| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 19(1); 2013 > Article |
ABSTRACT
Background/Aims
Methods
Results
Acknowledgements
Abbreviations
REFERENCES
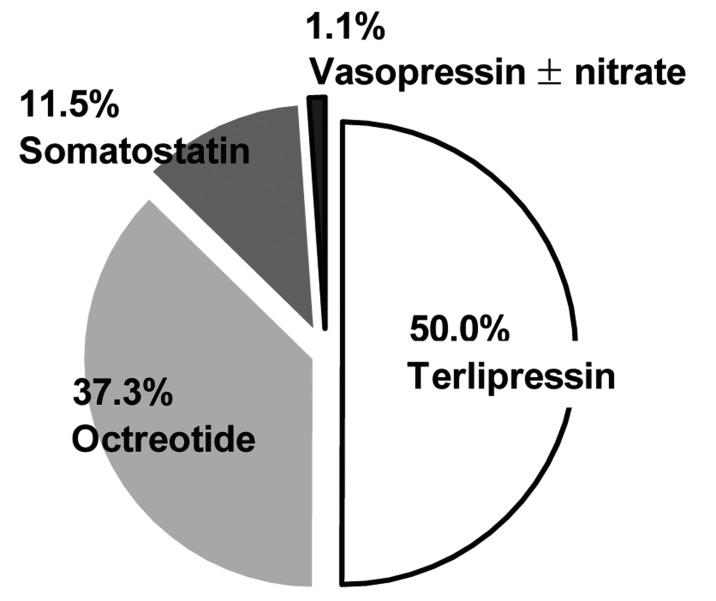
Figure┬Ā1
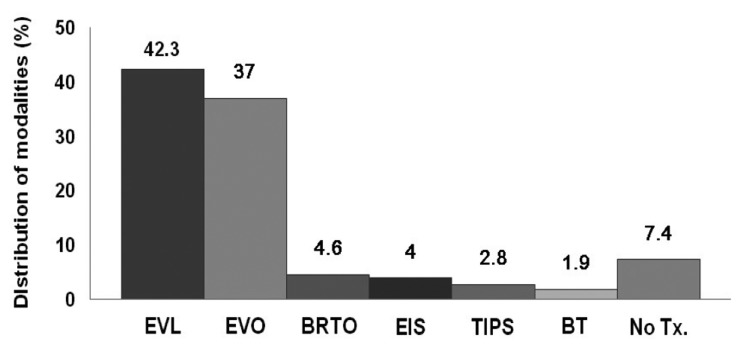
Figure┬Ā2
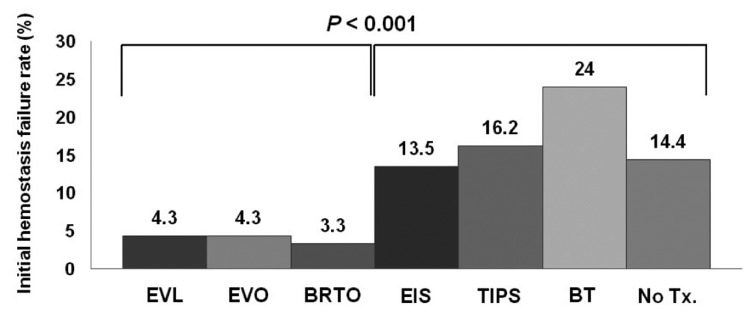
Figure┬Ā3
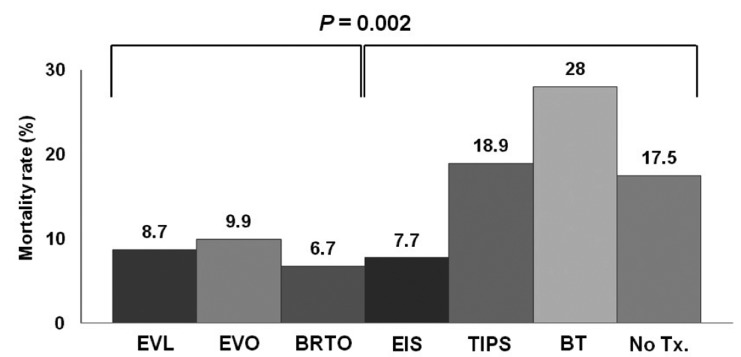
Figure┬Ā4
Table┬Ā1.
| Characteristic | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 55.0┬▒11.0 (16-87) | |
| Sex (males:females) | 1062 (81.2):246 (18.8) | |
| Etiology | Alcohol abuse | 603 (46.1) |
| HBV | 450 (34.4) | |
| HCV | 87 (6.7) | |
| Alcohol and virus | 93 (7.1) | |
| Autoimmune | 7 (0.5) | |
| Cryptogenic | 38 (2.9) | |
| Others | 30 (2.3) | |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 2.8┬▒0.6 (1.0-5.0) | |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 2.9┬▒4.2 (0.4-48.1) | |
| Prothrombin time (INR) | 1.6┬▒0.6 (0.7-8.2) | |
| Platelet count (103/mm3) | 100.8┬▒64.3 (12.0-510) | |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.1┬▒0.7 (0.4-12.2) | |
| Child-PughŌĆÖs score | 8.4┬▒2.0 (5-15) | |
| Child-Pugh class | A | 219 (16.7) |
| B | 715 (54.7) | |
| C | 374 (28.6) | |
| EV size | F0 | 150 (11.5) |
| F1 | 358 (27.4) | |
| F2 | 500 (38.2) | |
| F3 | 300 (22.9) | |
| GV type | GOV1 | 781 (59.7) |
| GOV2 | 378 (28.9) | |
| IGV1 | 119 (9.1) | |
| IGV2 | 30 (2.3) | |
| GV size | Small (Ōēż5 mm) | 241 (18.4) |
| Medium (6-9 mm) | 521 (39.8) | |
| Large (Ōēź10 mm) | 546 (41.7) | |
| PHG | None | 597 (45.6) |
| Mild | 354 (27.3) | |
| Severe | 357 (27.1) | |
| Splenomegaly | No | 356 (27.2) |
| Yes | 952 (72.8) | |
| EVB-endoscopic treatment history | No | 944 (72.2) |
| Yes | 364 (27.8) | |
| Initial hemostasis failure rate | 80 (6.1) | |
| Rebleeding rate | Overall | 151 (11.5) |
| Early* | 76 (5.8) | |
| LateŌĆĀ | 75 (5.7) | |
| Mortality rate | Overall | 135 (10.3) |
| Early* | 73 (5.6) | |
| LateŌĆĀ | 62 (4.7) |
Data are mean┬▒SD (range) or n (%) values.
EV, esophageal varix; EVH, esophageal variceal bleeding; GOV1, GVs associated with EVs along the lesser curvature; GOV2, GVs associated with EVs along the fundus; GV, gastric varix; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus; IGV1, isolated GVs present in isolation in the fundus; IGV2, isolated GVs present in isolation at ectopic sites in the stomach or the first part of the duodenum; INR, international normalized ratio; PHG, portal hypertensive gastropathy.
Table┬Ā2.
| Univariate analysis | |||
| ŌĆāParameter | P | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāPrevious EVL history* | 0.038 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāGV typeŌĆĀ | 0.121 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāGV sizeŌĆĪ | 0.130 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāChild-PughŌĆÖs score | <0.001 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāVasoactive agent applied | 0.722 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāKind of vasoactive agent | 0.360 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāModality of nonpharmacologic treatments┬¦ | <0.001 | ||
| Multivariate analysisŌłź | |||
| ŌĆāParameter | OR | P | 95% CI |
| ŌĆāŌĆāPrevious EVL history* | 0.564 | 0.083 | 0.300-1.058 |
| ŌĆāŌĆāChild-PughŌĆÖs score | 1.619 | <0.001 | 1.437-1.823 |
| ŌĆāŌĆāModality of nonpharmacologic treatments┬¦ | 0.221 | <0.001 | 0.131-0.371 |
P-values of univariate analysis were obtained by two sample t-test, ANOVA or chi-square test.
P-values of multivariate analysis were obtained by binary logistic regression analysis.
EVL, endoscopic variceal ligation; GV, gastric varix; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; GOV1, GVs associated with EVs along the lesser curvature; GOV2, GVs associated with EVs along the fundus; IGV1, isolated GVs present in isolation in the fundus; EVO, endoscopic variceal cular obturation; BRTO, balloonoccluded retrograde transvenous obliteration.
Table┬Ā3.
| Univariate analysis | |||
| ŌĆāParameters | P | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāPrevious EVL history* | 0.002 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāGV typeŌĆĀ | 0.434 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāGV sizeŌĆĪ | 0.369 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāChild-Pugh score | 0.002 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāVasoactive agent applied | 0.598 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāKind of vasoactive agent | 0.869 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāModality of nonpharmacologic treatments┬¦ | 0.033 | ||
| Multivariate analysisŌłź | |||
| ŌĆāParameter | OR | P | 95% CI |
| ŌĆāŌĆāPrevious EVL history* | 1.781 | 0.002 | 1.246-2.546 |
| ŌĆāŌĆāChild-Pugh score | 1.159 | <0.001 | 1.068-1.258 |
| ŌĆāŌĆāModality of nonpharmacologic treatments┬¦ | 0.619 | 0.026 | 0.406-0.944 |
P-values of univariate analysis were obtained by two sample t-test, ANOVA or chi-square test.
P-values of multivariate analysis were obtained by binary logistic regression analysis.
EVL, endoscopic variceal ligation; GV, gastric varix; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; GOV1, GVs associated with EVs along the lesser curvature; GOV2, GVs associated with EVs along the fundus; IGV1, isolated GVs present in isolation in the fundus; EVO, endoscopic variceal obturation; BRTO, balloonoccluded retrograde transvenous obliteration.
Table┬Ā4.
| Univariate analysis | |||
| ŌĆāParameter | P | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāPrevious EVL history* | 0.303 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāGV typeŌĆĀ | 0.576 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāGV sizeŌĆĪ | 0.077 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāChild-PughŌĆÖs score | <0.001 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāVasoactive agent applied | 0.405 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāKind of vasoactive agent | 0.249 | ||
| ŌĆāŌĆāModality of nonpharmacologic treatments┬¦ | 0.002 | ||
| Multivariate analysisŌłź | |||
| ŌĆāParameter | OR | P | 95% CI |
| ŌĆāŌĆāGV sizeŌĆĪ | 1.557 | 0.133 | 0.873-2.776 |
| ŌĆāŌĆāChild-PughŌĆÖs score | 1.795 | <0.001 | 1.621-1.988 |
| ŌĆāŌĆāModality of nonpharmacologic treatments┬¦ | 0.467 | 0.001 | 0.292-0.746 |
P-values of univariate analysis were obtained by two sample t-test, ANOVA or chi-square test.
P-values of multivariate analysis were obtained by binary logistic regression analysis.
EVL, endoscopic variceal ligation; GV, gastric varix; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; GOV1, GVs associated with EVs along the lesser curvature; GOV2, GVs associated with EVs along the fundus; IGV1, isolated GVs present in isolation in the fundus; EVO, endoscopic variceal obturation; BRTO, balloonoccluded retrograde transvenous obliteration.
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles
-
Clinical features of acute viral hepatitis B in Korea: a multi-center study2011 December;17(4)
Clinical features and prognosis of primary biliary cirrhosis in Korea2010 June;16(2)
Clinical Features and Prognostic Factors of Fulminant Hepatic Failure in Koreans2004 December;10(4)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



