situation, addition of unenhanced CT scan before contrast injection can successfully be used to detect moderate to severe degree hepatic steatosis, excluding the patient as potential liver donor candidate [47,50,51].
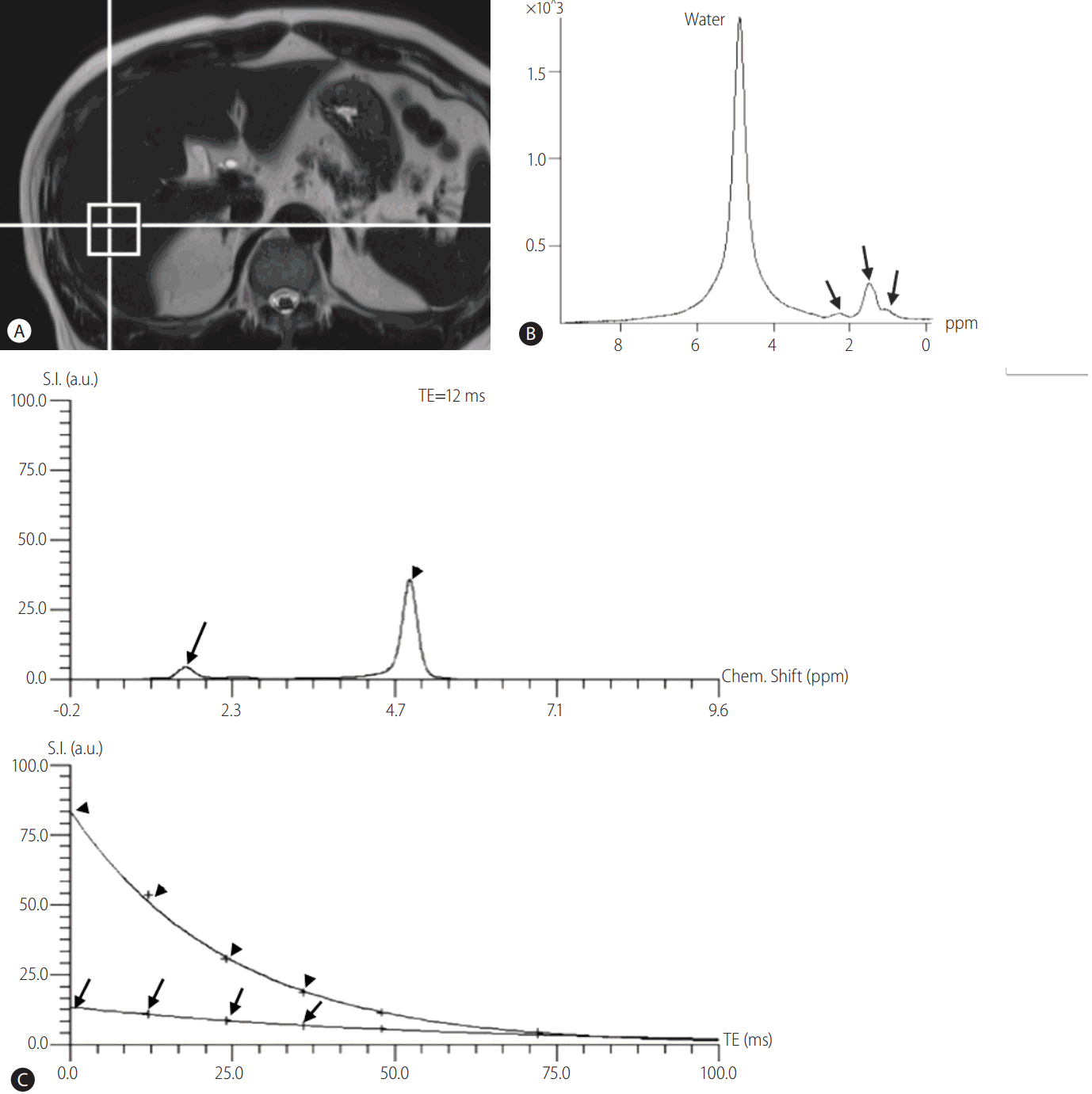
MRS can directly measure the chemical composition within tissue based on the frequency composition of the signal originated from the voxel of interest [52-54]. For the evaluation of hepatic steatosis, proton (1H) MRS has been the most commonly used method, and 1H-MRS (hereafter, MRS) measures proton signals and displays multiple peaks at different locations according to the chemical composition of protons in their corresponding frequency domains (Fig. 3) [16]. Regarding the liver parenchyma, most of protons are contained in the water and fat, and therefore, most of identifiable peaks on MRS of the liver are originated from water and fat protons. Water proton peak appears as a single peak at 4.7 ppm, and fat protons as multiple peaks owing to the various chemical bonds between the protons and adjacent atoms in fat (Fig. 3). Thus, fat detection using MRS is straightforward in principle, and requires only the detection of spectral peaks at certain frequencies corresponding to the protons in fat [54]. The signal intensities of fat and water peaks arising from voxel of interest can directly be measured by the spectral tracing of each peak, and thereby, proton density fat fraction (PDFF) can be calculated as the ratio of the sum of the signal intensities derived from the protons in fat divided by the sum of the signal intensities originated from the protons in both fat and water [16]. For the quantification of hepatic steatosis, MRS data are usually obtained from a single voxel, typically 2 cm x 2 cm x 2 cm to 3 cm x 3 cm x 3 cm in size, manually placed in the liver parenchyma usually right posterior segment of the liver, after the acquisition of 3-plane localizing images (Fig. 3). Shimming process is mandatory to obtain a homogenous magnetic field across the voxel, which enables more accurate measurement of signal intensities from water and fat protons, and inevitably needs some times. As MRS for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis measures signals from abundant protons in water and fat within the liver tissue, the signals intensities from water and fat protons in the liver are usually large, and therefore, MRS acquisition of the liver can successfully be done with a single acquisition [54]. As single acquisition of MRS of the liver can be obtained in a short time during a single breath-hold, problems arising from respiratory motion can effectively be avoided, and this single breath-hold MRS for the liver has been the preferred method for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis nowadays in clinical practice [55-57]. Even though the principle of MRS to quantify hepatic steatosis is straightforward, there have also been biases in MRS acquisition. T1 and T2-relaxation effects are well known biases of MRS to evaluate hepatic steatosis. To overcome and minimize T1-relaxation effect, a long repetition time (TR) can be used. In addition, multi-echo MRS can correct T2 relaxation effect by using the multiple data obtained from different echo times (TE), and are typically acquired within a single breath-hold [58,59]. These advances in MRS technology enable more accurate quantification of hepatic steatosis.
There have been many studies reporting the excellent diagnostic performance of MRS to detect and grade the hepatic steatosis [55,60-62]. Regarding the detection of mild degree steatosis which is a limitation for both US and CT, reported MRS sensitivities and specificities were 80.0-91.0% and 80.2-87.0%, respectively, and outperformed CT and US [18,19]. MRS can also provide excellent reproducibility of measurement, and changes in the standard deviation of PDFF values over repeated measurement were less than 1% for MRS [63]. Even though histopathologic examination has been considered as gold standard method to diagnose and quantify hepatic steatosis, several studies assessing the accurate fat content in the liver samples by using either biochemical lipid assays or computerized analysis of microscopic images showed that PDFF obtained from MRS was better correlated with actual fat content, compared to the histopathologic assessment of hepatic steatosis done by pathologists [64-66]. In addition, contrast to the MRS which can provide excellent measurement reproducibility, subjective nature with large intra- and inter-observer variability of histopathologic examination among the different pathologists could be another major problem of liver biopsy in the quantitative evaluation of hepatic steatosis, along with the invasive nature and potential of complications [67]. Therefore, MRS has been considered as an alternative reference of standard method to liver biopsy for diagnosing and grading hepatic steatosis, and has been used in many clinical trial needing the quantitative assessment of hepatic steatosis [68-71]. In addition, several studies reported that PDFF obtained from MRS could reflect efficacy of therapeutic interventions for patients with NAFLD, and might be used as an imaging biomarker to evaluate the changes in amount of fat in the liver [69,72,73]. One of major limitation of MRS is small sample volume, usually less than 3 cm x 3cm x 3cm in size, and this small sample volume may be problematic in patients with uneven fatty change.
In summary, MRS has straightforward principle to measure hepatic steatosis, and therefore, provides excellent diagnostic performance for quantitative assessment of hepatic steatosis with high reproducibility of measurement. In addition, MRS is non-invasive method, and there is no need of radiation exposure. Therefore, currently, MRS has been regarded as non-invasive reference of standard method to diagnose and quantify hepatic steatosis.
Several different methods have been developed and introduced in MRI for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis: chemical-shift imaging (CSI); spectral fat saturation; and fat-selective excitation approaches [74,75]. Among them, CSI has been the most widely used method for evaluation of hepatic steatosis using MRI due to its easy applicability as well as to higher accuracy compared to other techniques. In contrast to MRS which can directly measure signal intensities from the certain chemical composition within tissue including protons in water and fat at the corresponding locations on frequency domains, MRI shows the signal intensity as the vector sum of all signals from all kind of chemical compositions in an image pixel, including protons in water and fat [16]. As most of protons in the liver tissue are contained in water and fat, most of signal intensities from the liver appeared on MRI are originated from protons in water and fat. Chemical shift refers to the difference in resonance frequency between two proton signals, expressed in parts per million (ppm) of the resonance frequency of the static magnetic field B0 [54]. In MRI examination, protons in both water and fat are excited after the application of non-selective radiofrequency pulse, and generate signal intensity used for making image. However, the protons in water precess faster than the protons in fat by about 3.5 ppm [54]. Therefore, the protons in fat and water oscillate with regular interval and are positioned in opposed phase (OP) or in phase (IP) at certain TEs [16], and CSI uses this resonance frequency difference between protons in water and fat to separate signals originated from protons in fat from that originated from protons in water. Field strength affects value of TEs for OP and IP. For example, at 1.5 T MR unit, TE for first OP and IP is 2.3 milliseconds (ms) and 4.6 ms, respectively, and repeats at multiples of 4.6 ms after their first occurrence [16]. At IP, signals from protons in fat add to the signals from protons in water. However, at OP, signals from protons in fat are subtracted from the signal from protons in water. Therefore, the amount of signal intensity from protons in fat can be calculated by using the difference between signal intensity in IP and that in OP (Fig. 4). After Dixon firstly described this approach [76], dual echo CSI technique which uses a pair of OP and IP images has been widely used for quantitative assessment of hepatic steatosis in clinical practice. However, there are several biases in dual echo CSI technique for the quantification of hepatic steatosis which can results in measurement error, and T1- and T2*-relaxation effects are well known biases for quantification of hepatic steatosis using dual echo CSI. T1 relaxation time of proton in water is different from that of proton in fat, and this difference in T1 relaxation time between water proton and fat proton can affect the signal intensity of IP and OP images, in addition to proton densities of fat and water. The use of low flip angle can minimize T1 relaxation effect, and enables more accurate quantification of hepatic steatosis using CSI. As value of TEs for IP is longer than that for OP, T2*-related signal decay during the interval of OP and IP also affects the difference in signal intensity between OP and IP, leading to inaccurate quantification of hepatic steatosis, especially in the presence of iron in the liver which markedly enhances T2*-related decay [77,78]. To overcome T2*-relaxation effects, multiple echo acquisitions method usually using six echoes to correct T2*-related signal decay during the multiple OP and IP has been developed and introduced. In addition, this multiple echo approach can also be used for the calculation of T2* time of the liver which has been known to be correlated with the total liver iron content. These T1-independent, T2*-corrected multi-echo CSI enables unbiased fat quantification, and has been the most widely used MRI method for the quantification of hepatic steatosis [59,63,79,80]. Recently, an algorithm for accurate fat spectral modeling method which can reflect complex composition of protons in fat has been developed and implemented in the T1-independent T2*-corrected multi-echo CSI technique. This spectral fat modeling is based on the complex chemical composition of fat protons showing multiple peaks with slightly different resonance frequencies, and the signal intensities on OP and IP images are calculated from the signal interferences among the water proton and protons in multiple fat peaks. As this spectral fat modeling can reflect actual complex chemical composition of fat protons for obtaining accurate signal intensity from fat and water protons, more precise fat quantification can be possible. After the introduction of CSI technique in MRI for the quantification of hepatic steatosis, many of studies to validate this technique have been performed. For this validation studies, MRS has usually been chosen as the reference of standard method to diagnose and quantify hepatic steatosis as MRS estimates the PDFF by direct measuring the signal intensities from fat protons and water protons, whereas CSI technique calculates the PDFF indirectly from the signal intensity difference between OP and IP resulting from signal interference between water and fat proton, and therefore, MRS has been regarded as more accurate method for hepatic fat quantification than CSI. The results of validation studies have shown that PDFF calculated from T1-independent, T2*-corrected multi-echo CSI with spectral fat modeling algorithms showed the most perfect agreement with the estimated PDFF using MRS [56,81-83]. When compared to MRS, CSI technique has a potential merit for hepatic fat quantification. CSI technique can cover the entire liver, and therefore, CSI derived PDFF might accurately reflect the exact degree of hepatic steatosis even in case of uneven fatty change which is potential limitation of MRS having small sample volume. Potential limitation of CSI is dynamic range of PDFF. As CSI techniques utilize only the signal intensity information on OP and IP image without phase information, they cannot differentiate fat-dominant tissue from water-dominant tissue. For example, signal intensities of OP and IP images are actually almost the same for tissues containing 20% and 80% fat, as absolute value of signal difference in these two tissues with difference fat content is the same. Therefore, the dynamic range of CSI-derived PDFF is ranged from 0% to 50%. However, in human liver tissue, it is hardly possible to contain more than 50% of fat protons compared to total protons, and thus this potential limitation of CSI technique might not be problematic in routine clinical practice.
NAFLD having potential to progress into more advanced stage of fibrosis/cirrhosis has been the most common cause of chronic liver disease in Western counties, and the incidence of NAFLD has been known to be increasing. NAFLD is strongly associated with metabolic syndrome characterized by concomitant existence of obesity, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia and hypertension. Therefore, NAFLD can be considered as emerging major health problem. Traditionally, liver biopsy with histopathologic examination has been the gold standard method to diagnose and quantify hepatic steatosis. However, invasive nature with potential complication, small sample volume of biopsy specimen as well as high variability in measurement among the pathologists are major drawbacks of liver biopsy, and therefore, liver biopsy cannot be widely used for the evaluation of NAFLD. US which is widely available non-invasive imaging modality with no need of radiation exposure has been used for the screening of NAFLD for patients at risk, providing fairly good diagnostic accuracy to detect moderate to severe degree hepatic steatosis. However, limited diagnostic performances to detect mild degree hepatic steatosis and subjective nature examination with high intra- and inter-observer variability are major limitations of US. To overcome these limitations, several quantitative method using US images including hepatorenal ratio, ASQ and CAP have been implemented, showing promising results. However, these newly developed US quantitative methods require further clinical validation. Unenhanced CT scan can confidently detect moderate to severe degree hepatic steatosis. However, owing to potential risk of ionized radiation and to the limited accuracy to detect mild degree hepatic steatosis, CT can be considered as an unsuitable imaging modality for the evaluation of NAFLD, except specific clinical situation such as evaluation of living liver donor candidate. MRS and T1-independent, T2*-corrected multi-echo CSI with spectral fat modeling algorithms of MRI provide the PDFF, and both MRS and T2*-corrected multi-echo CSI with spectral fat modeling algorithms derived PDFF are highly accurate and reproducible for diagnosis and quantification of hepatic steatosis. Therefore, both MRS and T1-independent, T2*-corrected multi-echo CSI with spectral fat modeling algorithms of MRI have been considered as alternative reference of standard method for quantification of hepatic steatosis to liver biopsy, and many of clinical trials requiring quantitative assessment of hepatic steatosis use MRS and MRI based fat quantification method nowadays. However, limited availability of MR unit, especially compared to US, high cost of examination might be potential limitation of MRS and MRI based fat quantification method. Therefore, both physicians and radiologists managing the NAFLD patients should know the pros and cons of each imaging modality for quantitative evaluation of NAFLD, and select proper method for each patient.
Figure┬Ā1.
Evaluation of hepatic steatosis using US. (A) In normal liver, liver parenchymal echogenicity is similar to kidney cortex echogenicity. Wall of portal vein (arrows) are also well visualized. (B) In the presence of hepatic steatosis, liver parenchymal echogenicity increases compared to kidney cortex echogenicity. Wall of portal vein (arrows) are obscured owing to the increased parenchymal echogenicity. US, ultrasonography.
Figure┬Ā2.
Evaluation of hepatic steatosis using unenhanced CT scan. (A) Unenhanced transverse CT scan of normal liver shows attenuation value of liver parenchyma is 57 HU, slightly higher than that of spleen parenchyma of 48 HU. Calculated CTL-S is 9. (B) Unenhanced transverse CT scan of fatty liver shows attenuation value of liver parenchyma is -6 HU, lower than that of spleen parenchyma of 51 HU. Calculated CTL-S is -57, indicating the presence of moderate to severe degree hepatic steatosis. CT, computed tomography.
Figure┬Ā3.
Evaluation of hepatic steatosis using MRS. (a) After the acquisition of localizing images, a 2 cm ├Ś 2 cm ├Ś 2 cm sized voxel is placed on liver right posterior segment parenchyma. (b) Representative spectrums of water and fat. Water peak appears as single large peak at 4.7 ppm on frequency domain, whereas fat peaks appear as multiple peaks around the 1.3 ppm (arrows). (c) Multi-echo MRS for quantification of hepatic steatosis. Top: representative spectrum of MRS for echo time (TE) of 12 msec. Arrow indicates fat peaks around the 1.3 ppm and arrow head indicates water peak at 4.7 ppm. Bottom: plot of echo time versus signal intensity for water and fat protons extrapolated from top graph to echo time of 0 msec. Arrow indicates extrapolated line for fat and arrow head indicates extrapolated line for water. Using this extrapolation with the multi-echo MRS data, proton density fat fraction can accurately be calculated. MRS, magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Figure┬Ā4.
Evaluation of hepatic steatosis using dual echo chemical shift imaging of MRI. (a) At opposed phase (OP), water protons and fat protons are placed in opposite direction, and therefore, measured signal intensity at OP is the absolute value of difference between signal intensity from water protons and that from fat protons. (b) At in phase (IP), water protons and fat protons are placed in the same direction, and therefore, measured signal intensity at IP is the sum of signal intensity from water protons and fat protons. Using the signal intensity difference between OP and IP, signal intensity from fat protons can be calculated, and thus proton density fat fraction can be estimated. MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.

Abbreviations
ASQ
acoustic structure quantification
AUROCs
area under the ROCs
CSI
chemical-shift imaging
CT
computed tomography
CAP
controlled attenuation parameter
DECT
Dual energy CT
HU
Hounsfield units
IP
in phase
MRI
magnetic resonance imaging
MRS
magnetic resonance spectroscopy
ms
milliseconds
NAFLD
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
NASH
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
OP
opposed phase
PDFF
proton density fat fraction
TE
echo times
US
ultrasonography
REFERENCES
2. Adams LA, Lymp JF, St Sauver J, Sanderson SO, Lindor KD, Feldstein A, et al. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology 2005;129:113-121.


3. Adams LA, Sanderson S, Lindor KD, Angulo P. The histological course of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a longitudinal study of 103 patients with sequential liver biopsies. J Hepatol 2005;42:132-138.


4. Ekstedt M, Franz├®n LE, Mathiesen UL, Thorelius L, Holmqvist M, Bodemar G, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with NAFLD and elevated liver enzymes. Hepatology 2006;44:865-873.


5. Ascha MS, Hanouneh IA, Lopez R, Tamimi TA, Feldstein AF, Zein NN. The incidence and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010;51:1972-1978.


6. Sanyal AJ. American Gastroenterological A. AGA technical review on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2002;123:1705-1725.


7. Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005;41:1313-1321.


8. Farrell GC, Larter CZ. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology 2006;43(2 Suppl 1):S99-S112.


9. Bellentani S, Bedogni G, Miglioli L, Tiribelli C. The epidemiology of fatty liver. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004;16:1087-1093.


10. Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC, et al. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology 2004;40:1387-1395.


11. de Alwis NM, Day CP. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the mist gradually clears. J Hepatol 2008;48(Suppl 1):S104-S112.


12. Korenblat KM, Fabbrini E, Mohammed BS, Klein S. Liver, muscle, and adipose tissue insulin action is directly related to intrahepatic triglyceride content in obese subjects. Gastroenterology 2008;134:1369-1375.



13. Adams LA, Waters OR, Knuiman MW, Elliott RR, Olynyk JK. NAFLD as a risk factor for the development of diabetes and the metabolic syndrome: an eleven-year follow-up study. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:861-867.


14. Schwenzer NF, Springer F, Schraml C, Stefan N, Machann J, Schick F. Non-invasive assessment and quantification of liver steatosis by ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance. J Hepatol 2009;51:433-445.


16. Lee SS, Park SH. Radiologic evaluation of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:7392-7402.



17. Saadeh S, Younossi ZM, Remer EM, Gramlich T, Ong JP, Hurley M, et al. The utility of radiological imaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2002;123:745-750.


18. Lee SS, Park SH, Kim HJ, Kim SY, Kim MY, Kim DY, et al. Non-invasive assessment of hepatic steatosis: prospective comparison of the accuracy of imaging examinations. J Hepatol 2010;52:579-585.


19. van Werven JR, Marsman HA, Nederveen AJ, Smits NJ, ten Kate FJ, van Gulik TM, et al. Assessment of hepatic steatosis in patients undergoing liver resection: comparison of US, CT, T1-weighted dualecho MR imaging, and point-resolved 1H MR spectroscopy. Radiology 2010;256:159-168.


20. Hepburn MJ, Vos JA, Fillman EP, Lawitz EJ. The accuracy of the report of hepatic steatosis on ultrasonography in patients infected with hepatitis C in a clinical setting: a retrospective observational study. BMC Gastroenterol 2005;5:14.




21. Palmentieri B, de Sio I, La Mura V, Masarone M, Vecchione R, Bruno S, et al. The role of bright liver echo pattern on ultrasound B-mode examination in the diagnosis of liver steatosis. Dig Liver Dis 2006;38:485-489.


22. de Moura Almeida A, Cotrim HP, Barbosa DB, de Athayde LG, Santos AS, Bitencourt AG, et al. Fatty liver disease in severe obese patients: diagnostic value of abdominal ultrasound. World J Gastroenterol 2008;14:1415-1418.



23. Strauss S, Gavish E, Gottlieb P, Katsnelson L. Interobserver and intraobserver variability in the sonographic assessment of fatty liver. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007;189:W320-W323.


24. Webb M, Yeshua H, Zelber-Sagi S, Santo E, Brazowski E, Halpern Z, et al. Diagnostic value of a computerized hepatorenal index for sonographic quantification of liver steatosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009;192:909-914.


25. Borges VF, Diniz AL, Cotrim HP, Rocha HL, Andrade NB. Sonographic hepatorenal ratio: a noninvasive method to diagnose nonalcoholic steatosis. J Clin Ultrasound 2013;41:18-25.

26. Osawa H, Mori Y. Sonographic diagnosis of fatty liver using a histogram technique that compares liver and renal cortical echo amplitudes. J Clin Ultrasound 1996;24:25-29.


27. Matteoni CA, Younossi ZM, Gramlich T, Boparai N, Liu YC, McCullough AJ. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a spectrum of clinical and pathological severity. Gastroenterology 1999;116:1413-1419.


28. Kim SH, Lee JM, Kim JH, Kim KG, Han JK, Lee KH, et al. Appropriateness of a donor liver with respect to macrosteatosis: application of artificial neural networks to US images--initial experience. Radiology 2005;234:793-803.


29. Son JY, Lee JY, Yi NJ, Lee KW, Suh KS, Kim KG, et al. Hepatic Steatosis: Assessment with Acoustic Structure Quantification of US Imaging. Radiology 2016;278:257-264.


30. Xia MF, Yan HM, He WY, Li XM, Li CL, Yao XZ, et al. Standardized ultrasound hepatic/renal ratio and hepatic attenuation rate to quantify liver fat content: an improvement method. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2012;20:444-452.



31. Kuroda H, Kakisaka K, Kamiyama N, Oikawa T, Onodera M, Sawara K, et al. Non-invasive determination of hepatic steatosis by acoustic structure quantification from ultrasound echo amplitude. World J Gastroenterol 2012;18:3889-3895.



32. Karlas T, Berger J, Garnov N, Lindner F, Busse H, Linder N, et al. Estimating steatosis and fibrosis: Comparison of acoustic structure quantification with established techniques. World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:4894-4902.



33. Keller J, Kaltenbach TE, Haenle MM, Oeztuerk S, Graeter T, Mason RA, et al. Comparison of Acoustic Structure Quantification (ASQ), shearwave elastography and histology in patients with diffuse hepatopathies. BMC Med Imaging 2015;15:58.



35. Sasso M, Beaugrand M, de Ledinghen V, Douvin C, Marcellin P, Poupon R, et al. Controlled attenuation parameter (CAP): a novel VCTEŌäó guided ultrasonic attenuation measurement for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis: preliminary study and validation in a cohort of patients with chronic liver disease from various causes. Ultrasound Med Biol 2010;36:1825-1835.


36. de Ledinghen V, Vergniol J, Foucher J, Merrouche W, le Bail B. Non-invasive diagnosis of liver steatosis using controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) and transient elastography. Liver Int 2012;32:911-918.


37. Myers RP, Pollett A, Kirsch R, Pomier-Layrargues G, Beaton M, Levstik M, et al. Controlled Attenuation Parameter (CAP): a noninvasive method for the detection of hepatic steatosis based on transient elastography. Liver Int 2012;32:902-910.


38. de L├®dinghen V, Vergniol J, Capdepont M, Chermak F, Hiriart JB, Cassinotto C, et al. Controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) for the diagnosis of steatosis: a prospective study of 5323 examinations. J Hepatol 2014;60:1026-1031.


39. Shi KQ, Tang JZ, Zhu XL, Ying L, Li DW, Gao J, et al. Controlled attenuation parameter for the detection of steatosis severity in chronic liver disease: a meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;29:1149-1158.


40. Kwok R, Choi KC, Wong GL, Zhang Y, Chan HL, Luk AO, et al. Screening diabetic patients for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with controlled attenuation parameter and liver stiffness measurements: a prospective cohort study. Gut 2016;65:1359-1368.


41. Shen F, Zheng RD, Shi JP, Mi YQ, Chen GF, Hu X, et al. Impact of skin capsular distance on the performance of controlled attenuation parameter in patients with chronic liver disease. Liver Int 2015;35:2392-2400.



42. Kim DY, Park SH, Lee SS, Kim HJ, Kim SY, Kim MY, et al. Contrastenhanced computed tomography for the diagnosis of fatty liver: prospective study with same-day biopsy used as the reference standard. Eur Radiol 2010;20:359-366.


43. Lawrence DA, Oliva IB, Israel GM. Detection of hepatic steatosis on contrast-enhanced CT images: diagnostic accuracy of identification of areas of presumed focal fatty sparing. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2012;199:44-47.


44. Birnbaum BA, Hindman N, Lee J, Babb JS. Multi-detector row CT attenuation measurements: assessment of intra- and interscanner variability with an anthropomorphic body CT phantom. Radiology 2007;242:109-119.


45. Pickhardt PJ, Park SH, Hahn L, Lee SG, Bae KT, Yu ES. Specificity of unenhanced CT for non-invasive diagnosis of hepatic steatosis: implications for the investigation of the natural history of incidental steatosis. Eur Radiol 2012;22:1075-1082.


46. Patrick D, White FE, Adams PC. Long-term amiodarone therapy: a cause of increased hepatic attenuation on CT. Br J Radiol 1984;57:573-576.


47. Park YS, Park SH, Lee SS, Kim DY, Shin YM, Lee W, et al. Biopsyproven nonsteatotic liver in adults: estimation of reference range for difference in attenuation between the liver and the spleen at nonenhanced CT. Radiology 2011;258:760-766.


48. Artz NS, Hines CD, Brunner ST, Agni RM, Kuhn JP, Roldan-Alzate A, et al. Quantification of hepatic steatosis with dual-energy computed tomography: comparison with tissue reference standards and quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in the ob/ob mouse. Invest Radiol 2012;47:603-610.



49. Mendler MH, Bouillet P, Le Sidaner A, Lavoine E, Labrousse F, Sautereau D, et al. Dual-energy CT in the diagnosis and quantification of fatty liver: limited clinical value in comparison to ultrasound scan and single-energy CT, with special reference to iron overload. J Hepatol 1998;28:785-794.


50. Park SH, Kim PN, Kim KW, Lee SW, Yoon SE, Park SW, et al. Macrovesicular hepatic steatosis in living liver donors: use of CT for quantitative and qualitative assessment. Radiology 2006;239:105-112.


51. Lee SW, Park SH, Kim KW, Choi EK, Shin YM, Kim PN, et al. Unenhanced CT for assessment of macrovesicular hepatic steatosis in living liver donors: comparison of visual grading with liver attenuation index. Radiology 2007;244:479-485.


52. Thomsen C, Becker U, Winkler K, Christoffersen P, Jensen M, Henriksen O. Quantification of liver fat using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Imaging 1994;12:487-495.


53. Chang JS, Taouli B, Salibi N, Hecht EM, Chin DG, Lee VS. Opposed-phase MRI for fat quantification in fat-water phantoms with 1H MR spectroscopy to resolve ambiguity of fat or water dominance. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2006;187:W103-W106.


54. Cassidy FH, Yokoo T, Aganovic L, Hanna RF, Bydder M, Middleton MS, et al. Fatty liver disease: MR imaging techniques for the detection and quantification of liver steatosis. Radiographics 2009;29:231-260.


55. Pineda N, Sharma P, Xu Q, Hu X, Vos M, Martin DR. Measurement of hepatic lipid: high-speed T2-corrected multiecho acquisition at 1H MR spectroscopy--a rapid and accurate technique. Radiology 2009;252:568-576.


56. Meisamy S, Hines CD, Hamilton G, Sirlin CB, McKenzie CA, Yu H, et al. Quantification of hepatic steatosis with T1-independent, T2-corrected MR imaging with spectral modeling of fat: blinded comparison with MR spectroscopy. Radiology 2011;258:767-775.



57. Kang BK, Yu ES, Lee SS, Lee Y, Kim N, Sirlin CB, et al. Hepatic fat quantification: a prospective comparison of magnetic resonance spectroscopy and analysis methods for chemical-shift gradient echo magnetic resonance imaging with histologic assessment as the reference standard. Invest Radiol 2012;47:368-375.


58. Yokoo T, Bydder M, Hamilton G, Middleton MS, Gamst AC, Wolfson T, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: diagnostic and fat-grading accuracy of low-flip-angle multiecho gradient-recalled-echo MR imaging at 1.5 T. Radiology 2009;251:67-76.



59. Lee SS, Lee Y, Kim N, Kim SW, Byun JH, Park SH, et al. Hepatic fat quantification using chemical shift MR imaging and MR spectroscopy in the presence of hepatic iron deposition: validation in phantoms and in patients with chronic liver disease. J Magn Reson Imaging 2011;33:1390-1398.


60. Bohte AE, Koot BG, van der Baan-Slootweg OH, van Werven Jr, Bipat S, Nederveen AJ, et al. US cannot be used to predict the presence or severity of hepatic steatosis in severely obese adolescents. Radiology 2012;262:327-334.


61. Idilman IS, Aniktar H, Idilman R, Kabacam G, Savas B, Elhan A, et al. Hepatic steatosis: quantification by proton density fat fraction with MR imaging versus liver biopsy. Radiology 2013;267:767-775.


62. Hwang I, Lee JM, Lee KB, Yoon JH, Kiefer B, Han JK, et al. Hepatic steatosis in living liver donor candidates: preoperative assessment by using breath-hold triple-echo MR imaging and 1H MR spectroscopy. Radiology 2014;271:730-738.


63. Yokoo T, Shiehmorteza M, Hamilton G, Wolfson T, Schroeder ME, Middleton MS, et al. Estimation of hepatic proton-density fat fraction by using MR imaging at 3.0 T. Radiology 2011;258:749-759.



64. Roldan-Valadez E, Favila R, Martinez-Lopez M, Uribe M, Rios C, Mendez-Sanchez N. In vivo 3T spectroscopic quantification of liver fat content in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Correlation with biochemical method and morphometry. J Hepatol 2010;53:732-737.


65. Raptis DA, Fischer MA, Graf R, Nanz D, Weber A, Moritz W, et al. MRI: the new reference standard in quantifying hepatic steatosis? Gut 2012;61:117-127.


66. Urdzik J, Bjerner T, Wanders A, Weis J, Duraj F, Haglund U, et al. The value of pre-operative magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the assessment of steatohepatitis in patients with colorectal liver metastasis. J Hepatol 2012;56:640-646.


67. Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Heurtier A, Gombert S, Giral P, Bruckert E, et al. Sampling variability of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2005;128:1898-1906.


68. Le TA, Chen J, Changchien C, Peterson MR, Kono Y, Patton H, et al. Effect of colesevelam on liver fat quantified by magnetic resonance in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology 2012;56:922-932.



69. Noureddin M, Lam J, Peterson MR, Middleton M, Hamilton G, Le TA, et al. Utility of magnetic resonance imaging versus histology for quantifying changes in liver fat in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease trials. Hepatology 2013;58:1930-1940.



70. Ryan MC, Itsiopoulos C, Thodis T, Ward G, Trost N, Hofferberth S, et al. The Mediterranean diet improves hepatic steatosis and insulin sensitivity in individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 2013;59:138-143.


71. Wong VW, Chan RS, Wong GL, Cheung BH, Chu WC, Yeung DK, et al. Community-based lifestyle modification programme for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized controlled trial. J Hepatol 2013;59:536-542.


72. Cowin GJ, Jonsson JR, Bauer JD, Ash S, Ali A, Osland EJ, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy for monitoring liver steatosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 2008;28:937-945.


73. Johnson NA, Sachinwalla T, Walton DW, Smith K, Armstrong A, Thompson MW, et al. Aerobic exercise training reduces hepatic and visceral lipids in obese individuals without weight loss. Hepatology 2009;50:1105-1112.


74. Qayyum A, Goh JS, Kakar S, Yeh BM, Merriman RB, Coakley FV. Accuracy of liver fat quantification at MR imaging: comparison of out-of-phase gradient-echo and fat-saturated fast spin-echo techniques-initial experience. Radiology 2005;237:507-511.


75. Cotler SJ, Guzman G, Layden-Almer J, Mazzone T, Layden TJ, Zhou XJ. Measurement of liver fat content using selective saturation at 3.0 T. J Magn Reson Imaging 2007;25:743-748.


77. Westphalen AC, Qayyum A, Yeh BM, Merriman RB, Lee JA, Lamba A, et al. Liver fat: effect of hepatic iron deposition on evaluation with opposed-phase MR imaging. Radiology 2007;242:450-455.


78. McPherson S, Jonsson JR, Cowin GJ, OŌĆÖRourke P, Clouston AD, Volp A, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy accurately estimate the severity of steatosis provided the stage of fibrosis is considered. J Hepatol 2009;51:389-397.


79. OŌĆÖRegan DP, Callaghan MF, Wylezinska-Arridge M, Fitzpatrick J, Naoumova RP, Hajnal JV, et al. Liver fat content and T2*: simultaneous measurement by using breath-hold multiecho MR imaging at 3.0 T--feasibility. Radiology 2008;247:550-557.


80. Guiu B, Petit JM, Loffroy R, Ben Salem D, Aho S, Masson D, et al. Quantification of liver fat content: comparison of triple-echo chemical shift gradient-echo imaging and in vivo proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 2009;250:95-102.


81. Yu H, Shimakawa A, McKenzie CA, Brodsky E, Brittain JH, Reeder SB. Multiecho water-fat separation and simultaneous R2* estimation with multifrequency fat spectrum modeling. Magn Reson Med 2008;60:1122-1134.



- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- ORCID iDs
-
Dong Ho Lee

https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8983-851X - Related articles
-
Recent updates on pharmacologic therapy in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease2024 January;30(1)
Letter regarding ŌĆ£Risk factors in nonalcoholic fatty liver diseaseŌĆØ2023 October;29(4)
Letter regarding ŌĆ£Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Definition and subtypesŌĆØ2023 July;29(3)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



